
What is gray box penetration testing?
Gray box penetration testing is a security assessment method where testers have partial knowledge of an application. It sits between black box testing, where the tester has no internal information, and white box testing, where the tester has full access. In gray box testing, you provide limited insider information such as credentials, API documentation, or architecture notes so testing can focus on authenticated workflows and privilege boundaries.
Think of gray box penetration testing as inspecting a building with a floor plan and a guest badge. You can move through some areas with access privileges while still simulating an attacker who does not have full administrative control. That perspective enables realistic, high-value findings without the time cost of full source code review.
Gray box testing matters because it reveals vulnerabilities that only appear for logged-in users, such as broken access control, business logic flaws, and privilege escalation paths. It strikes a useful balance between depth and efficiency and maps well to DevSecOps practices like continuous testing and authenticated API checks.
What is the purpose of a gray box penetration test?
- Simulate insider threat scenarios
Gray box penetration testing models what a malicious insider or a compromised account can do. This helps you identify lateral movement, data exposure, and privilege escalation risks that external-only tests would miss.
- Balance realism with depth
By combining partial knowledge with active probing, gray box testing gives you deeper findings than unauthenticated scans while remaining faster and less resource intensive than full white box audits.
- Improve testing efficiency and coverage
Supplying targeted credentials or API information lets testers focus effort on the most critical paths. You get broader vulnerability coverage in less time.
- Identify authenticated user vulnerabilities
Many high-risk bugs only appear after login. Gray box testing finds issues in session handling, role-based access control, and business logic flows.
- Support compliance requirements
Authenticated testing is often required for standards like PCI DSS and ISO 27001. Gray box tests provide evidence that authenticated workflows are tested and mitigated.
How long does a gray box pentest take?
A typical gray box penetration test lasts 3 to 7 days for small to medium web applications. Complex enterprise systems can take 2 to 3 weeks. If you use an automated platform like Beagle Security, the initial authenticated scan can complete in a few hours, with follow-up verification and manual review taking additional days depending on scope.
Factors that affect duration:
Application complexity: simple apps 3 to 5 days; complex enterprise apps 2 to 3 weeks
Scope size: more endpoints and user roles increase test time
Authentication methods: multi-factor or single sign-on setups add configuration time
Integration depth: connected APIs and third-party services extend assessment effort
Automation reduces repetitive work and supports continuous testing in CI/CD pipelines, turning a point-in-time pentest into an ongoing assurance process.
How to use Beagle Security for your gray box penetration testing?
Getting started
This section walks you through the accurate setup flow used to achieve gray box testing in Beagle Security. Gray box testing is not selected from a test type dropdown. Instead, you configure authentication and related settings to run authenticated scans.
Step 1: Log in and add your application
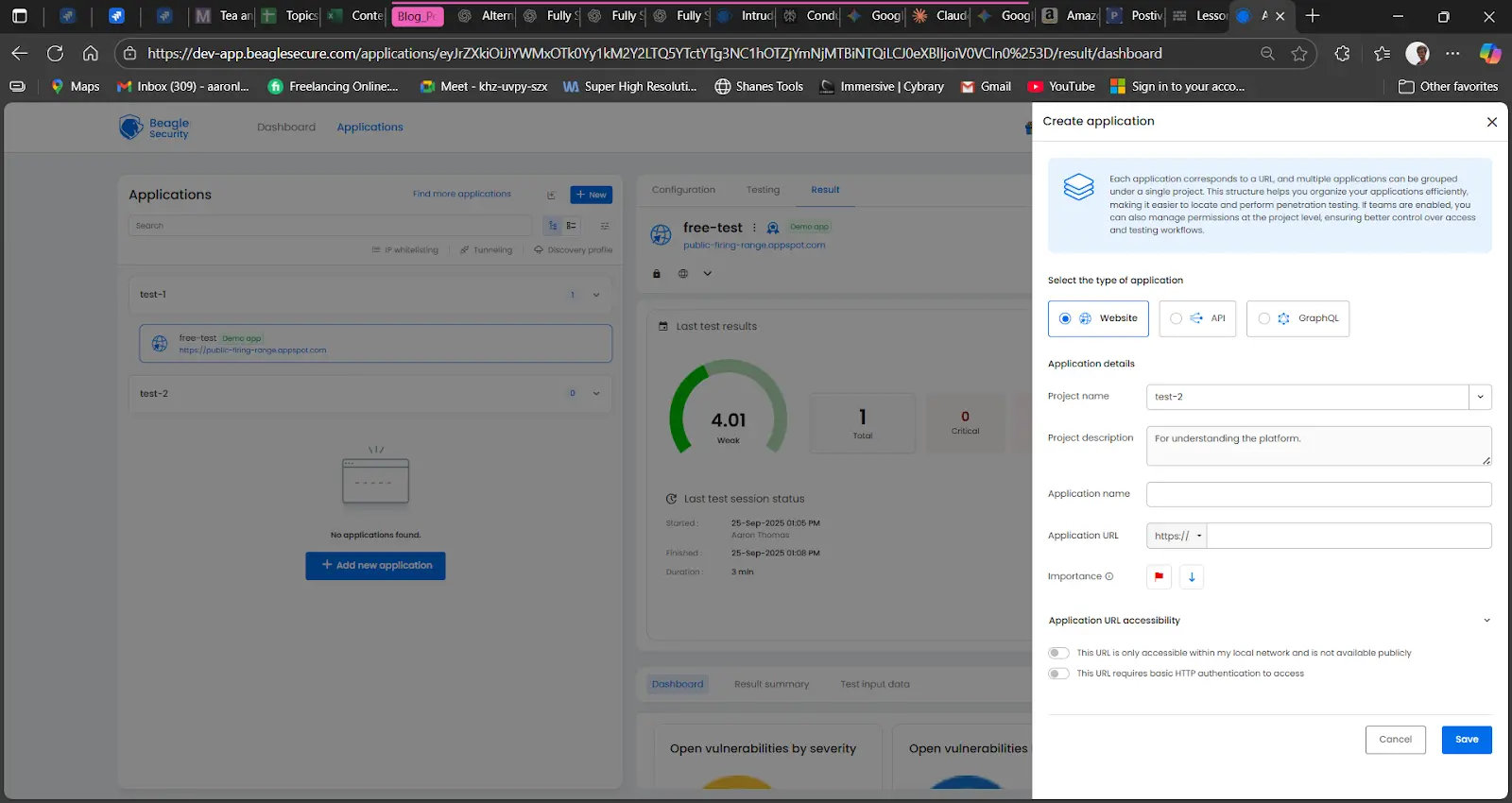
Click Add Application on the Beagle Security dashboard. Provide the required details:
Application name
Base URL or primary domain
Environment: production, staging, or development
Verify ownership by uploading a verification file, adding a DNS TXT record, inserting an HTML meta tag, or using the WordPress plugin if applicable.
