
Payment card data is often a key target for attackers. As the volume of online transactions increases, organizations must ensure that their systems handling cardholder data are secure. PCI DSS penetration testing plays a critical role in this, serving both as a compliance requirement and a practical security measure.
This guide provides an overview of PCI DSS penetration testing, its purpose, duration, and practical advice on how to implement and automate the process effectively.
What is PCI DSS penetration testing?
PCI DSS penetration testing is a security assessment designed to identify and exploit vulnerabilities within systems, networks, and applications that store, process, or transmit payment card data. The goal is to validate the effectiveness of security controls and demonstrate that cardholder environments are resilient against real-world attack scenarios.
At its core, PCI DSS penetration testing helps ensure that your organization’s Cardholder Data Environment (CDE) complies with Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) Requirement 11.4, which mandates penetration testing to verify that system defenses remain effective after significant changes or annually.
Key components of PCI DSS penetration testing
A typical PCI DSS penetration testing engagement includes several layers of assessment:
External penetration testing: Simulates attacks from outside the organization, focusing on internet-facing assets like web applications, APIs, and exposed infrastructure.
Internal penetration testing: Conducted from within the network to identify lateral movement risks, misconfigurations, or privilege escalation paths.
Web application penetration testing: Targets business logic flaws, authentication weaknesses, and data exposure in web portals or customer-facing apps.
Network segmentation validation: Confirms that systems storing cardholder data are effectively isolated from non-scoped networks.
What is the purpose of a PCI DSS penetration test?
The main goal of PCI DSS penetration testing is to identify and fix vulnerabilities before attackers can exploit them. Beyond compliance, it strengthens overall payment security and resilience.
A well-executed PCI DSS pentest helps you:
Validate security controls: Confirm that firewalls, access controls, and intrusion prevention systems protect cardholder data effectively.
Uncover hidden risks: Detect issues like misconfigurations, API flaws, or logic errors that traditional scans may overlook.
Verify compensating controls: Ensure alternative safeguards meet PCI DSS intent where direct compliance isn’t possible.
Reduce breach risk: Prevent data theft and fraud by addressing weaknesses proactively.
Prove compliance: Provide documented assurance to PCI assessors, acquiring banks, and auditors.
Maintain continuous assurance: Automate tests to assess every new code release or system update for PCI DSS impact.
When integrated with ongoing vulnerability management, PCI DSS penetration testing evolves from a checklist task into a continuous security assurance practice.
How long does a PCI DSS penetration test take?
The duration of a PCI DSS penetration test varies depending on several factors including environment size, scope complexity, testing methodology, and whether the engagement is manual or automated.
Typical timeframes
| Scope type | Description | Estimated duration |
|---|---|---|
| External pentest | Internet-facing systems and web apps | 3–7 days |
| Internal pentest | Internal network, CDE systems, databases | 5–10 days |
| Web application testing | Application logic, APIs, authentication | 7–14 days |
| Network segmentation validation | Connectivity and isolation checks | 2–5 days |
In automated or CI/CD-integrated environments, these cycles can be dramatically reduced. Continuous DAST-based PCI DSS penetration testing allows for incremental, short-duration scans that run in sync with deployments, ensuring compliance without slowing down development velocity.
PCI DSS requirements
Here’s a streamlined overview of the 12 core PCI DSS v4.0 requirements to help your team align controls, testing, and remediation workflows effectively.
1. Build and maintain a secure network and systems
Implement and maintain strong network security controls (firewalls, routers) to protect the Cardholder Data Environment (CDE).
Segment trusted and untrusted networks; restrict inbound/outbound access.
Mitigate risks from dual-connected devices (e.g., remote or mobile access).
2. Apply secure configurations to all system components
Enforce secure configurations across all system components and devices.
Remove vendor defaults, disable unnecessary services, and harden OS/app settings.
Secure all wireless networks and devices that can impact the CDE.
