
Every secure application starts with one question: how can you pinpoint the unknowns? As modern applications grow increasingly complex, security testing must evolve to match the sophistication of potential attacks.
That’s where OWASP penetration testing comes in: a structured, community-driven methodology that helps organizations identify vulnerabilities and strengthen their defenses before attackers exploit them.
This guide walks you through what OWASP penetration testing is, why it matters, and how to align your testing workflow with OWASP best practices to protect your applications.
What is OWASP penetration testing?
OWASP penetration testing refers to performing security assessments based on the testing principles and methodologies defined by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP). OWASP provides frameworks, guides, and tools to help testers uncover vulnerabilities in web applications, APIs, and cloud environments.
The foundation of OWASP penetration testing lies in the OWASP Testing Guide (v5): a comprehensive resource outlining the OWASP penetration testing methodology across different phases of assessment, including reconnaissance, configuration review, authentication testing, input validation, and business logic testing.
OWASP’s methodology is technology-agnostic, meaning it applies equally well to traditional web apps, single-page applications, and modern API-driven architectures.
What is the purpose of an OWASP penetration test?
OWASP penetration testing systematically identifies, exploits, and documents vulnerabilities using OWASP’s structured testing approach. Unlike automated scans, it focuses on real-world exploitability and business impact.
An OWASP test helps you to:
Validate risk: Show actual impact beyond static findings.
Assess controls: Test authentication, sessions, and encryption.
Drive improvement: Build a repeatable, integrated testing process.
In addition, an OWASP security pentest can help to identify key vulnerabilities such as those listed in the OWASP Top Ten. These are:
Cryptographic failures
Injection flaws
Insecure design
Identification and authentication failures
Software and data integrity failures
Security logging and monitoring failures
How long does an OWASP pentest take?
The duration of an OWASP manual penetration test varies depending on the application’s size, complexity, and test scope.
| Scope / Complexity | Typical Duration | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Small web app (limited pages, simple logic) | 3–7 days | Focused scope, minimal roles, minimal integration |
| Moderate complexity (multiple user roles, APIs, moderate logic) | 1–2 weeks | More pages/endpoints, integration surfaces, more business logic |
| Large/complex application (many user roles, rich business logic, APIs, third-party integrations, heavy backend) | 2–4 weeks (or more) | Extensive coverage, deep manual testing, many endpoints, likely retests & reporting complexity |
Automated testing integrated into CI/CD pipelines can shorten testing cycles, providing continuous coverage while taking less time than manual testing.
How to use Beagle Security for your OWASP penetration testing
Leveraging an automated penetration testing platform like Beagle Security can greatly minimize both the time and costs associated with penetration testing. Here’s how you can approach it:
Getting started
Add a new application: Choose Add application, then pick the kind of target you want to test. It can be a traditional website, a RESTful API, or a GraphQL endpoint.
Enter application information: Provide a clear name and the full URL that will act as the main testing target for your AI-driven penetration test. You can also indicate the application’s priority and adjust access settings (e.g., public vs. restricted) to reflect how testers should reach the asset.
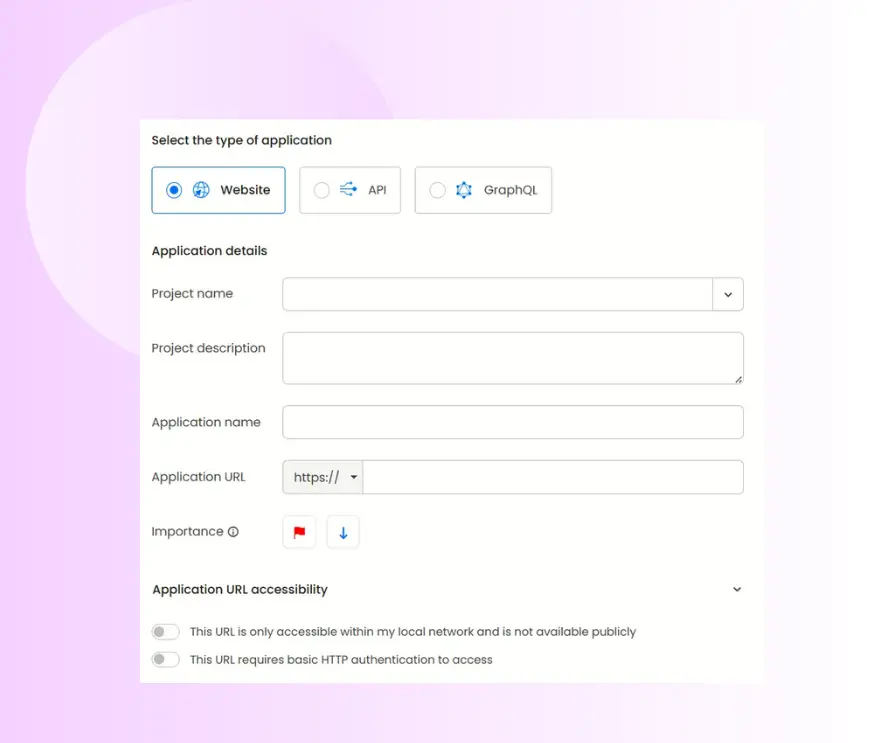
Deciding between black box and grey box penetration testing selection
When deciding a penetration test, an early choice is the tester’s knowledge level: do you want a black box or grey box approach?
Black box testing mimics an external attacker who has no prior information about your environment.
Grey box testing supplies the tester with limited inside details such as credentials or architecture notes. This allows deeper, targeted checks.
For external assessments, it’s common to begin with a black box approach. After you register the application, simply click the ‘Start test’ button to initiate a test that evaluates your public-facing systems from an outsider’s viewpoint, without granting any privileged access.