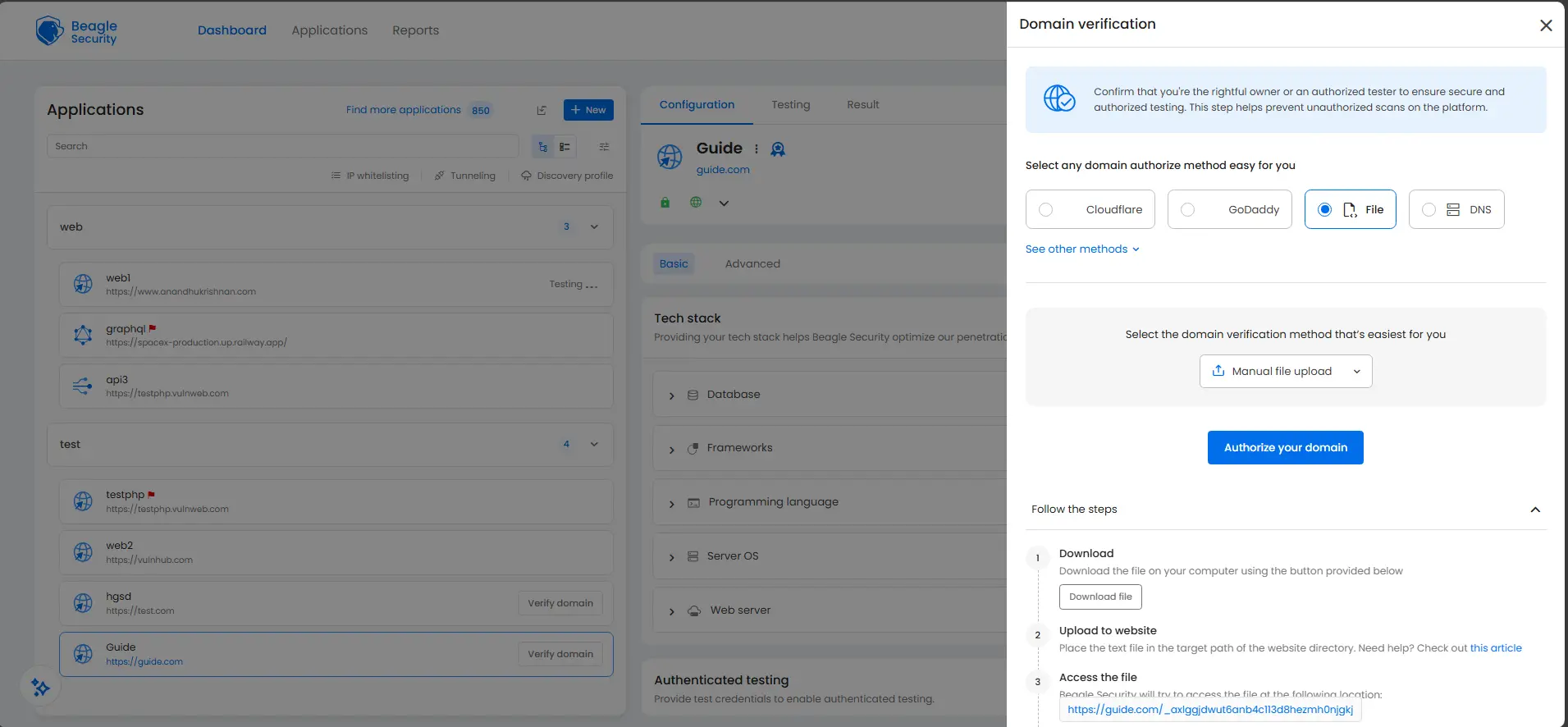
Step 2: Configure authenticated testing
Authenticated testing is the configuration that makes the assessment a gray box penetration test. Navigate to Authentication Settings in the application configuration.
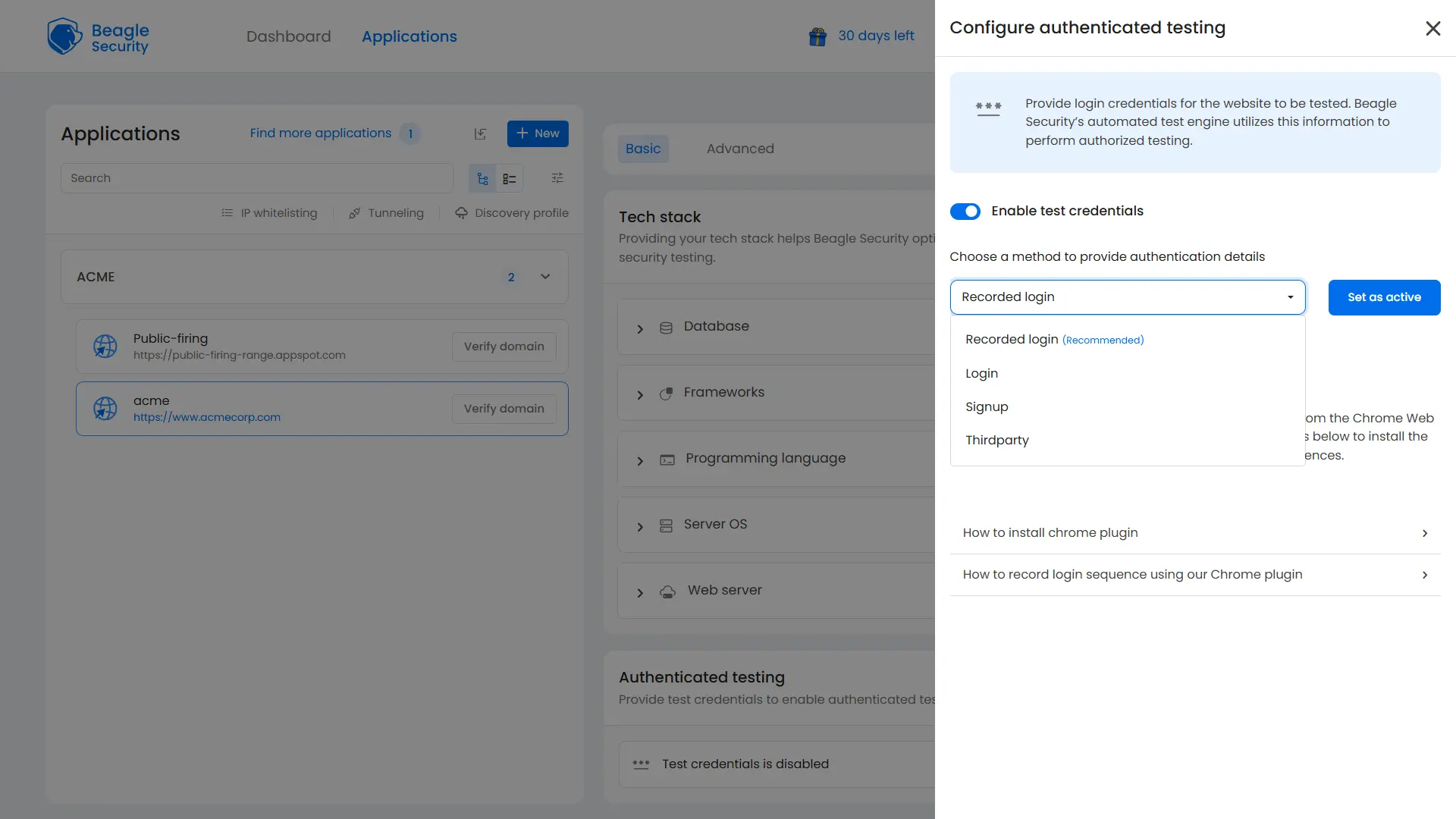
Choose one of the supported authentication methods:
Recorded login
Login
Signup
Thirdparty
When to use login form vs recorded
The login form method is best suited for applications with a single-step login process and a straightforward authentication flow. It is quick to configure and works well for most web applications.