3. Protect stored account data
Safeguard Primary Account Numbers (PAN) and Sensitive Authentication Data (SAD).
Store only essential data; use encryption, hashing, or tokenization.
Protect and manage cryptographic keys securely.
4. Protect cardholder data in transit
Encrypt PAN and cardholder data using strong cryptography (TLS, IPSec) over public networks.
Avoid deprecated protocols; manage certificates and encryption configurations.
5. Protect systems and networks from malware
Implement anti-malware or equivalent solutions to detect and prevent threats.
Keep defenses updated, monitor continuously, and respond to infections swiftly.
6. Develop and maintain secure systems and software
Follow a secure SDLC including threat modeling, code reviews, and patch management.
Secure both custom and third-party applications; address vulnerabilities quickly.
7. Restrict access by business need-to-know
Enforce least-privilege access to systems and cardholder data.
Review access rights regularly and monitor privileged accounts.
8. Identify and authenticate users
Use unique IDs, strong authentication (including MFA), and robust account management.
Apply strong authentication for all access to the CDE and admin functions.
9. Restrict physical access to cardholder data
Control and monitor physical entry to CDE areas and devices storing card data.
Maintain visitor logs, secure hardware, and ensure proper media disposal.
10. Log and monitor all access
Maintain detailed audit logs for access to systems and cardholder data.
Protect logs from tampering, review regularly, and ensure time synchronization.
Detect and alert on critical control failures.
11. Test security regularly
Conduct frequent vulnerability scans, penetration tests, and segmentation testing.
Include authenticated internal scans and tamper/change detection per v4.0 updates.
12. Maintain an information security policy
Establish and enforce comprehensive security policies and governance programs.
Include risk management, training, vendor oversight, and incident response planning.
How to choose the right PCI DSS testing partner?
Selecting the right partner for PCI DSS penetration testing is crucial to ensure compliance, reduce risk, and maintain trust with customers. A reliable partner doesn’t just run automated scans but rather, they understand your business, your environment, and the nuances of the standard. Here are key factors to consider:
Expertise in PCI DSS standards: Look for a partner with demonstrated experience in PCI DSS 4.0, including knowledge of scoping, segmentation, and specific testing requirements like authenticated scans and CDE validation.
Integration with development workflows: Partners who support CI/CD integration can help you automate tests, trigger scans on build or deployment, and maintain continuous compliance without slowing development.
Actionable and compliance-ready reporting: Beyond identifying vulnerabilities, your partner should provide detailed, audit-friendly reports that map findings to PCI DSS requirements and prioritize remediation.
Scalability and flexibility: Every organization is unique. The partner should accommodate your application architecture, from legacy systems to modern microservices and cloud-native environments.
How to use Beagle Security for your PCI DSS penetration testing
Conducting PCI DSS penetration testing manually can be time-consuming, resource-intensive, and prone to inconsistencies. An automated solution like Beagle Security helps you streamline this process reducing both effort and cost while ensuring compliance-ready coverage across your web applications and APIs.
Here’s how you can efficiently set up, execute, and map your penetration testing workflow for PCI DSS using Beagle Security.