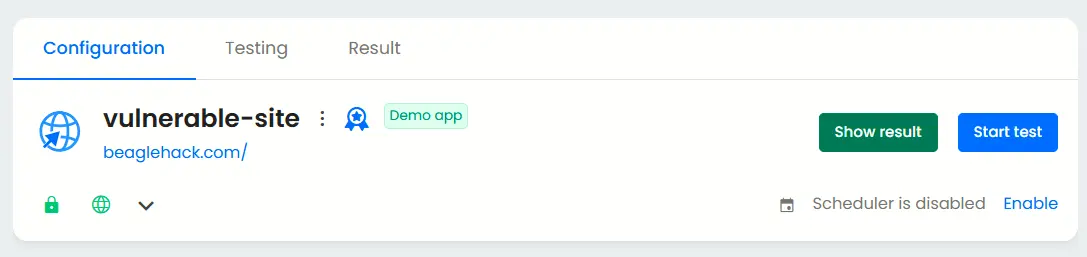
Additional configurations for grey box penetration test
Now that we’ve explored black box testing, let’s look at how gray box penetration **testing works. It is a balanced approach combining the realism of external testing with the insight of authenticated access.
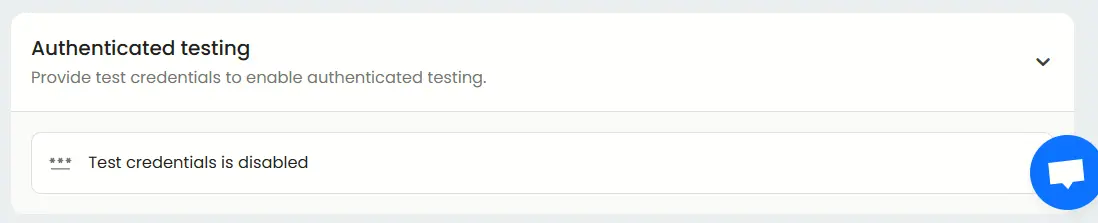
Authenticated testing
In a gray box penetration test, enabling authenticated testing is crucial. This configuration allows the testing platform to assess post-login functionality, role-based access controls, and privileged user attack surfaces.
To set this up, enable the ‘Authenticated testing’ option under the Basic tab and provide valid test credentials.
Here you can set up credential type which includes logins, signup and third-party log in.
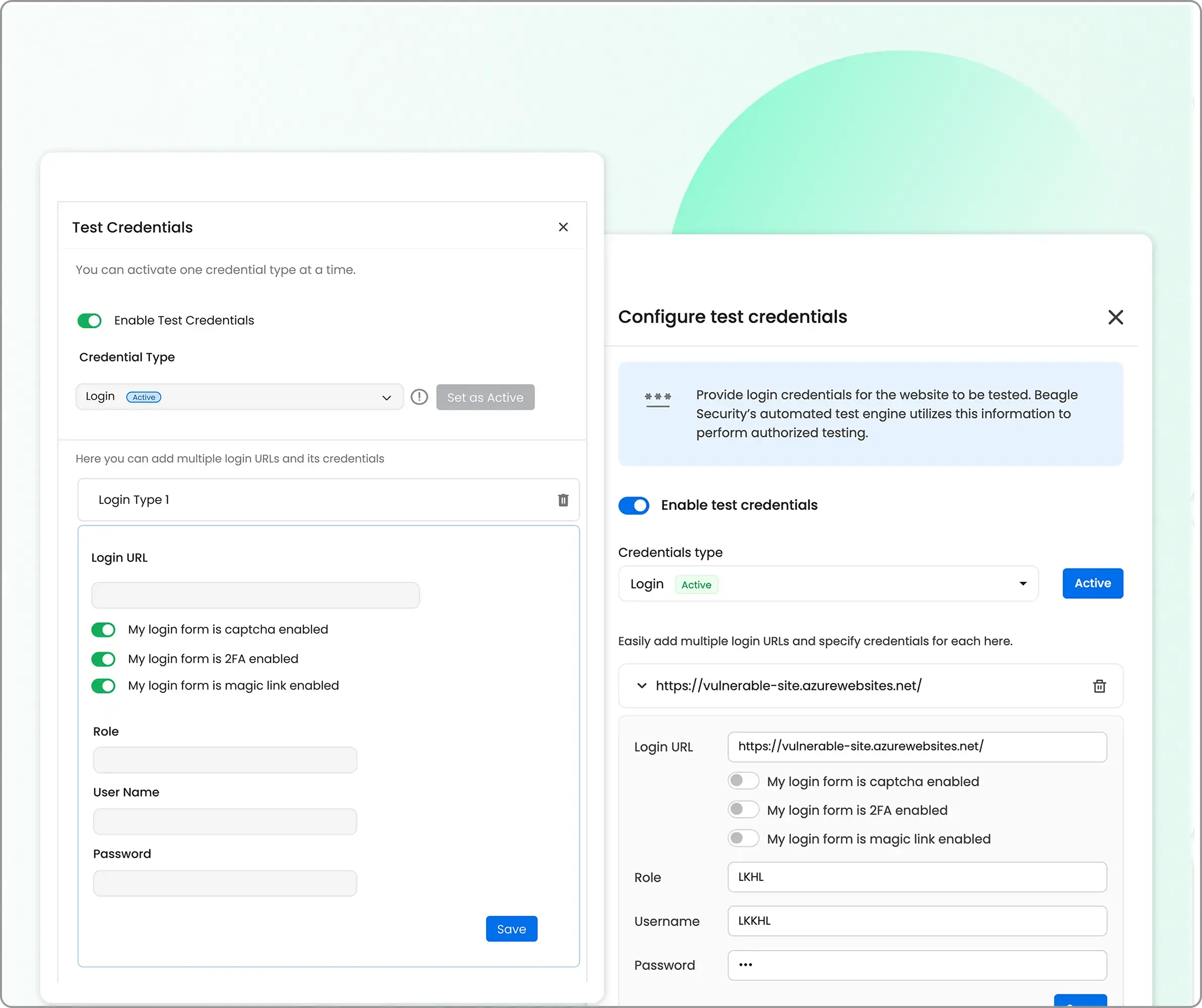
The recommended login is the “recorded login” option which can be set up using Beagle Security’s chrome extension.