For more complex scenarios involving JavaScript-rendered login forms, redirects, or multi-step authentication flows (such as OTPs or multi-factor prompts), the recorded login method provides better accuracy by capturing user interactions directly.
Deciding when to do a gray box penetration test vs a black box penetration test
Understanding when to choose gray box or black box testing depends on your goals and available information.
When to choose gray box testing:
You want to assess authenticated user workflows and internal logic.
You need deeper insight into vulnerabilities behind login walls.
You want realistic simulations of compromised user accounts.
When to choose black box testing:
You are testing from an external attacker’s point of view.
You need to validate public-facing defenses.
You have limited internal access or credentials.
In Beagle Security, this distinction is made through configuration, not test type selection.
For black box testing, simply skip the authentication configuration.
For gray box testing, configure authentication, record business logic, and define the tech stack.
There is no dropdown to toggle gray box or black box, your setup determines the test type.
Additional configurations for grey box penetration test
Gray box penetration testing in Beagle Security offers several configuration options that enhance test depth and accuracy.
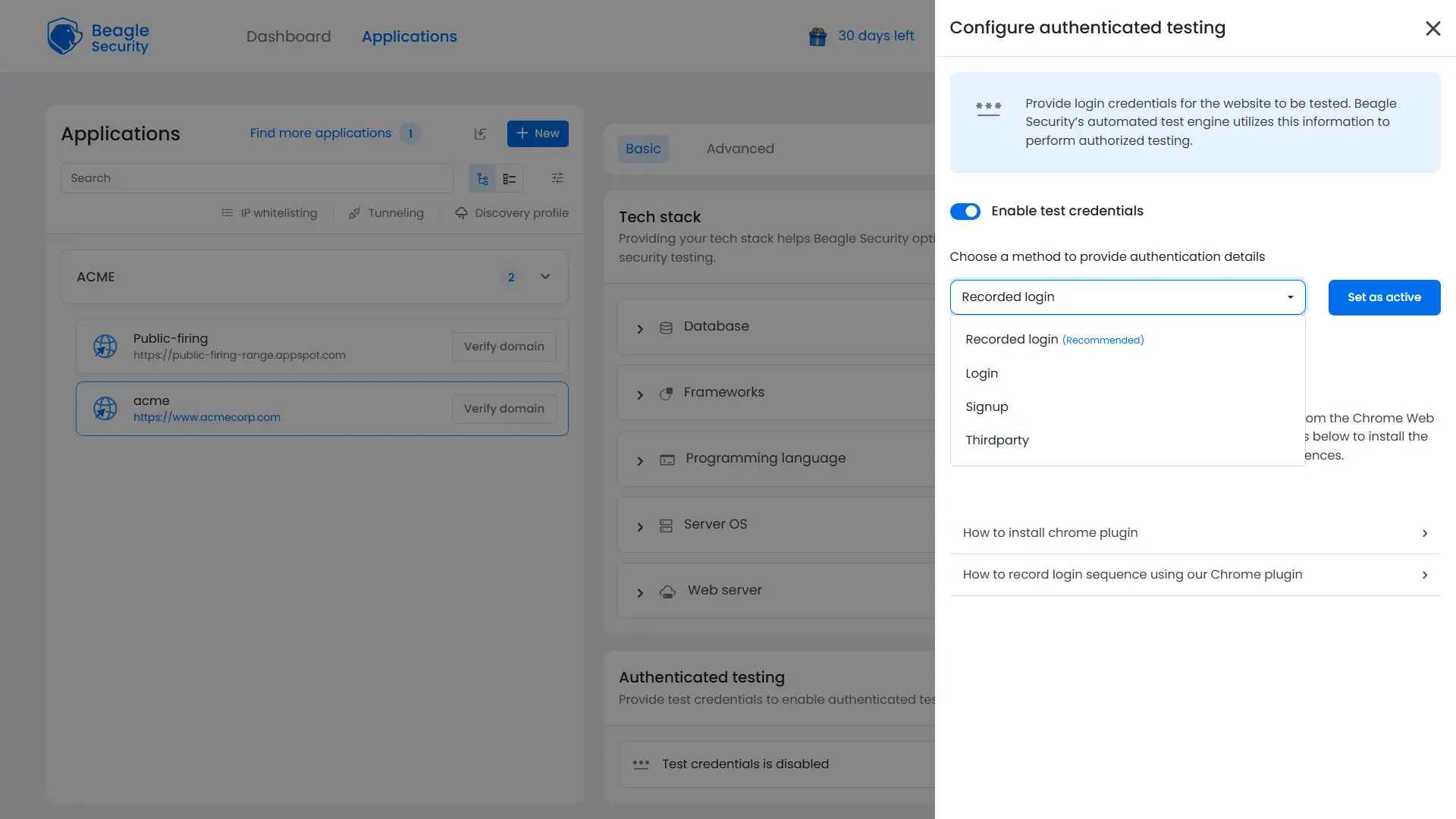
Authenticated testing
Authenticated testing allows Beagle Security to analyze vulnerabilities that only appear for logged-in users. It ensures deeper coverage of session handling, access control, and business workflows.
Beagle Security supports multiple authentication methods:
Recorded login
Login
Signup
Thirdparty
Setting up login form method
Step 1: Navigate to Authentication settings
Go to your application’s configuration and click Configure Authentication. This opens the Configure authenticated testing panel.
