![Top 10 SDLC tools [2025] Top 10 SDLC tools [2025]](/blog/images/blog-banner-three.webp)
Modern software development has become more complex than ever. Teams now manage distributed systems, microservices, cloud deployments, rapid release cycles, and increasingly demanding user expectations.
Delivering high-quality software at speed requires more than just strong engineering skills. It demands the right ecosystem of SDLC tools that streamline development, improve collaboration, automate testing, and strengthen security across every phase of the software development lifecycle.
Organizations that invest in powerful SDLC tools consistently outperform those that rely on manual processes or outdated systems.
They release features faster, catch defects earlier, improve team productivity, maintain higher code quality, and adopt DevSecOps practices more easily. However, selecting the right tools is often overwhelming because the market is crowded with hundreds of platforms, each claiming to be essential.
This guide breaks through the noise. It helps you understand what SDLC tools are, the categories they fall into, and the top 10 tools shaping the development landscape in 2025.
Whether you are building your first toolchain or optimizing an existing one, this article will give you a clear framework for choosing the right combination of platforms that will improve your velocity, quality, and security.
What are SDLC tools
SDLC tools are software platforms that support and enhance different phases of the software development lifecycle. They help teams create, design, build, test, deploy, secure, and maintain software systems more efficiently. These tools automate repetitive tasks, streamline collaboration, improve code quality, and ensure that development workflows remain structured and predictable.
The purpose of SDLC tools is to solve real-world development challenges.
These tools support planning and estimation, source control and collaboration, continuous testing, deployment automation, and post-release monitoring. They help teams follow consistent development processes so that software is shipped faster and with fewer defects.
Integrations between SDLC tools also play a major role, since modern engineering workflows rely on connected platforms that share data and trigger automated actions.
Over the years, SDLC tools have evolved significantly. Early tools were siloed and handled only one part of the development process. Today, modern platforms offer integrated experiences that connect planning, development, testing, deployment, and observability in a unified lifecycle.
DevOps and DevSecOps practices accelerated this evolution, encouraging teams to shift left by addressing quality and security earlier in the lifecycle. AI-assisted automation is now emerging as a powerful force, improving productivity and reducing manual effort.
An effective software development toolchain is built by selecting complementary tools that work well together. Teams must balance capability, complexity, and integration depth. Too many tools create unnecessary overhead while too few tools limit productivity. The goal is to build an ecosystem that supports team workflows while enhancing speed, quality, and security.
Types of SDLC tools
SDLC tools span several categories that support different phases of development. Effective engineering teams build toolchains that pull from multiple categories, ensuring that planning, coding, testing, security, deployment, and monitoring are all well supported.
Automation tools
Automation tools support continuous integration, continuous delivery, build automation, release orchestration, and infrastructure as code. They allow teams to automate repetitive tasks, enforce consistency, and speed up the release cycle.
Tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and CircleCI handle builds, run automated tests, trigger deployments, and enforce quality gates.
Infrastructure as code tools like Terraform and Ansible give teams predictable infrastructure management and version-controlled server configurations. Test automation frameworks help ensure that new changes are validated continuously. These automation tools are essential for improving development velocity and reducing human error.
Automation plays a central role in DevOps practices by removing manual bottlenecks. With strong automation workflows, teams can release updates multiple times a day rather than once every few weeks. Automated pipelines also help maintain alignment between development, operations, and QA.
Whether a team manages monolithic applications or distributed microservices, automation tools ensure that software flows smoothly through each stage of the pipeline.
Monitoring and maintenance tools
Monitoring and maintenance tools help teams maintain production stability by providing visibility into application performance, server health, logs, and errors.
Platforms like Datadog, New Relic, and Prometheus provide application performance monitoring while tools like Sentry and Rollbar detect exceptions in real time. Log aggregation tools centralize logs for debugging, compliance, and incident response.