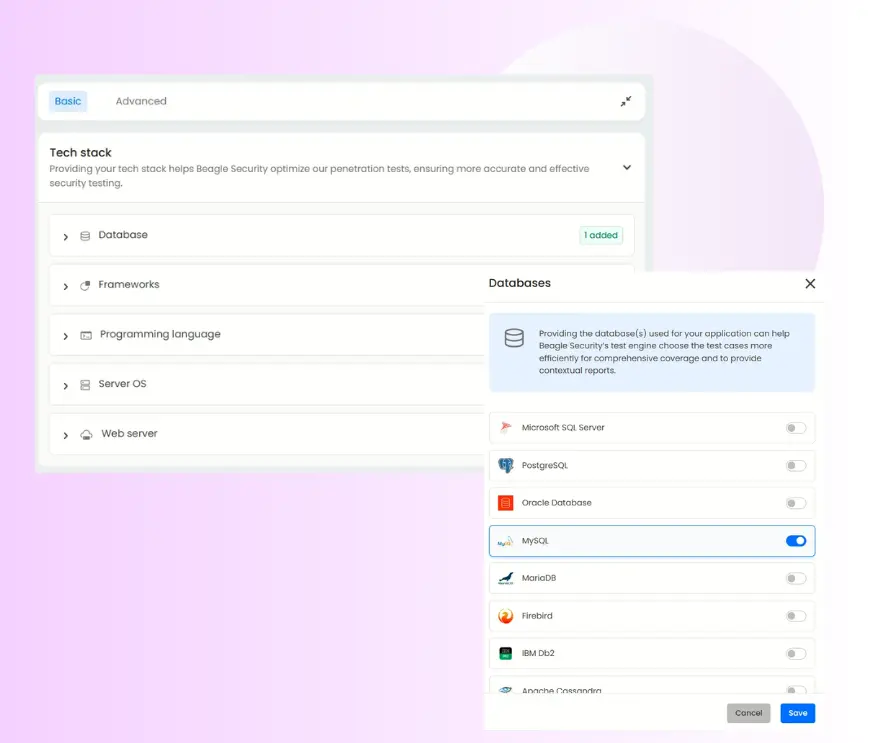
Tech stack configuration
The tech stack configuration option, located under the Basic tab, helps customize your **penetration testing process based on your application’s underlying technologies.
By specifying your frameworks, libraries, and environments, Beagle Security’s AI engine can tailor its test cases for platform-specific vulnerabilities.
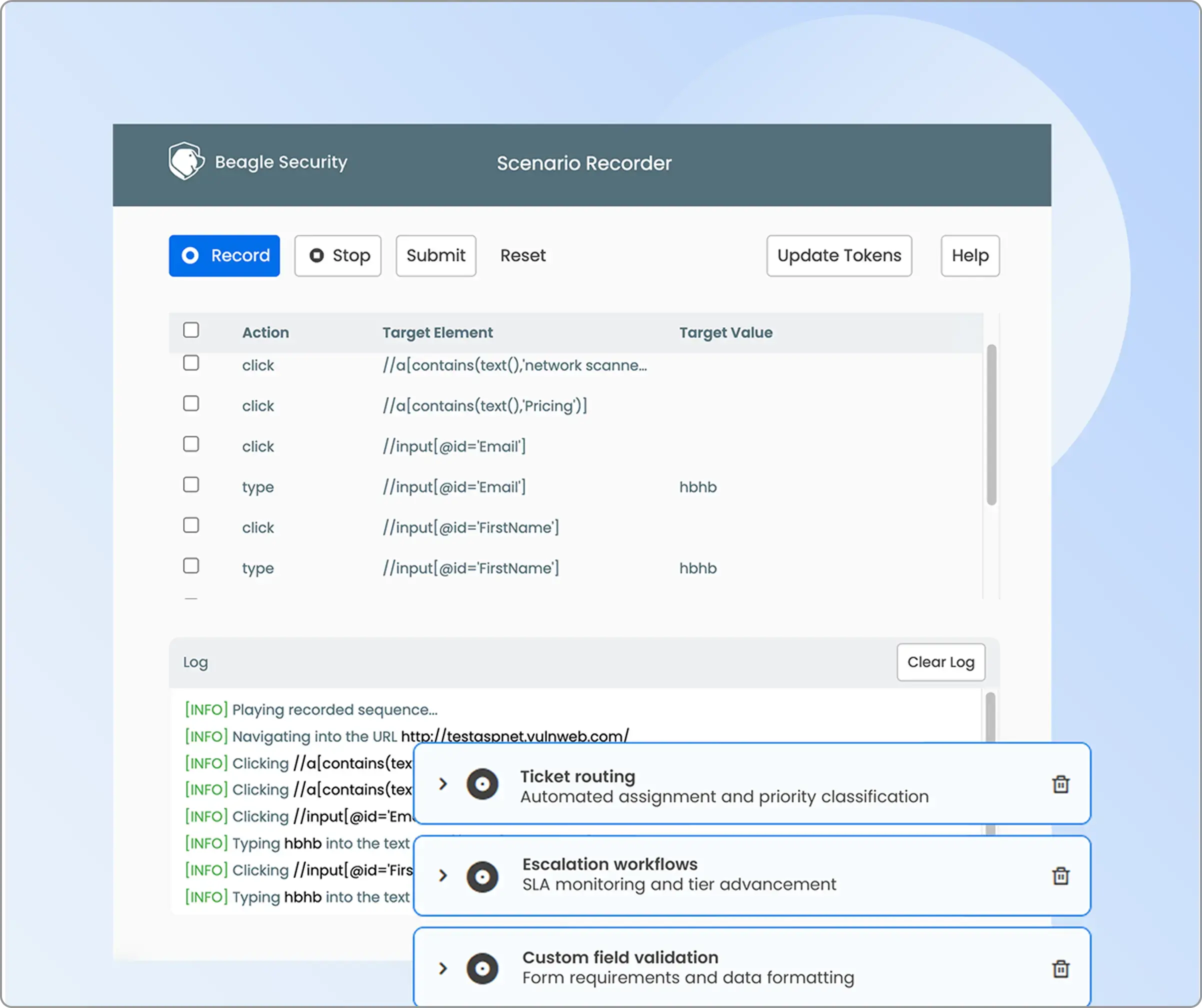
Business logic recording
The business logic recording section is located under the advanced tab.