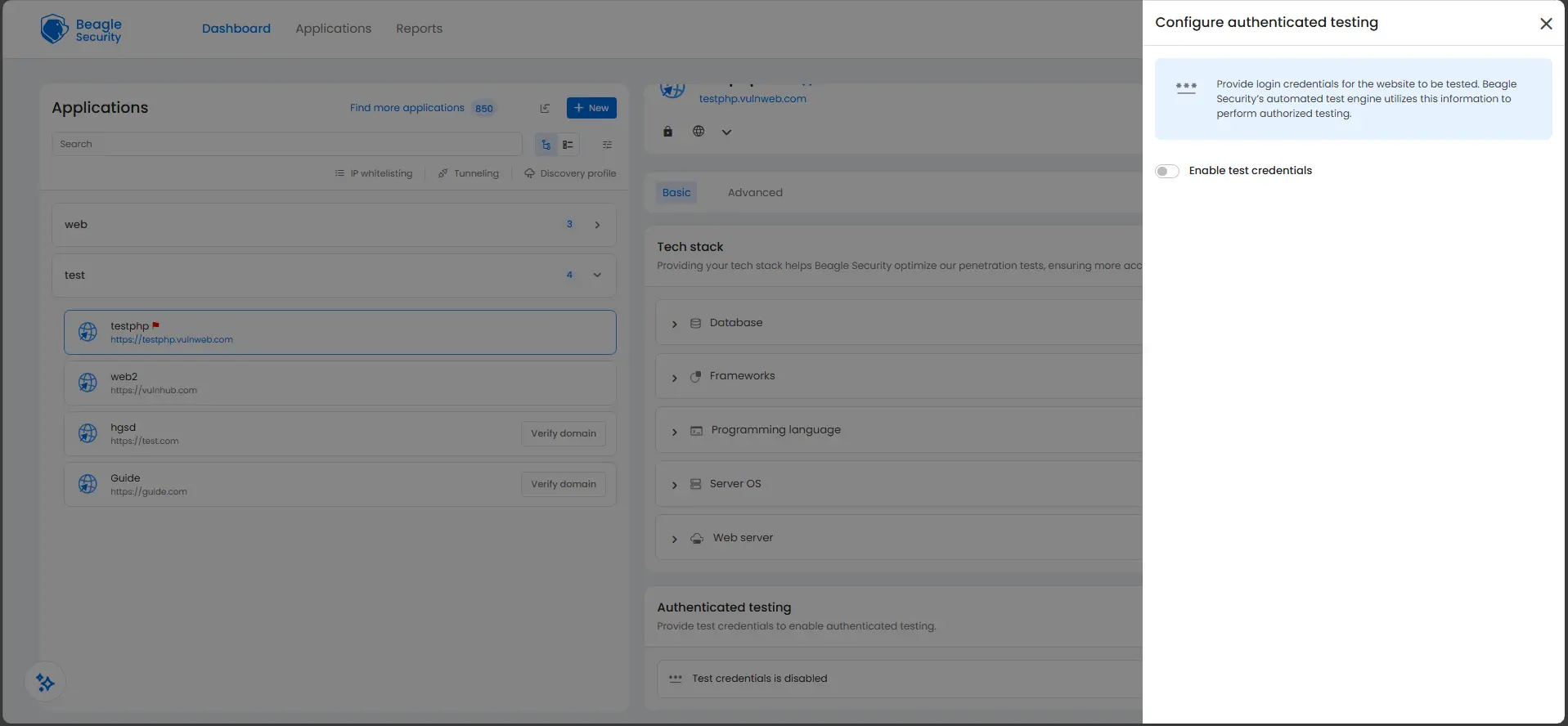
Step 2: Enable test credentials
Toggle the Enable test credentials switch to ON. The toggle turns blue when activated. This enables Beagle Security to use the credentials you provide during the authentication process.
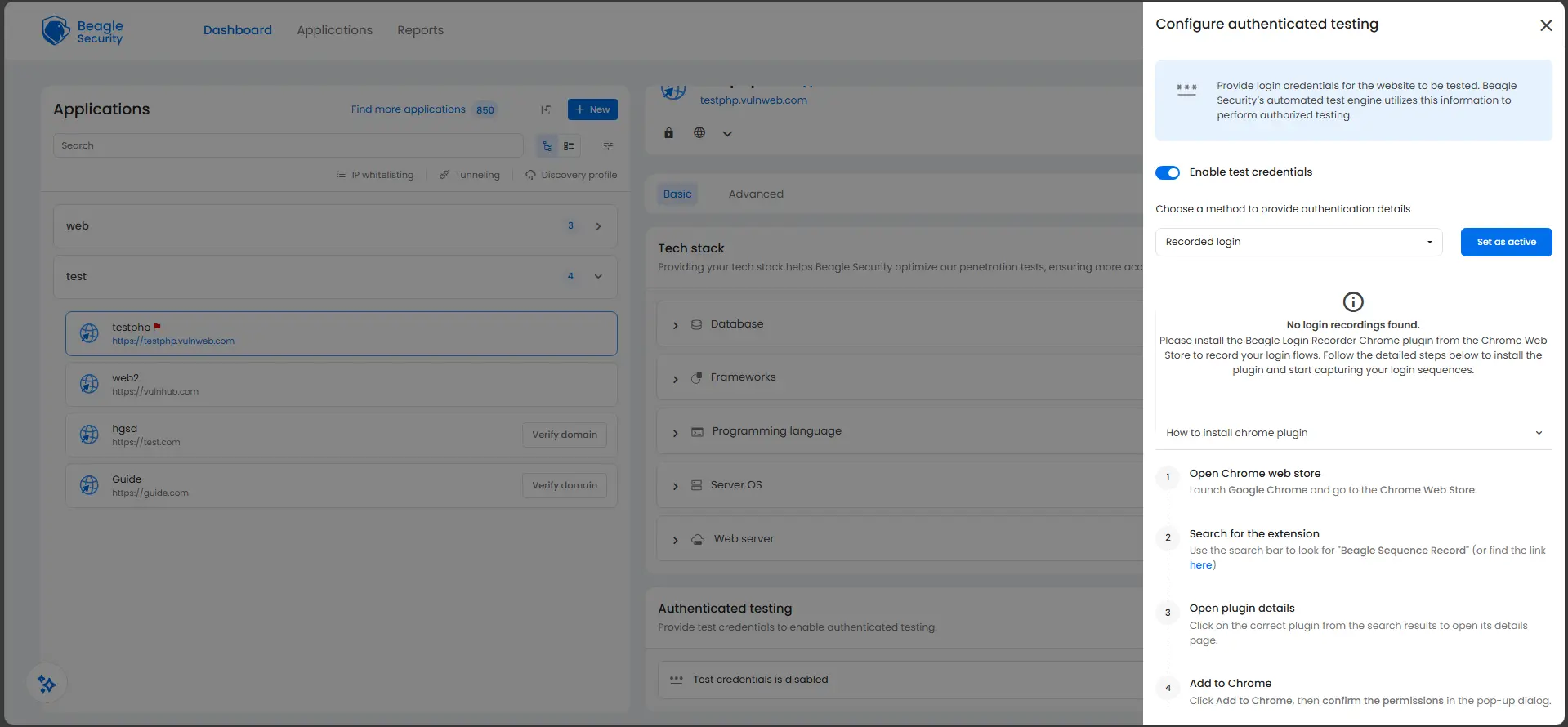
Step 3: Choose Login as the authentication method
From the dropdown labeled Choose a method to provide authentication details, select Login and click the blue Set as active button on the right.