Monitoring tools help identify issues early and give development teams the data they need for troubleshooting. They enable continuous observability and ensure that teams stay informed about the behavior of deployed applications.
As systems become more distributed, monitoring tools are now essential for maintaining uptime, reducing incident severity, and achieving operational excellence.
Testing tools
Testing tools ensure software quality by validating functionality, performance, compatibility, and reliability. They include unit testing frameworks, integration testing platforms, cross-browser testing tools like BrowserStack, and performance testing suites.
API testing platforms validate backend services while end to end test automation ensures that user flows work across all devices. Testing tools allow teams to introduce quality gates in CI pipelines and automate test execution. They reduce manual QA workload and catch issues earlier in development cycles.
Testing tools are essential because they provide confidence in every release. Modern applications are complex, so automated tests must cover a wide range of use cases. When integrated into CI/CD workflows, testing tools help teams maintain rapid delivery without sacrificing quality.
Security tools
Security tools help identify vulnerabilities early and protect applications from attacks. Categories include static application security testing (SAST), dynamic application security testing (DAST), software composition analysis (SCA), container scanning, and infrastructure security.
These tools shift security left by embedding security checks into development and deployment pipelines. DAST tools like Beagle Security test running applications for vulnerabilities in real time. SAST tools like Semgrep scan source code for risks. SCA tools detect vulnerable dependencies.
Security tools are now essential for modern SDLC because security can no longer be an afterthought. Continuous security validation ensures that vulnerabilities are caught before applications reach production, reducing risk and improving compliance readiness.
Planning tools
Planning tools support project management, agile workflows, sprint planning, backlog management, and requirement tracking.
Tools like Jira and Asana enable teams to plan work, visualize progress, track tasks, and coordinate releases. Planning tools support collaboration across engineering, product, and design teams. They also provide reporting features such as sprint velocity, project timelines, and burndown charts.
Effective planning tools ensure that development teams stay aligned and that work is prioritized correctly. They form the backbone of agile development by enabling transparency and accountability. Strong planning tools are essential for predictable development cycles and cross-team coordination.
Documentation tools
Documentation tools provide structured spaces for technical documentation, knowledge bases, API documentation, and collaborative writing.
Confluence and Notion serve as centralized knowledge systems while Swagger and Postman help generate API documentation. These tools support onboarding, improve communication, and preserve team knowledge. They also enable documentation as code practices, where documentation is version-controlled alongside software.
Teams rely on documentation tools to ensure that information remains accessible and updated. Well-documented systems reduce onboarding time, prevent knowledge loss, and support long-term maintainability.
Design and modeling tools
Design and modeling tools support system architecture planning, UML diagrams, database modeling, flowcharts, wireframing, and API specification.
Tools like Modelio, Lucidchart, and Figma help teams visualize ideas, validate system structures, and communicate design decisions. API modeling tools such as OpenAPI allow teams to design and document services before implementation.
These tools are essential for aligning teams on architectural decisions and preventing misunderstandings. Strong design practices lead to more maintainable systems and better long-term scalability.
Top 10 SDLC tools in 2025
A wide range of SDLC tools are available today, but only a handful stand out in terms of capability, usability, ecosystem, and adoption.
This list highlights the top ten tools across key SDLC categories. Each tool excels in a specific domain and contributes meaningfully to an effective development workflow. Rather than focusing on a single category, this list covers a range of capabilities, from planning to security to testing and automation.
The goal is to help teams build an integrated toolchain that improves development speed, quality, and reliability. Each tool below includes an overview, key capabilities, SDLC coverage, integrations, best fit, and reasons why development teams prefer it.
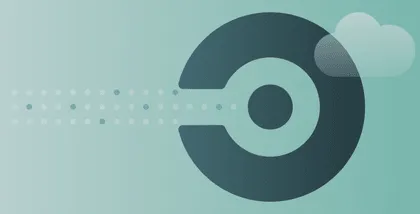
1. Beagle Security
Category: Security tools (DAST and automated penetration testing)
Beagle Security is a modern automated penetration testing platform that brings continuous security validation into the SDLC. It enables development teams to integrate security testing directly into their CI/CD pipelines and catch vulnerabilities early in the lifecycle.