By activating Scenario Recording, you can simulate and test application-specific logic paths, ensuring the penetration test identifies flaws traditional vulnerability scanners may overlook.
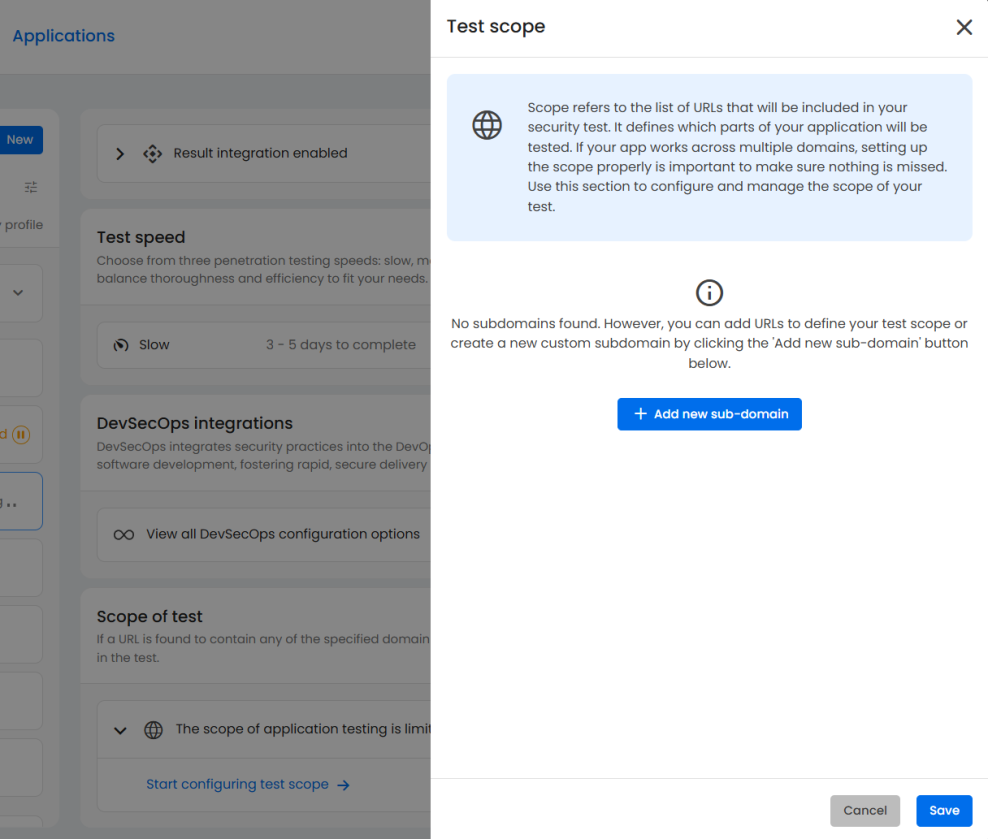
Pentesting scope
The scope determines which URLs, domains, or subdomains will be included in the assessment.
If your application spans multiple domains or environments, it’s crucial to list each one to ensure no part of your infrastructure is overlooked. Here, you can easily configure the test scope by adding new subdomains or specifying particular URLs.
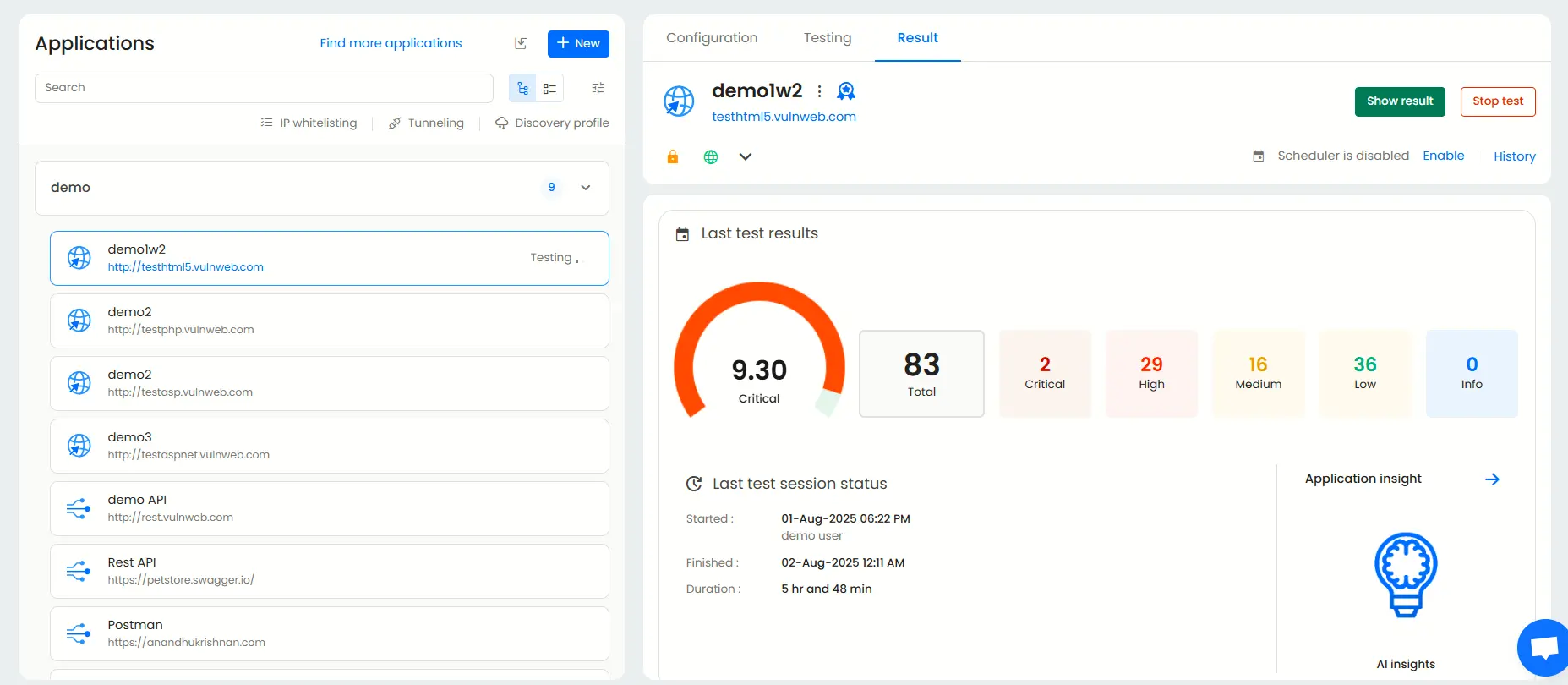
Viewing the penetration test results and reports
Application dashboard
This is where you can get an overview of each individual application. It shows important information such as the last test results, status and what vulnerabilities to prioritize.