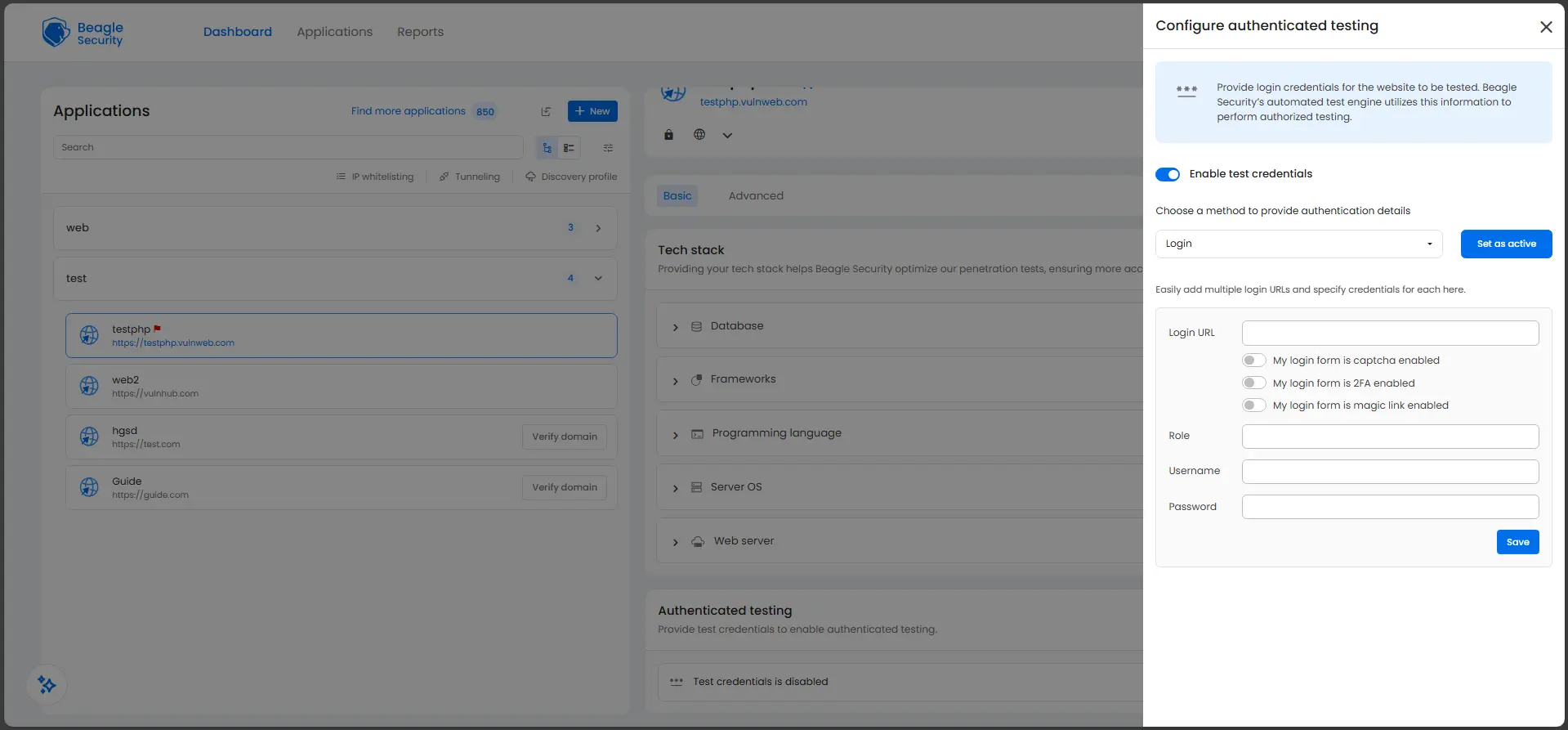
Step 4: Configure login form details
Fill in the following fields in the form:
Login URL: Enter the full URL of your application’s login page.
Role: Specify the user role being tested (for example, admin, user, or guest).
Username: Enter a valid test username.
Password: Enter the corresponding password (displayed as masked dots).
Optional settings available via checkboxes:
My login form is captcha enabled
My login form is 2FA enabled
My login form is magic link enabled
Step 5: Save the configuration
Click the blue Save button at the bottom right to store your configuration. Beagle Security will now use these credentials to automatically authenticate during the penetration test.
Tech stack configuration
Providing your application’s tech stack helps Beagle Security tailor its vulnerability checks to your environment.
Step 1: Access Advanced Configuration > Tech Stack.
Step 2: Select or enter:
Frontend framework (React, Angular, Vue, etc.)
Backend language (Python, Node.js, Java, etc.)
Database system
Third-party libraries
This configuration ensures targeted tests and fewer false positives.
Business logic recording
Business logic testing captures unique workflows that automated scanners might miss. This helps identify logic-based vulnerabilities like privilege misuse or faulty transaction handling.
Step 1: Open Business Logic Recording.
Step 2: Perform a key user flow such as payment checkout, profile update, or file upload.
Step 3: Save the recorded flow for replay during scans.
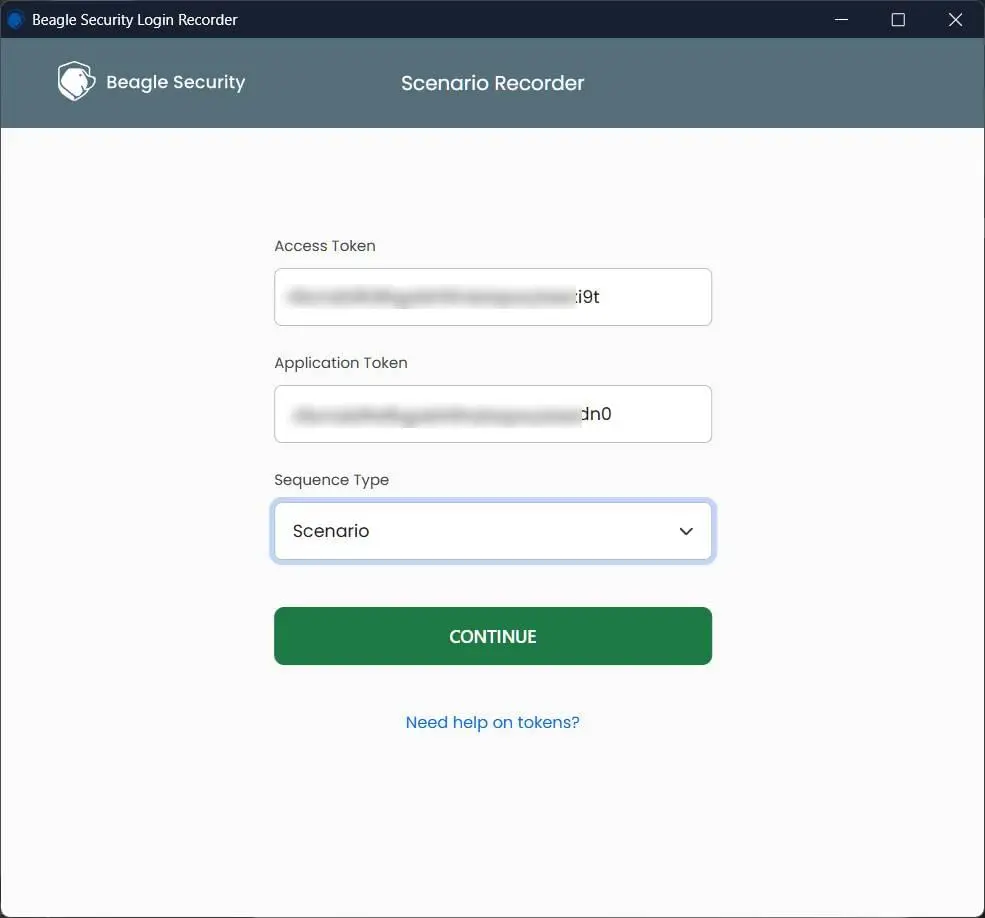
Examples of critical flows to record:
Login and password reset
Shopping cart and checkout
File upload or data entry forms
Role-specific actions (admin, user)
Scope of test selection
Defining scope boundaries ensures tests are efficient and respect ownership.
Step 1: Navigate to Scope Settings.
Step 2: Include or exclude specific URLs, subdomains, or API paths.