By automating dynamic application security testing, Beagle Security helps developers validate the security of web applications and APIs without the need for manual penetration testing. It fits naturally into DevSecOps workflows by offering automated testing triggered by code pushes or deployments.
The platform supports shift left security by allowing teams to validate business logic, authentication flows, and API endpoints using automated DAST techniques.
Developers receive actionable vulnerability insights with detailed remediation guidance that fits into existing workflows. Beagle Security supports modern application architectures, including microservices and distributed systems. This makes it suitable for organizations seeking continuous validation across multiple environments.
A major advantage of Beagle Security is its comprehensive API security testing support. It handles REST APIs & GraphQL while providing authenticated testing, parameter validation, and business logic checks.
Its CI/CD integrations allow developers to incorporate security testing as part of automated pipelines. The platform maps findings to OWASP Top 10, OWASP API Top 10, PCI DSS, HIPAA, and ISO 27001 requirements which helps teams maintain compliance.
Key capabilities:
Automated DAST penetration testing
White-label reporting for professional, branded vulnerability reports
API security testing for REST, GraphQL, and SOAP
Business logic and authenticated testing
OWASP Top 10 and compliance coverage
Detailed vulnerability reports with remediation steps
CI/CD pipeline integrations and shift left capabilities
Continuous and scheduled testing options
SDLC phase coverage: Testing, security, deployment, and continuous validation
Integration highlights: Jenkins, GitHub, GitLab, Jira, Slack, CircleCI
Best for: Development teams adopting DevSecOps, API driven organizations, and companies needing continuous automated security testing
Why teams choose Beagle Security: It provides reliable security validation without slowing development and delivers actionable insights that developers can fix quickly.