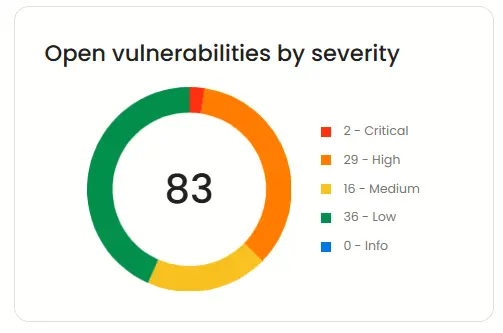
Open vulnerabilities by severity
This widget allows you to see vulnerabilities that exist currently and how severe they are.
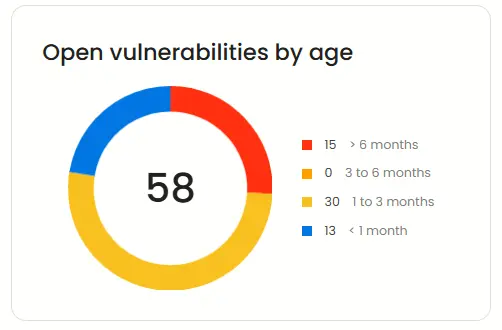
Open vulnerabilities by age
Beagle Security also categorizes risks present in your application based on how long they have been in your application, as shown in the dashboard widget below.
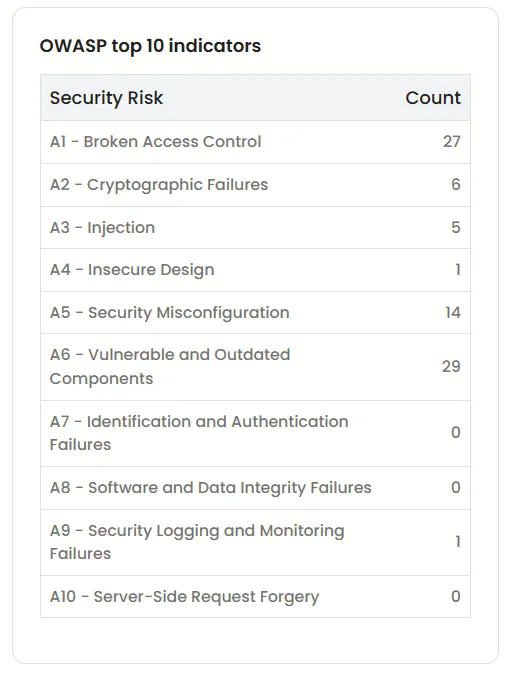
OWASP top 10 indicators
The OWASP Top 10 is a standard that represents a broad consensus of the ten most critical security risks to web applications. Beagle Security provides you with a list of OWASP vulnerabilities and their count present in your application.
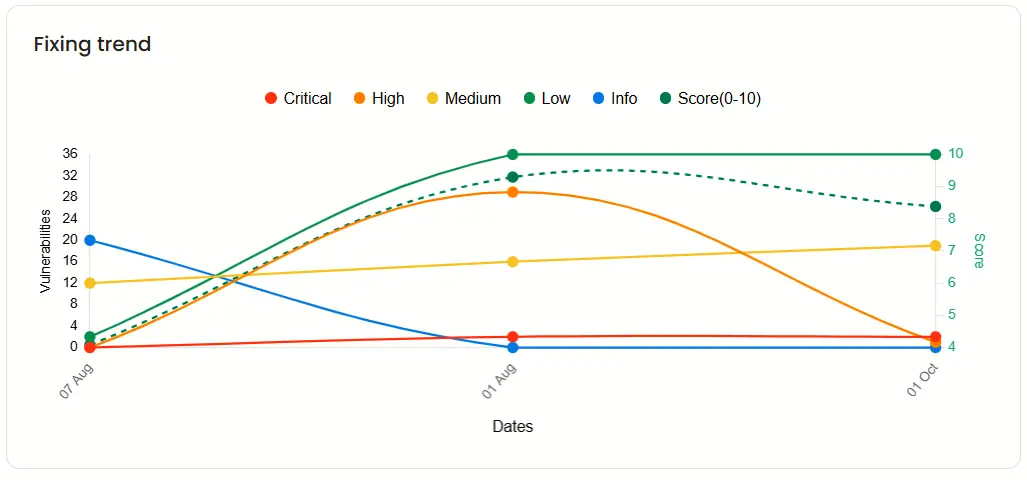
Fixing trend
This enables you to see the timeline and severity of vulnerabilities you’ve fixed, helping you keep track of your progress so far.