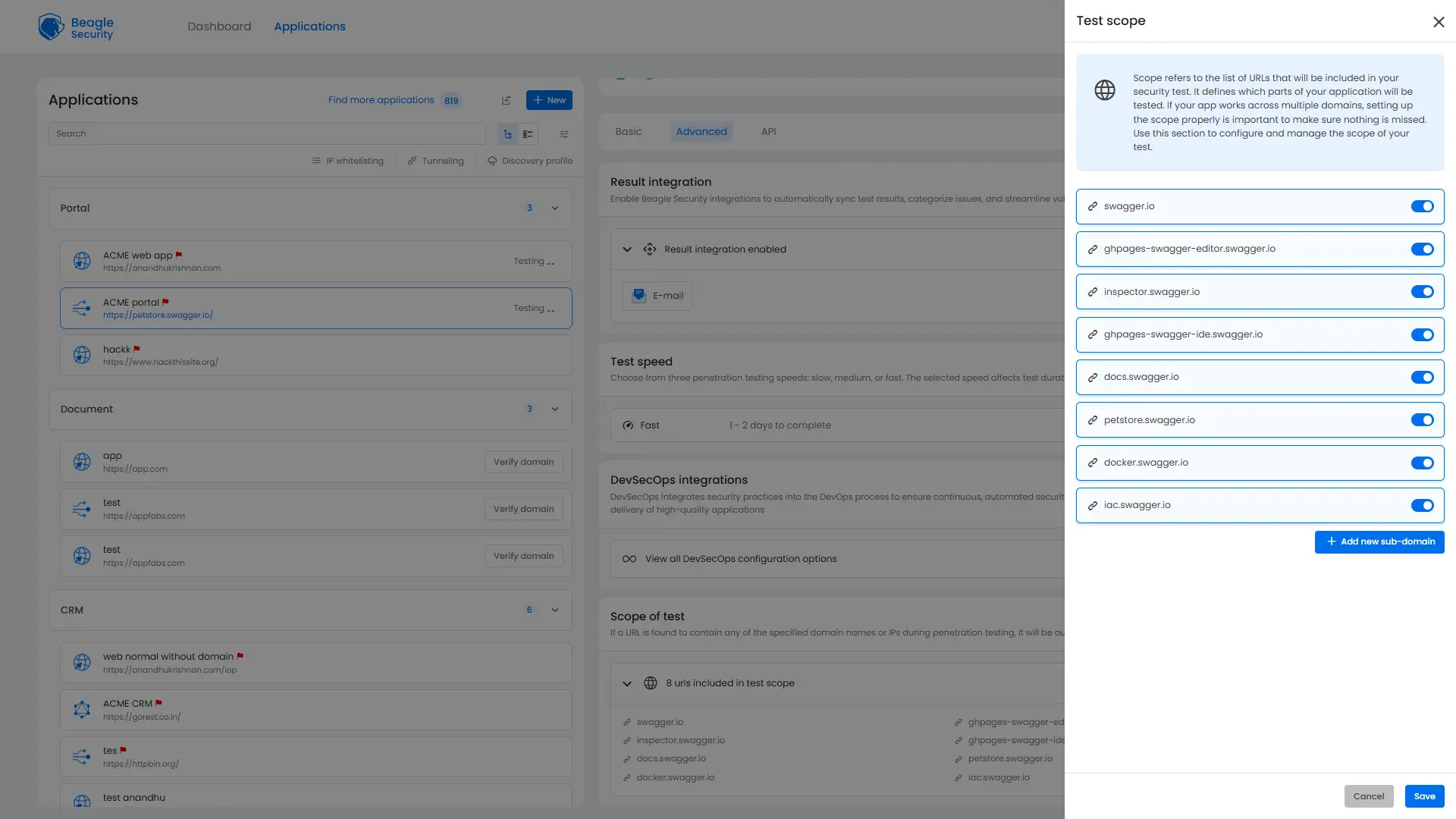
Scope considerations:
Include only owned domains and environments.
Exclude third-party platforms.
Limit scope for faster turnaround on smaller tests.
Viewing the penetration test results and reports
Once your gray box penetration test completes, Beagle Security provides detailed dashboards and compliance-ready reports.
Application dashboard
The Application dashboard offers a summary of your security posture.
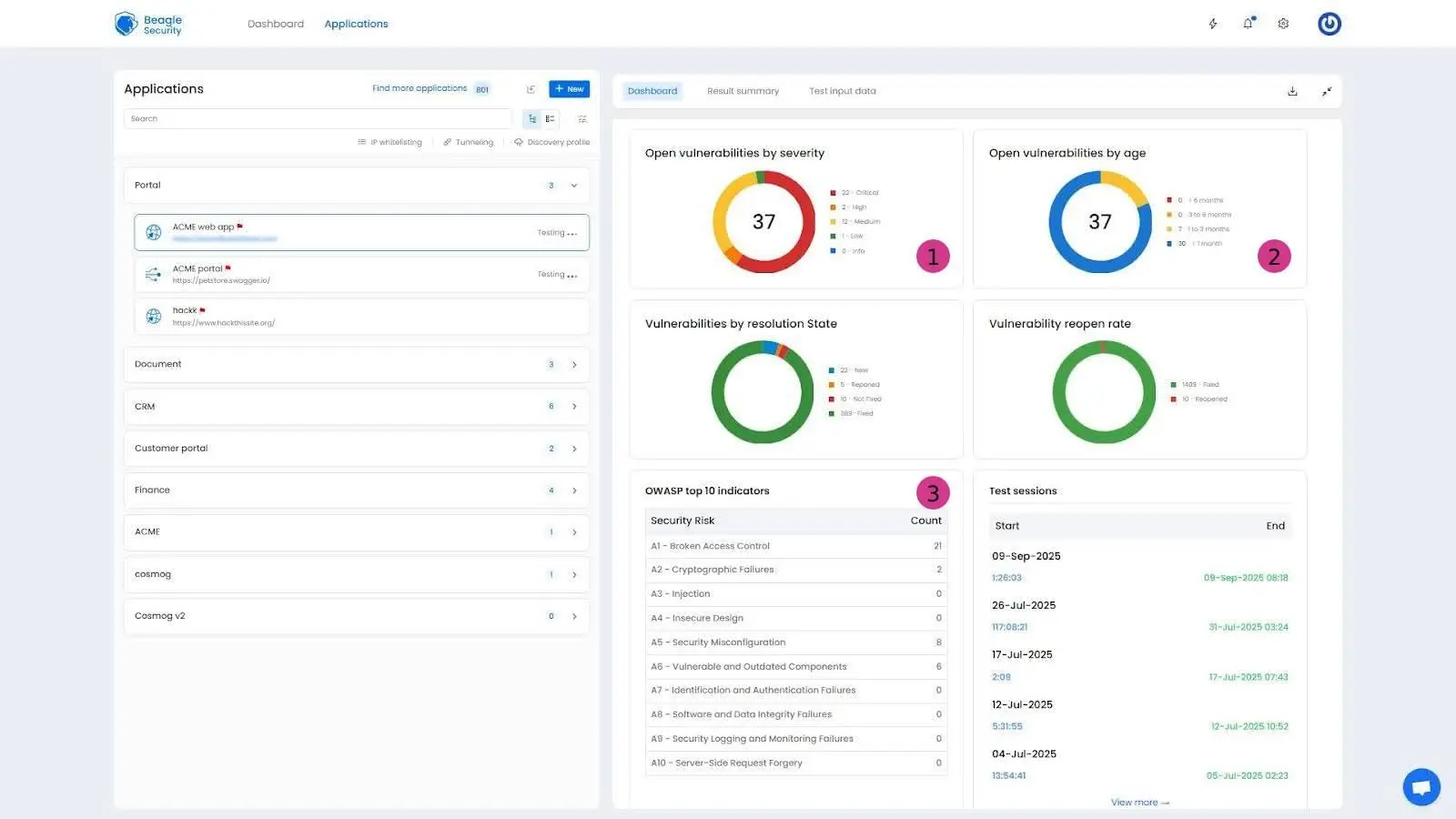
Open vulnerabilities by severity: Shows how many vulnerabilities fall under critical, high, medium, and low. Prioritize the highest-risk issues first.