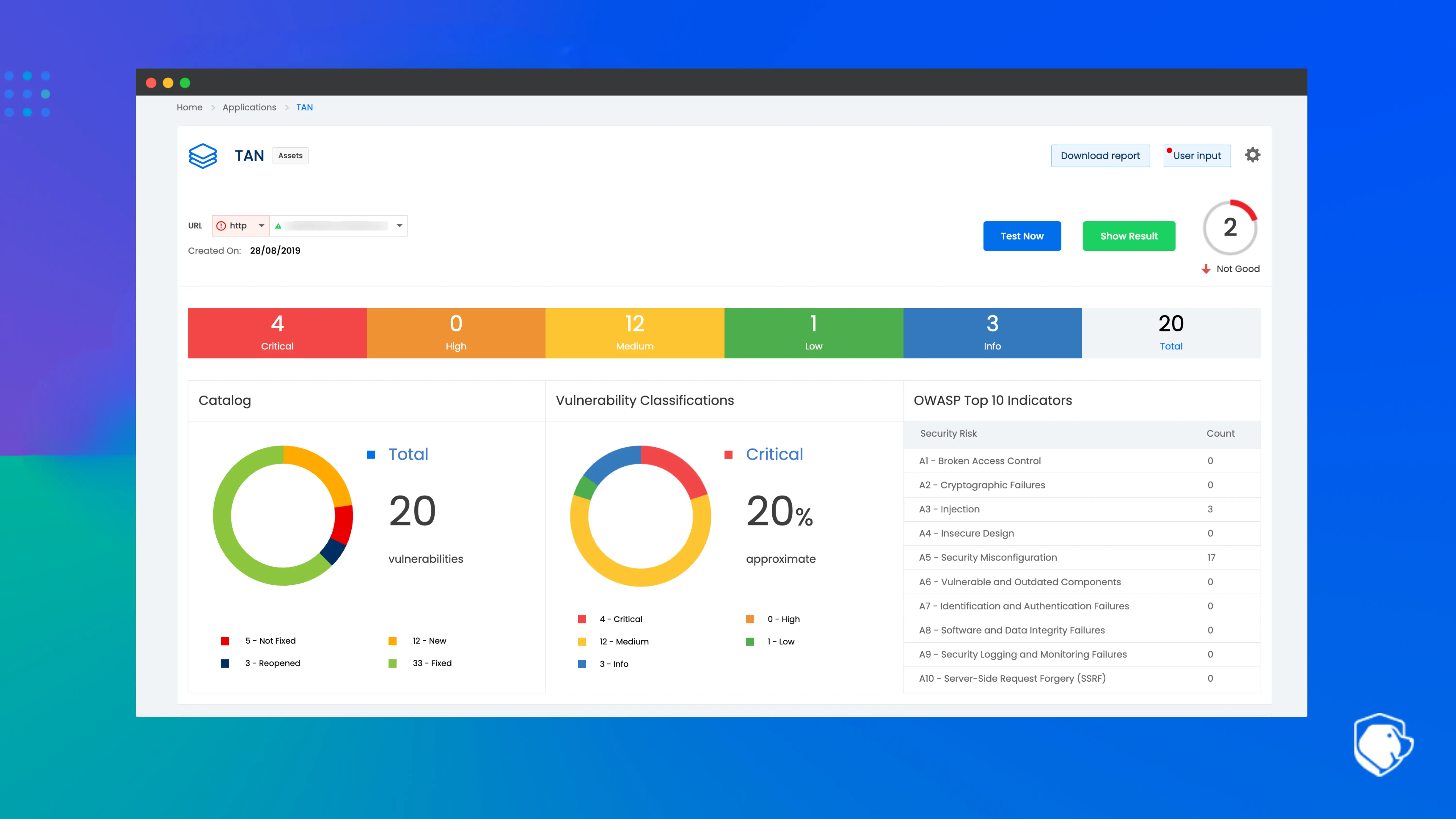
2. Jira
Category: Planning tools
Jira is one of the most widely used planning and project management tools in the SDLC ecosystem. It helps teams plan, track, and manage software development tasks through agile workflows.
Jira supports Scrum, Kanban, and hybrid methodologies, making it suitable for both small teams and large enterprises. Its customizable workflows allow organizations to model their processes, track progress, and ensure that development work remains structured and predictable.
The platform provides powerful backlog management features that allow teams to prioritize work, break down large initiatives, and estimate tasks.
Sprint planning tools help teams coordinate releases and measure velocity. Jira’s dashboards offer real-time visibility into project health, team performance, and ongoing work. These dashboards can be customized to track KPIs, workflows, and progress across different engineering teams.
Jira integrates deeply with the broader Atlassian ecosystem, including Confluence, Bitbucket, and Opsgenie. It also integrates with external development tools like GitHub, GitLab, Figma, Slack, and testing platforms. Jira acts as the central coordination hub for development teams and enables seamless collaboration across product managers, designers, developers, and QA teams.
Key capabilities:
Agile project management for Scrum and Kanban
Backlog prioritization and sprint planning
Customizable workflows and issue templates
Real-time dashboards and reporting
Extensive plugin and integration ecosystem
SDLC phase coverage: Planning, development coordination, and release management
Integration highlights: Confluence, Bitbucket, GitHub, Slack, Figma, testing tools
Best for: Agile teams and organizations needing structured project tracking
Why teams choose Jira: It provides unmatched flexibility, strong reporting, and deep integrations that support complex engineering workflows.