Getting started with Beagle Security
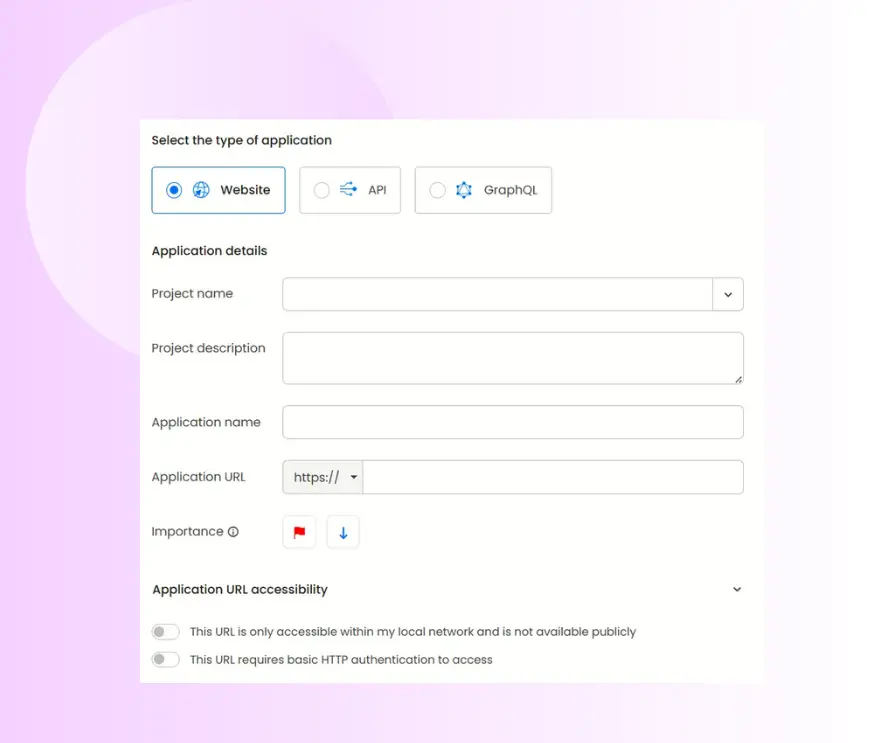
Start by adding a new application to the platform.
Add application: Click on “Add Application” and select the target you want to test such as a standard web application, REST API, or GraphQL endpoint.
Provide application details: Enter the application name and URL. This will serve as the main target for your AI-driven penetration testing.
Set access controls: You can define whether the target is public or restricted to ensure testers understand access boundaries.
Assign priority: Categorize your applications based on their business criticality to focus on what matters most.
This initial setup ensures your testing aligns with PCI DSS scope definitions and minimizes the risk of missing key in-scope assets.
Deciding between black box and grey box penetration testing selection
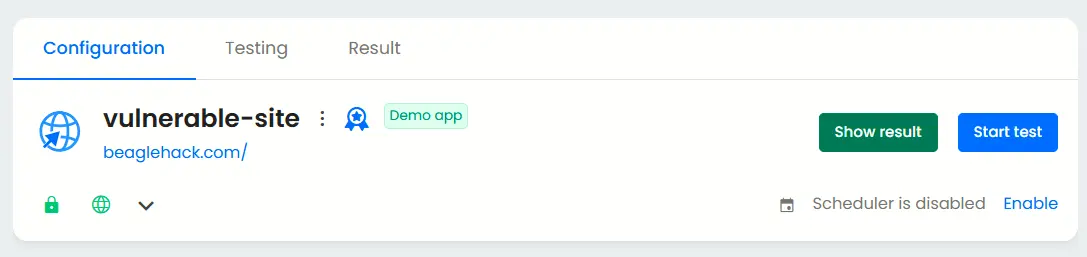
Penetration testing methods vary depending on system exposure and data sensitivity. Beagle Security supports both black box and grey box testing to match your compliance and risk requirements.
Black box testing: Simulates an external attacker with no prior knowledge of the system. Ideal for validating perimeter security and access control effectiveness.
Grey box testing: Conducted with limited internal information, simulating a compromised user or insider threat. This approach provides deeper insights into internal system weaknesses.
After selecting the preferred testing approach, simply click “Start Test” to begin your scan. The system evaluates your public-facing applications just as a real-world attacker would i.e. without requiring privileged access.