Open vulnerabilities by age: Highlights how long vulnerabilities have been open to help track SLA performance.
OWASP top 10 indicators: Maps findings to OWASP categories for easy compliance alignment.
Fixing trend: Shows the rate of issue resolution versus discovery.
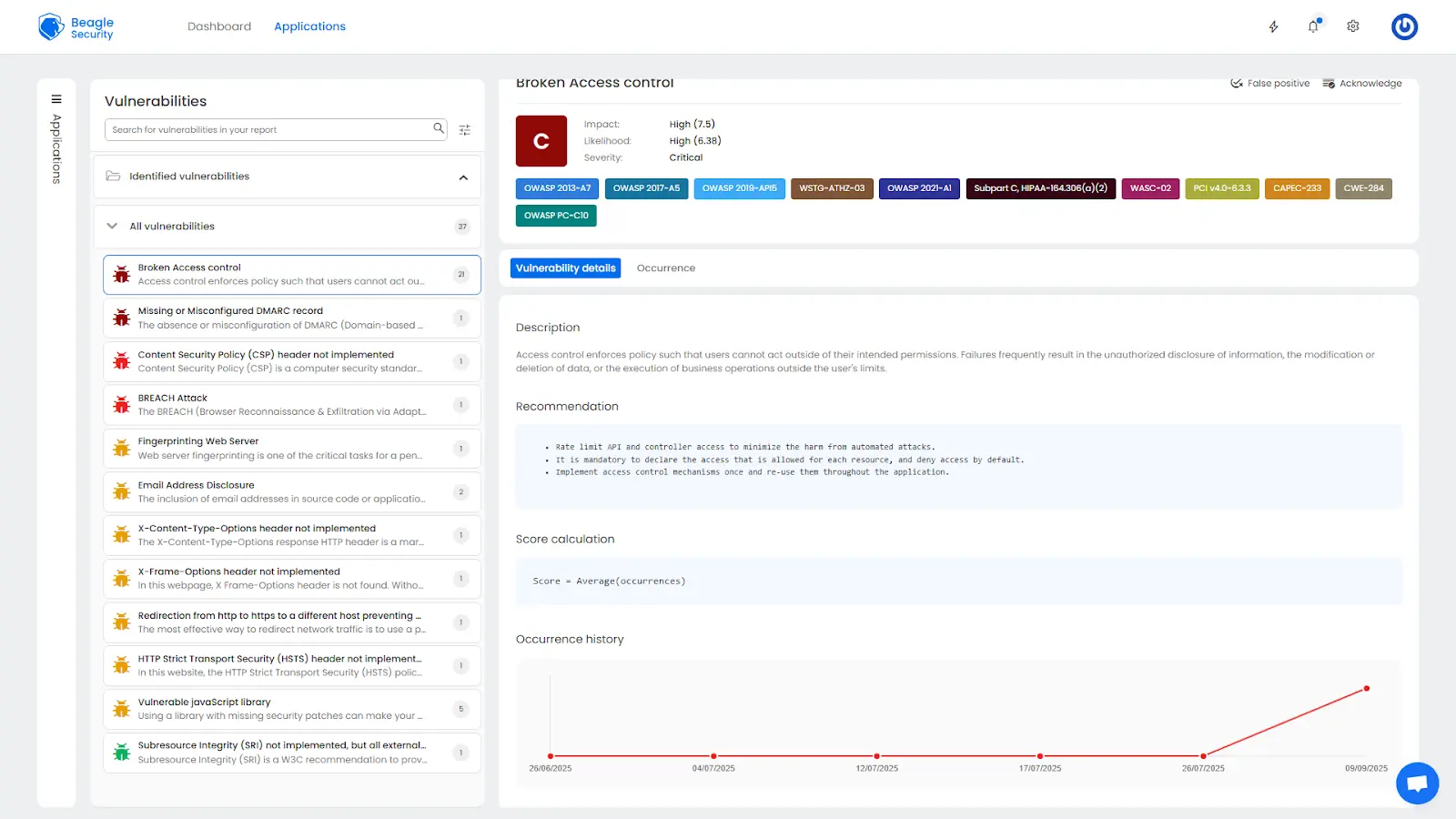
Vulnerability trend: Tracks overall security posture improvement across test cycles.
Result dashboard
The Result dashboard provides deep technical and compliance views.
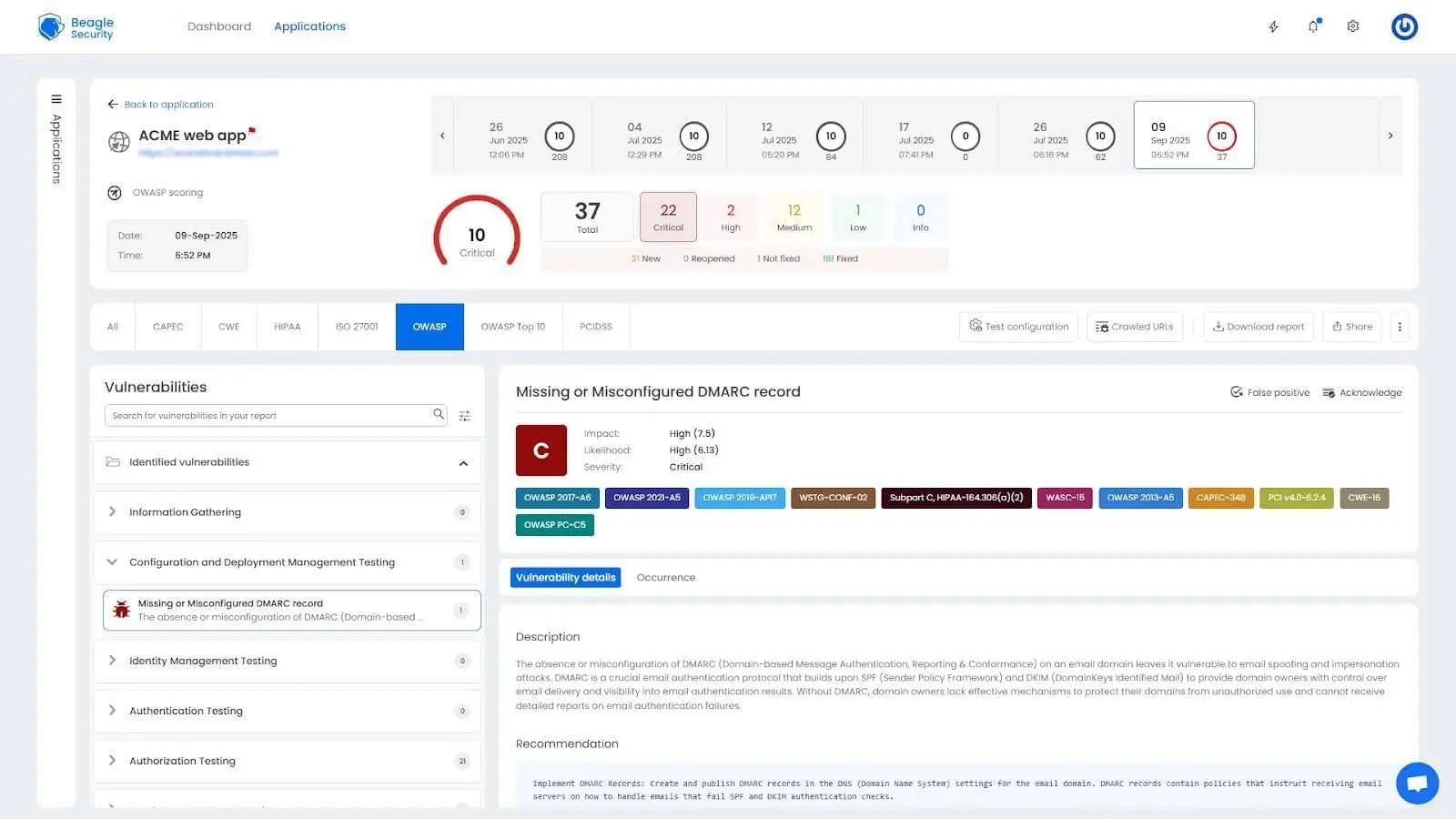
Mapping with ISO27001, OWASP & OWASP Top 10: Aligns vulnerabilities with ISO 27001, OWASP Testing Guide, and OWASP Top 10.