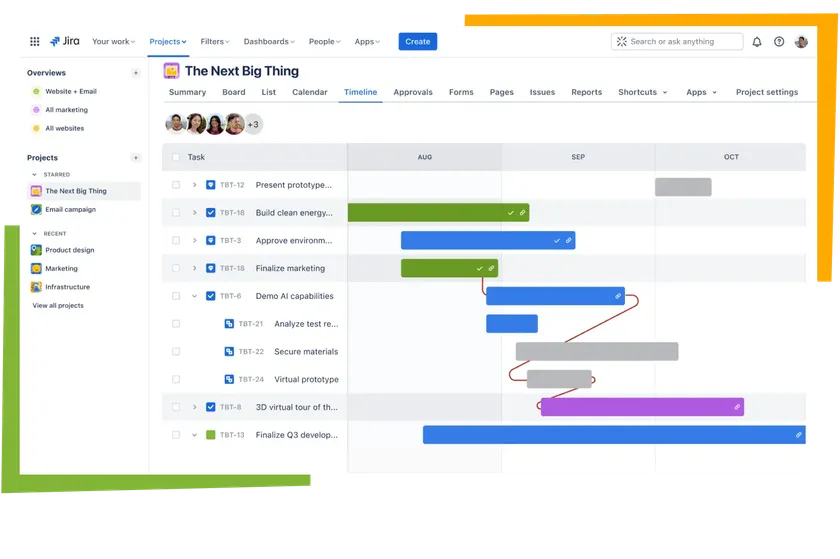
3. BrowserStack
Category: Testing tools
BrowserStack is a leading cloud-based cross-browser and device testing platform that enables QA engineers and developers to test web and mobile applications across thousands of real device combinations. It eliminates the need for physical device labs and provides instant access to real browsers, operating systems, and devices. With BrowserStack, teams can perform manual testing, automated testing, visual regression testing, and responsive testing.
The platform supports integration with major automation frameworks, including Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, and Appium. BrowserStack’s real device cloud provides accurate test results and supports parallel testing which significantly reduces test execution time.
Its visual regression testing capabilities help teams detect UI inconsistencies before release. For mobile developers, BrowserStack offers real device testing for both Android and iOS, ensuring that applications perform reliably across devices.
BrowserStack integrates directly with CI/CD pipelines, enabling automated cross browser tests during build and deployment stages. It supports debugging tools such as video recordings, screenshots, network logs, and console logs which help teams reproduce and resolve issues faster.
Key capabilities:
Real device testing for web and mobile
Automated testing with Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, and Appium
Visual regression testing
Responsive design testing
CI/CD pipeline integrations
SDLC phase coverage: Testing, quality assurance, pre-release validation
Integration highlights: Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, CircleCI, Jira
Best for: QA teams needing comprehensive cross-browser and cross-device testing
Why teams choose BrowserStack: It provides the reliability of real device testing and reduces the need for physical device infrastructure.
4. LinearB
Category: Monitoring and maintenance tools
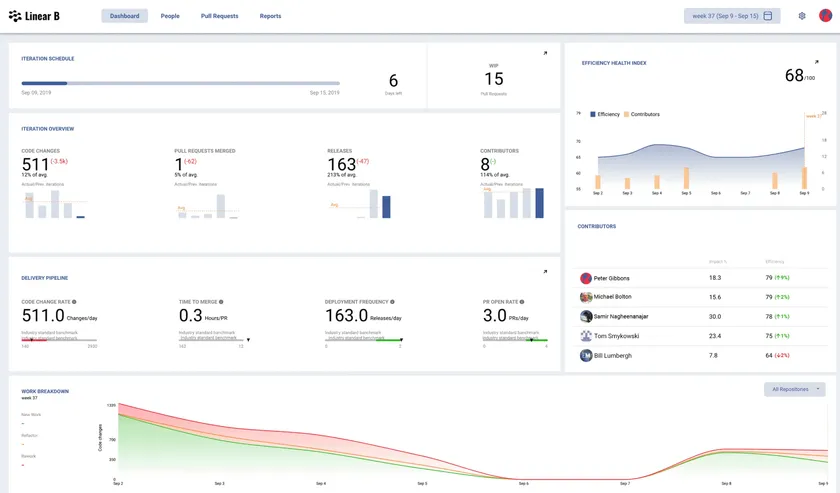
LinearB is an engineering metrics and workflow optimization platform that helps teams understand their performance and improve development processes.