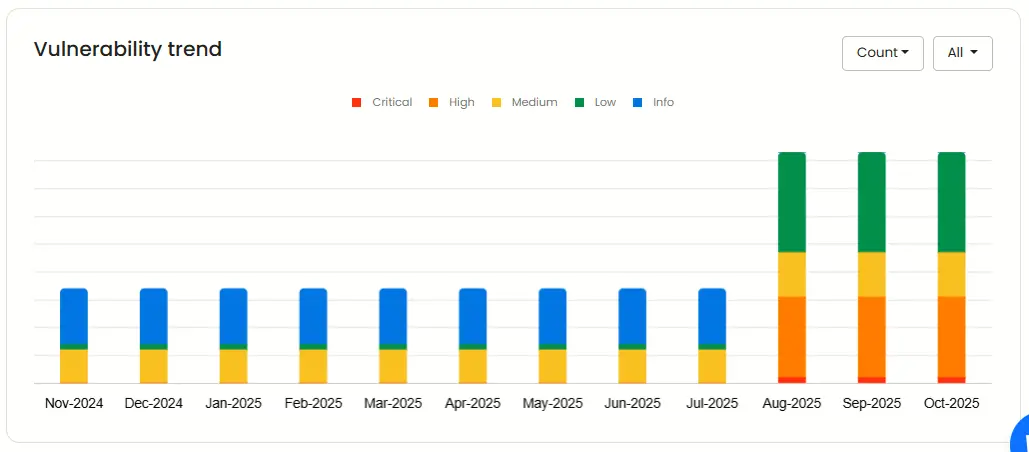
Vulnerability trend
This shows the trend of your vulnerabilities over the past year. It also provides the option to sort by severity and count.
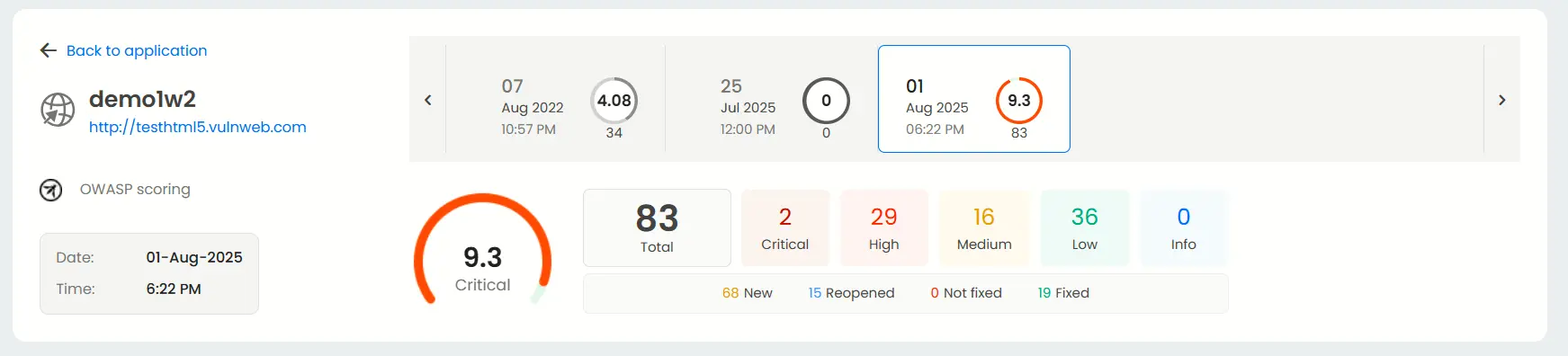
Result dashboard
The result dashboard is unique to each application and shows you the overview. Keep track of how many vulnerabilities are present, the severity of each one, and the date and time of your previous scans.
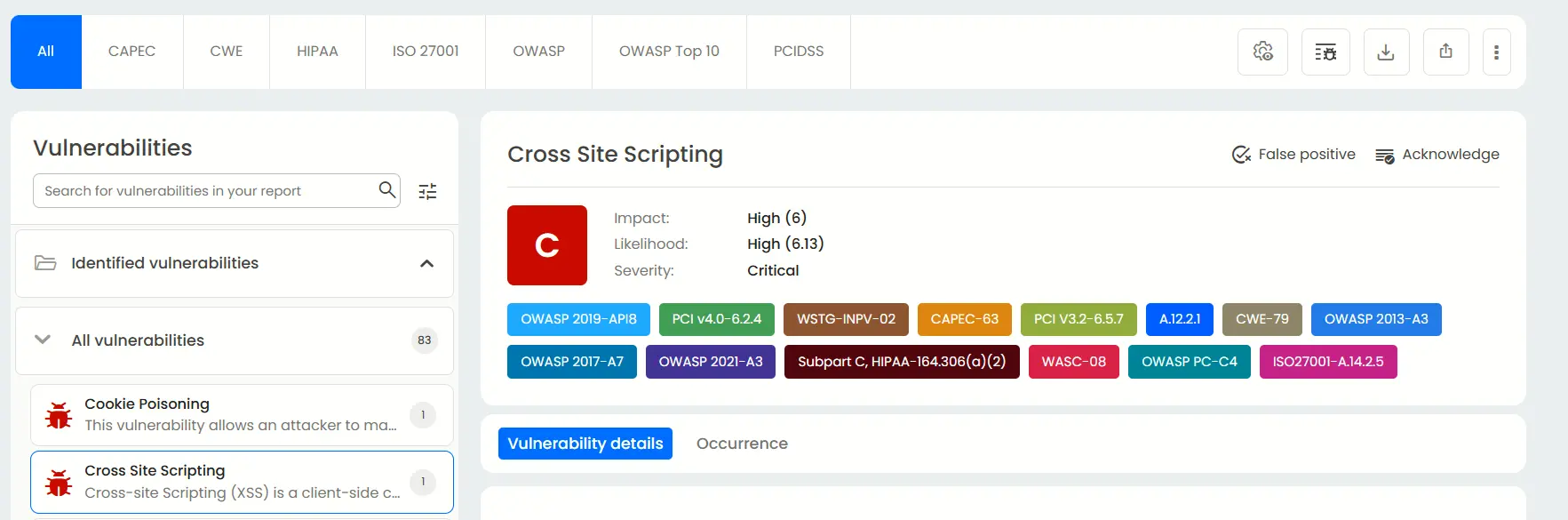
Mapping with ISO27001, OWASP & OWASP Top 10
In addition to OWASP and OWASP Top 10, Beagle Security provides you various compliance reports with other compliance metrics such as ISO 27001, HIPAA and PCIDSS.