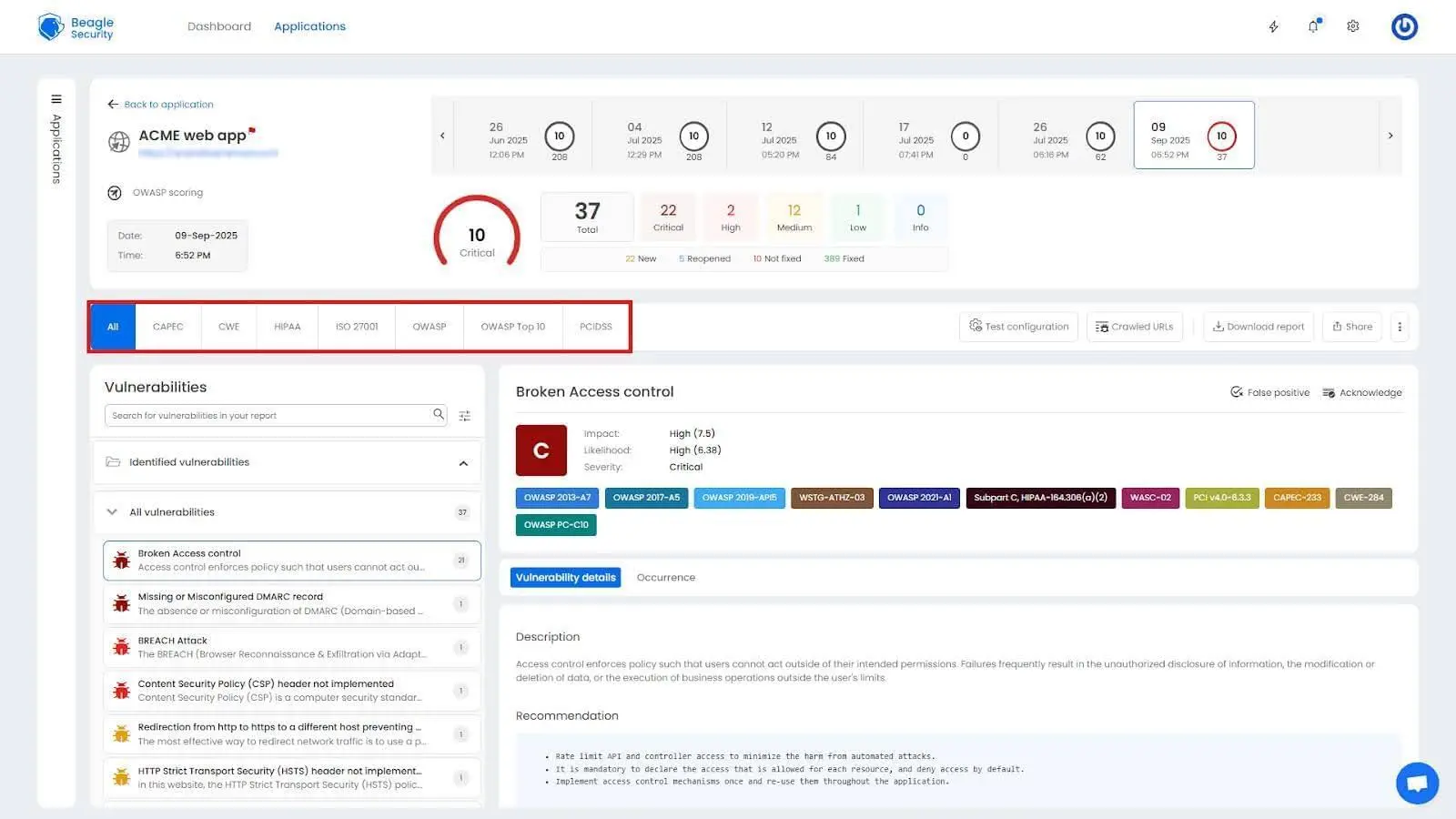
Detailed findings, fix recommendations & occurrence details
OWASP reports: Shows exact affected URLs, parameters, and request/response pairs.
Compliance reports: Specialized reports for HIPAA and PCI DSS readiness.
Final thoughts
Gray box penetration testing bridges the gap between black box and white box testing, offering the best of both worlds: realistic attack simulation with the added depth of authenticated insight. It helps teams uncover vulnerabilities that surface only when users are logged in, validating not just the application’s perimeter but also its core logic, user roles, and workflow security.
With Beagle Security, running a gray box penetration test becomes straightforward. Its authentication options, configurable test scopes, and real-time vulnerability analysis allow organizations to simulate real-world attack scenarios with precision. The detailed dashboards and compliance-ready reports make it easy to prioritize fixes, communicate findings, and improve your overall security posture.
In today’s continuous deployment environment, this approach enables security testing to evolve alongside your code and ensures every new release remains resilient against emerging threats.
FAQ
What is the cost for a gray penetration test?
Manual gray box tests typically range from $3,000 to $15,000 depending on scope. Automated platforms like Beagle Security offer subscription plans starting at $99 per month for continuous testing.
What’s the difference between black box and gray box pentesting?
Black box pentesting tests without internal information to simulate an external attacker. Gray box pentesting provides limited insider access such as credentials or API specs to test authenticated user paths and privilege escalation.



![Acunetix vs Nessus: Which is right for you? [2026] Acunetix vs Nessus: Which is right for you? [2026]](/blog/images/acunetix-vs-nessus-which-is-right-for-you-2026-cover.webp)
![OpenVAS vs Nessus: Which is the best choice for you? [2025] OpenVAS vs Nessus: Which is the best choice for you? [2025]](/blog/images/openvas-vs-nessus-which-is-the-best-choice-for-you-2025-cover.webp)


![Top enterprise application security tools [2026] Top enterprise application security tools [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-four-cover.webp)
![Top vendor application security testing tools [2026] Top vendor application security testing tools [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-six-cover.webp)
![Best API security tool for developers [2026] Best API security tool for developers [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-five-cover.webp)

![Top Bright Security alternatives [2026] Top Bright Security alternatives [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-one-cover.webp)