Additional configurations for grey box penetration test
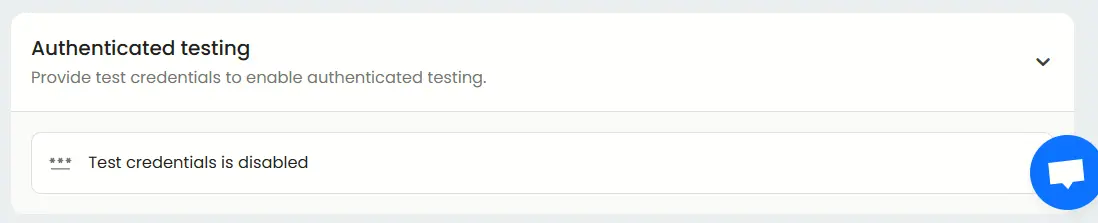
For PCI DSS compliance, authenticated testing is crucial to validate internal controls and post-login functionalities.
Enable authenticated testing: Under the Basic tab, toggle on the authenticated testing option and enter valid credentials.
Credential configuration: Choose from various authentication methods including standard login forms, signup flows, and third-party OAuth logins.
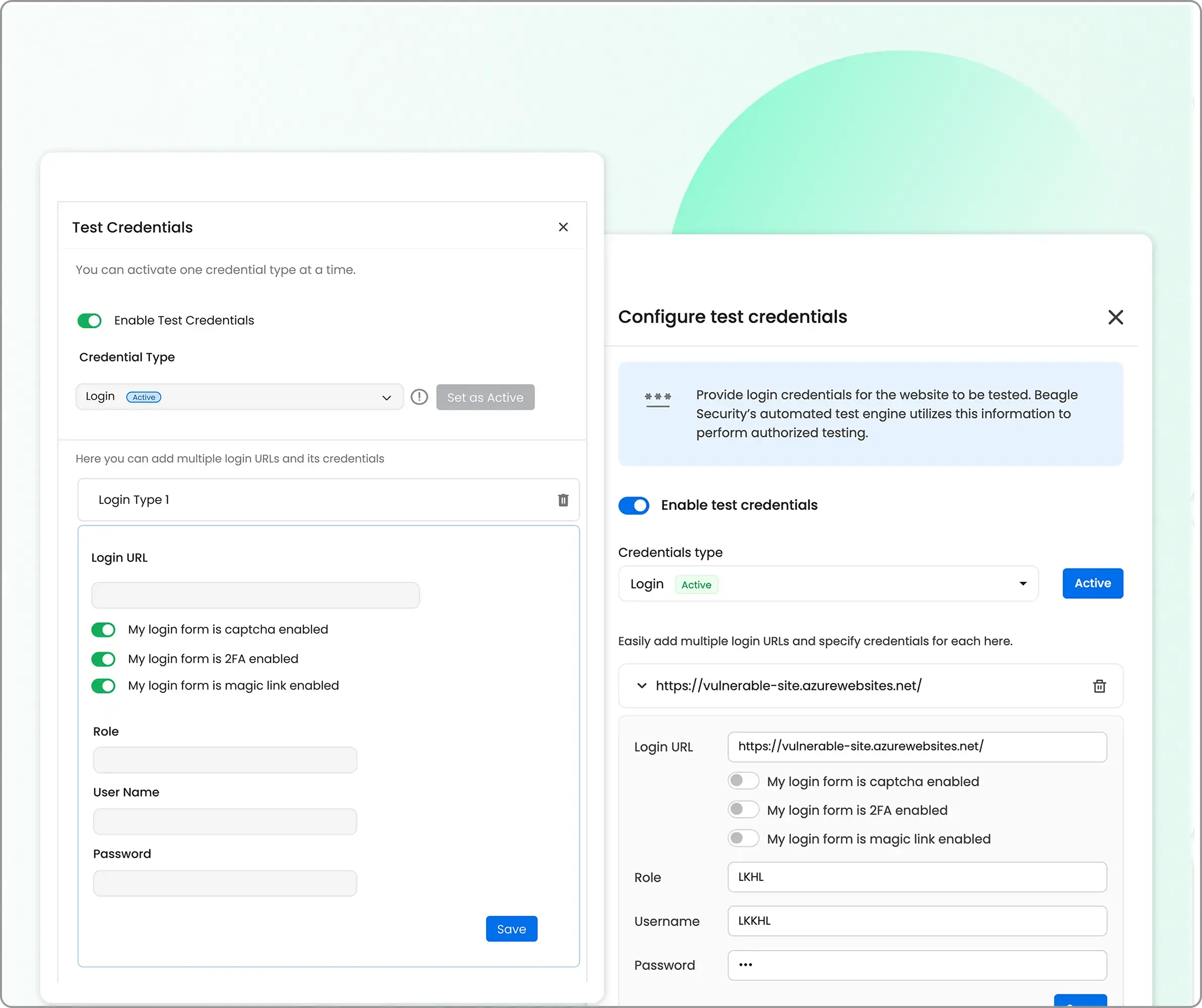
Recorded login (recommended): Using Beagle Security’s Chrome Extension to record login sessions ensures accuracy and eliminates session timeout issues during automated testing.