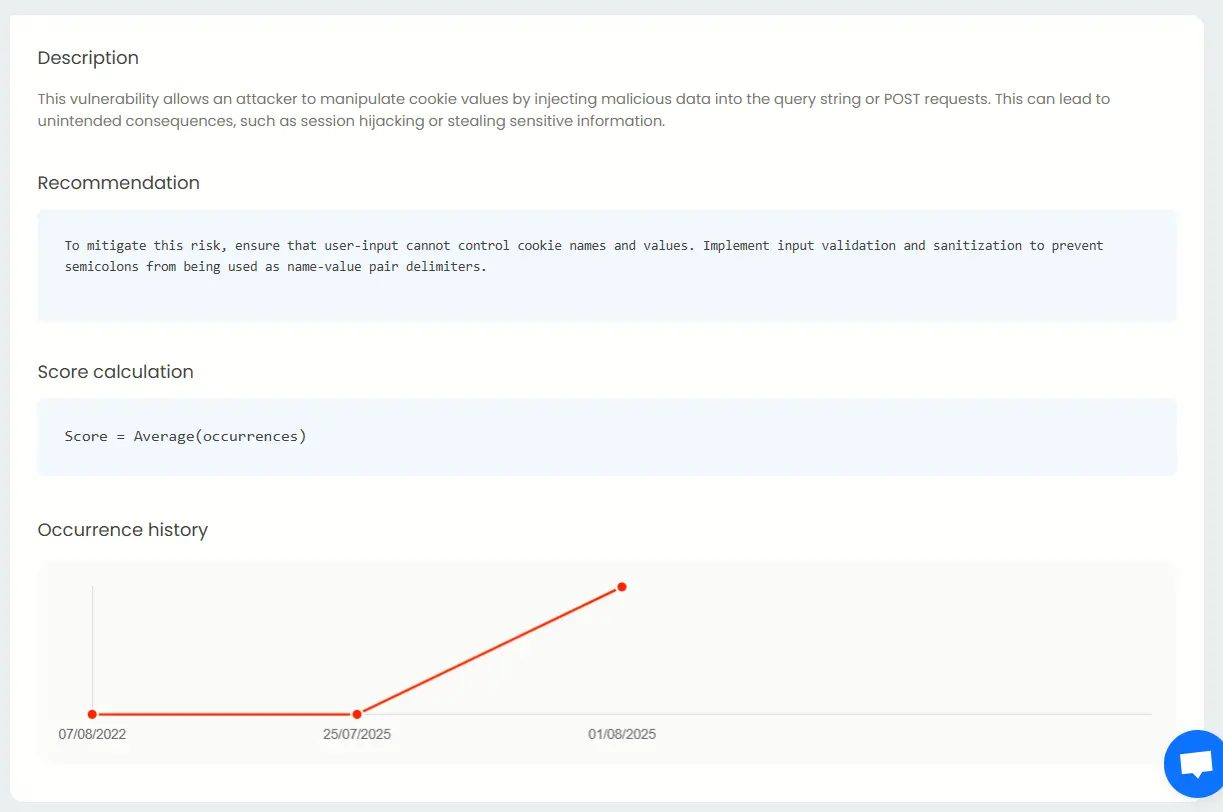
Detailed findings, fix recommendations & occurrence details
For each vulnerability detected in your application, Beagle Security gives you a description, a recommendation on how to mitigate it, and an occurrence history.
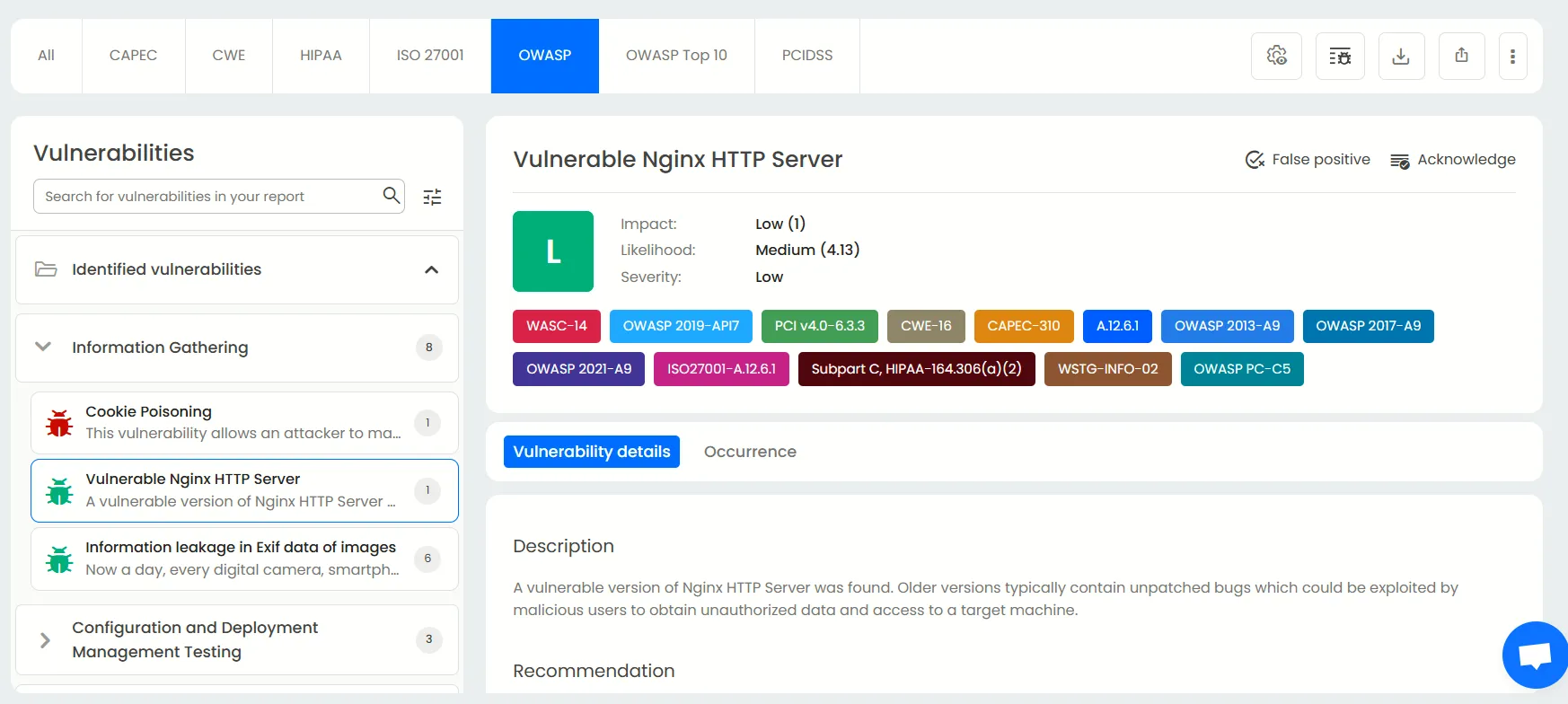
OWASP reports
While OWASP top 10 focuses on the ten most common vulnerabilities, the OWASP report focuses more on all vulnerabilities highlighted by OWASP regardless of their popularity. This ensures you don’t miss any threat no matter how niche they are.