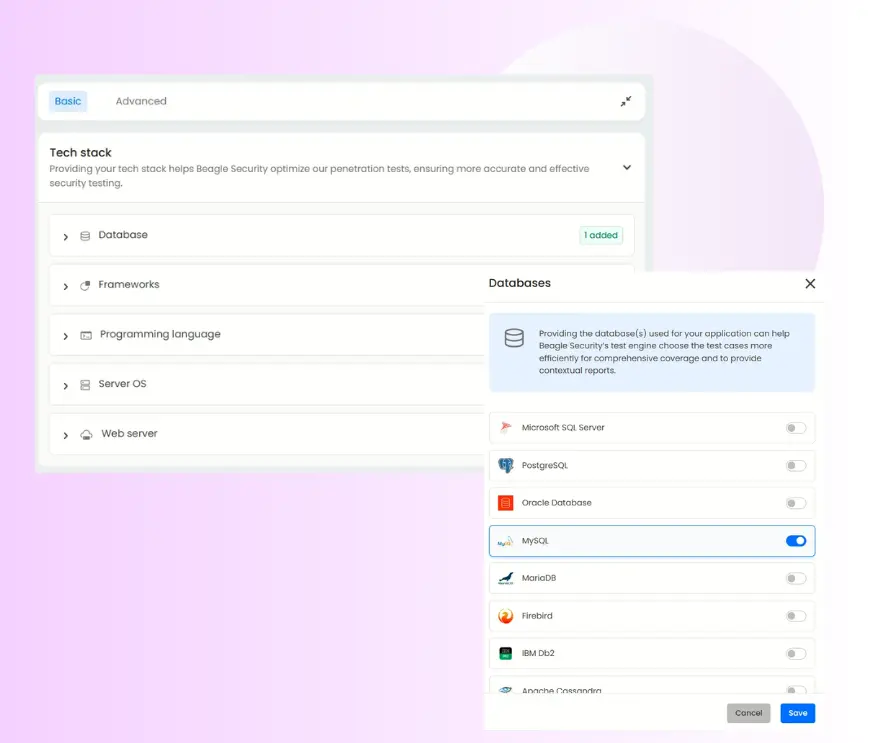
Tech stack configuration
Beagle Security allows you to customize the Tech Stack section to match your application’s architecture.
This context helps Beagle’s AI algorithms tailor the testing approach to detect vulnerabilities relevant to your environment.
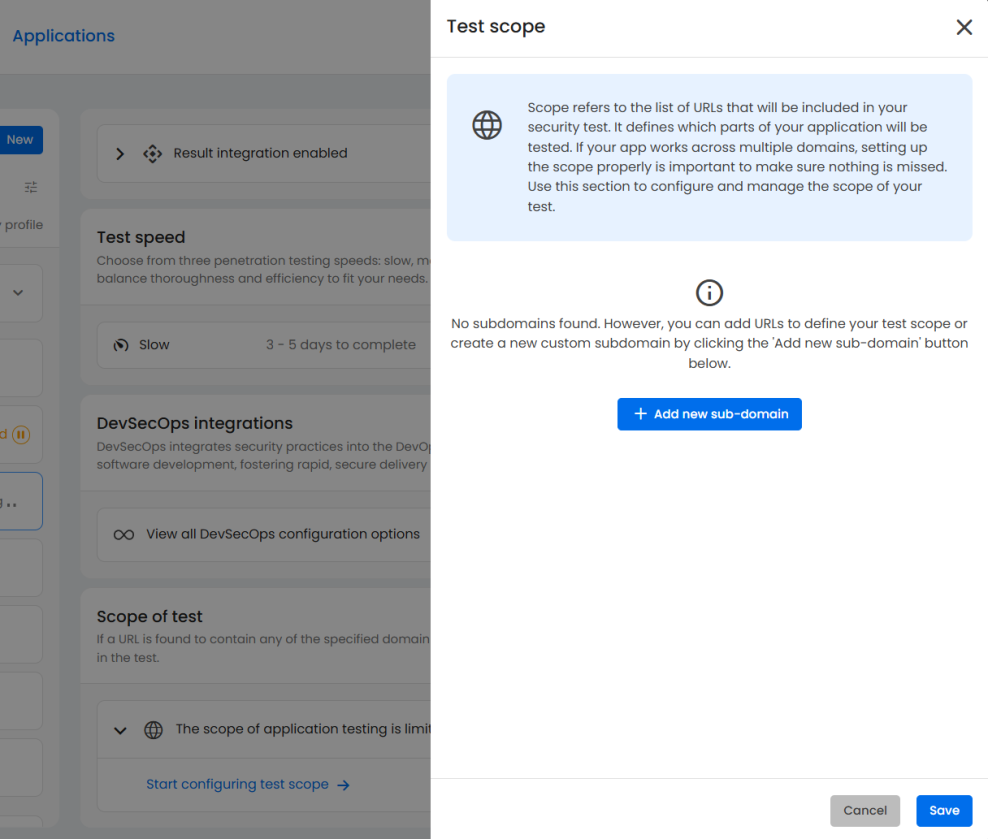
Pentest scope
Properly defining your testing scope is essential for PCI DSS compliance. This includes all systems involved in storing, processing, or transmitting cardholder data.
In Beagle Security, you can:
Include multiple URLs, domains, or subdomains
Add specific paths or API endpoints for granular coverage
Group related environments to maintain clarity across complex architectures
A well-defined scope ensures no component is overlooked during the PCI DSS assessment.
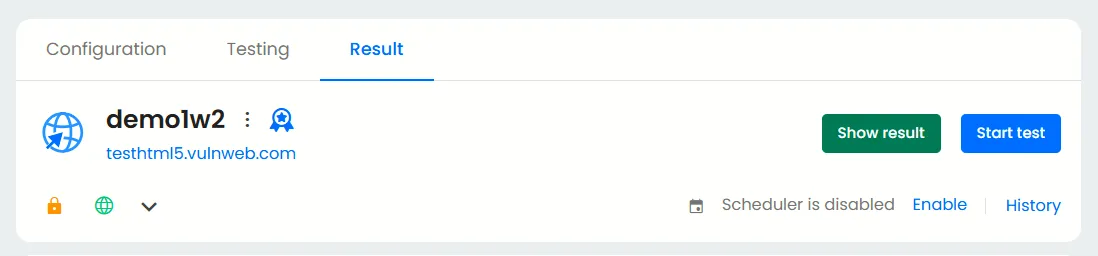
Viewing the penetration test results and mapping PCI DSS
Once the test is complete, navigate to the Applications tab and select “Show results.”
Here, click on the PCI DSS section. You’ll find an overview of vulnerabilities identified across your assets mapped directly to PCI DSS requirements.