Compliance reports – HIPAA, PCI DSS
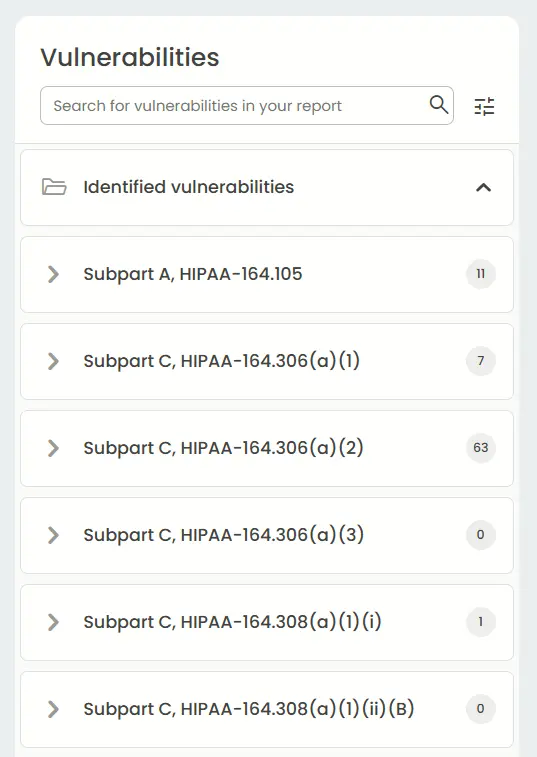
HIPAA and PCI DSS compliance reports help organizations demonstrate that they are meeting industry-specific security and privacy requirements.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) compliance report verifies that an organization handling protected health information (PHI) adheres to required privacy, security, and breach notification standards.
It typically assesses administrative, physical, and technical safeguards covering areas like access control, data encryption, and incident response.
HIPAA report:
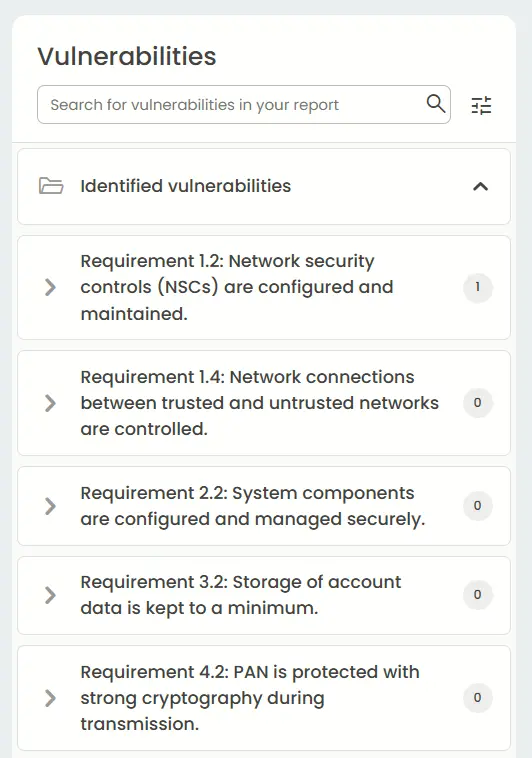
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) compliance report confirms that an organization securely processes, stores, or transmits cardholder data. It evaluates controls such as network segmentation, encryption, vulnerability management, and access restrictions.
The report validates alignment with 12 PCI DSS requirements, ensuring protection against payment data breaches and maintaining trust with customers and payment processors.
PCI DSS report:
Final thoughts
Adopting OWASP penetration testing as a core part of your application security program helps bridge the gap between development speed and security assurance. By following the OWASP penetration testing methodology, teams can gain structured visibility into vulnerabilities, improve remediation workflows, and align with globally recognized best practices.
If you’re looking for an pentesting platform that helps you align yourself to OWASP and other compliance frameworks, why not try Beagle Security? Check out our 14-day trial or go through our interactive demo to see if we’re the right fit for you.
FAQ
What is the OWASP testing framework?
The OWASP testing framework is a structured methodology developed by the Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) that outlines best practices for identifying, verifying, and remediating security vulnerabilities in web applications.
What is the cost for an OWASP penetration test?
The cost of an OWASP penetration test varies based on application complexity, scope, and testing depth, but typically ranges from $3,000 to $20,000 for most small to mid-sized organizations.
What’s the difference between PTES and OWASP?
PTES (Penetration Testing Execution Standard) defines a high-level process for conducting penetration tests, while OWASP provides a detailed, application-specific testing methodology focused on web and API security.



![Acunetix vs Nessus: Which is right for you? [2026] Acunetix vs Nessus: Which is right for you? [2026]](/blog/images/acunetix-vs-nessus-which-is-right-for-you-2026-cover.webp)
![OpenVAS vs Nessus: Which is the best choice for you? [2025] OpenVAS vs Nessus: Which is the best choice for you? [2025]](/blog/images/openvas-vs-nessus-which-is-the-best-choice-for-you-2025-cover.webp)


![Top enterprise application security tools [2026] Top enterprise application security tools [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-four-cover.webp)
![Top vendor application security testing tools [2026] Top vendor application security testing tools [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-six-cover.webp)
![Best API security tool for developers [2026] Best API security tool for developers [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-five-cover.webp)

![Top Bright Security alternatives [2026] Top Bright Security alternatives [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-one-cover.webp)