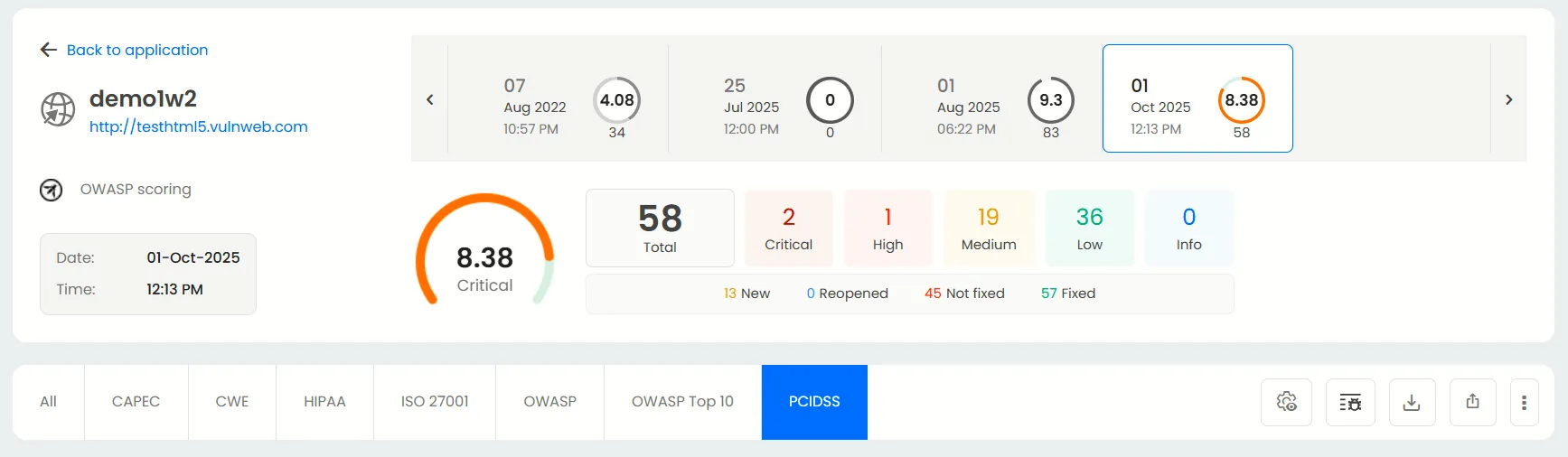
In the PCI DSS view:
The left panel categorizes vulnerabilities by relevant PCI DSS control sections.
The right panel provides detailed insights for each finding including descriptions, severity ratings, remediation recommendations, and recurrence history.
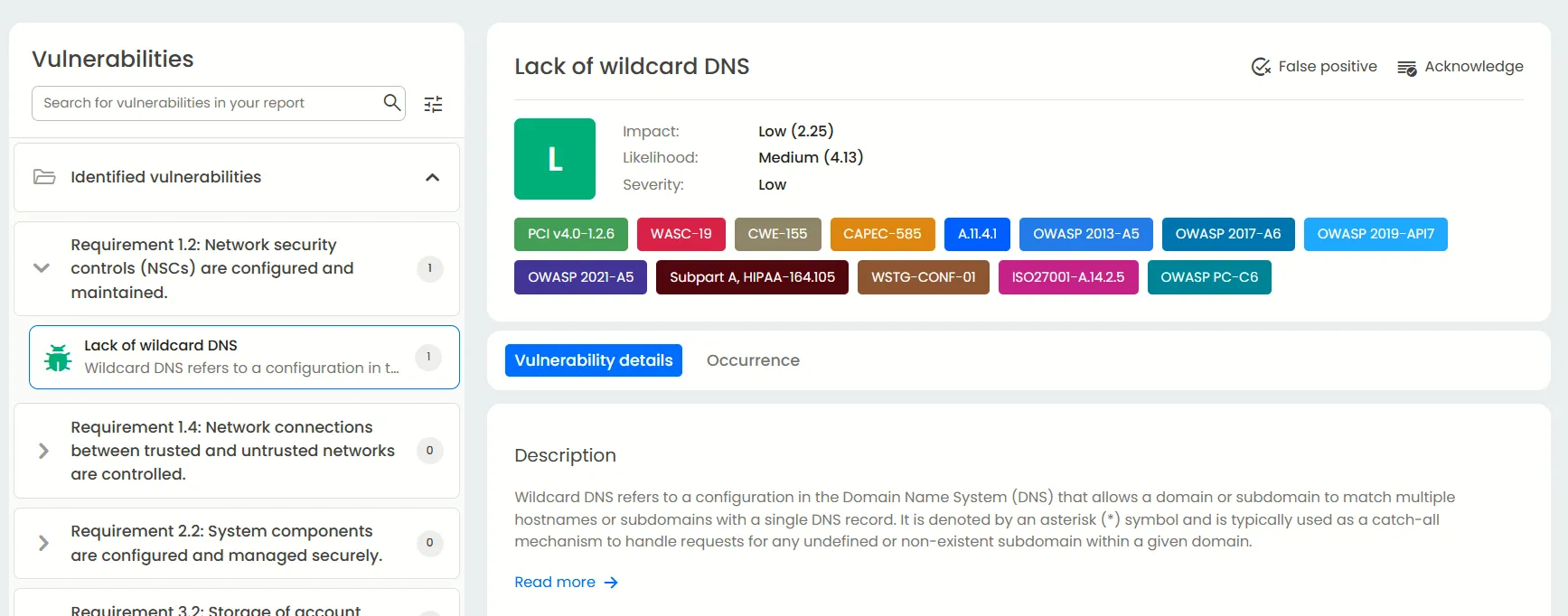
This structured reporting helps teams correlate technical findings with specific compliance obligations, streamlining audit preparation and evidence gathering.
Conclusion
PCI DSS penetration testing isn’t just a compliance checkbox: it’s a crucial process that validates your organization’s ability to protect cardholder data in real-world scenarios.
By combining structured methodologies with automation through DAST tools, organizations can transform static, annual assessments into continuous security assurance.
Platforms like Beagle Security make that journey practical and scalable, helping teams shift from one-off audits to continuous, evidence-driven assurance of data protection. Check out our free 14-day advanced trial, or look into our interactive demo to see if we’re the right fit for you.
FAQ
What is PCI DSS and why is it important?
PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) is a global framework that protects payment card data and helps prevent fraud, breaches, and compliance penalties.
What is PCI DSS penetration testing?
It’s a simulated cyberattack used to identify vulnerabilities within the Cardholder Data Environment (CDE) and validate security controls for PCI compliance.
How often should PCI DSS penetration testing be conducted?
At least annually, after major system changes, or following a suspected security incident.
What happens if a company fails to comply with PCI DSS?
Non-compliance can lead to fines, increased processing fees, loss of privileges, and severe reputational damage.



![Acunetix vs Nessus: Which is right for you? [2026] Acunetix vs Nessus: Which is right for you? [2026]](/blog/images/acunetix-vs-nessus-which-is-right-for-you-2026-cover.webp)
![OpenVAS vs Nessus: Which is the best choice for you? [2025] OpenVAS vs Nessus: Which is the best choice for you? [2025]](/blog/images/openvas-vs-nessus-which-is-the-best-choice-for-you-2025-cover.webp)


![Top enterprise application security tools [2026] Top enterprise application security tools [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-four-cover.webp)
![Top vendor application security testing tools [2026] Top vendor application security testing tools [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-six-cover.webp)
![Best API security tool for developers [2026] Best API security tool for developers [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-five-cover.webp)

![Top Bright Security alternatives [2026] Top Bright Security alternatives [2026]](/blog/images/blog-banner-one-cover.webp)