It provides real time visibility into developer productivity, cycle time, bottlenecks, and project health. LinearB uses data from source control and project management tools to calculate key engineering metrics including DORA metrics, PR review time, deployment frequency, and lead time for changes.
The platform helps engineering leaders identify inefficiencies and improve workflow automation. It provides actionable insights that help reduce PR delays, streamline handoff processes, and optimize sprint performance. LinearB also offers workflow automations such as PR routing, risk alerts, and backlog optimization recommendations.
LinearB integrates with popular development tools such as GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, and Jira. These integrations allow teams to build complete visibility into engineering operations. The platform supports both small engineering teams and large enterprise organizations looking to improve operational efficiency.
Key capabilities:
Engineering metrics and DORA measurement
Workflow automation and optimization
PR review insights and bottleneck detection
Team performance dashboards
Sprint health and project progress analytics
SDLC phase coverage: Monitoring, workflow optimization, development efficiency
Integration highlights: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Jira
Best for: Engineering leaders focused on improving team productivity and operational performance
Why teams choose LinearB: It provides data driven insights that help teams improve efficiency and optimize workflows across the SDLC.
5. Modelio
Category: Design and modeling tools
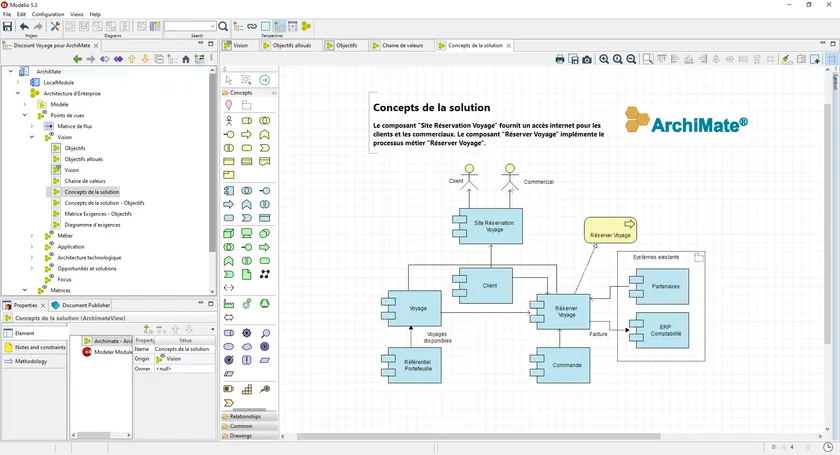
Modelio is an open source modeling platform that provides comprehensive support for UML diagrams, BPMN processes, system architecture designs, and database modeling.
It enables architects and development teams to design and document complex systems before implementation. Modelio provides a flexible modeling environment where teams can create diagrams that represent system behavior, interactions, and data flows.
Modelio supports code generation and reverse engineering which helps maintain alignment between system design and implementation.
The platform allows teams to create professional documentation and export models into multiple formats. Its extensible architecture means organizations can build custom modules for specialized modeling needs.
Modelio is valuable for teams working on large enterprise systems, embedded solutions, or any project that requires detailed architectural planning. Its ability to visualize relationships and dependencies improves communication across teams and ensures that system design decisions are well documented.
Key capabilities:
UML and BPMN modeling
Database and ERD design
Code generation and reverse engineering
Extensible plugin framework
Exportable documentation and diagrams
SDLC phase coverage: Design, architecture, documentation
Integration highlights: Code repositories, documentation tools
Best for: Architects and engineering teams designing complex systems
Why teams choose Modelio: It provides powerful modeling capabilities and flexibility in an open source, extensible platform.
6. Slack
Category: Planning tools (communication and collaboration)
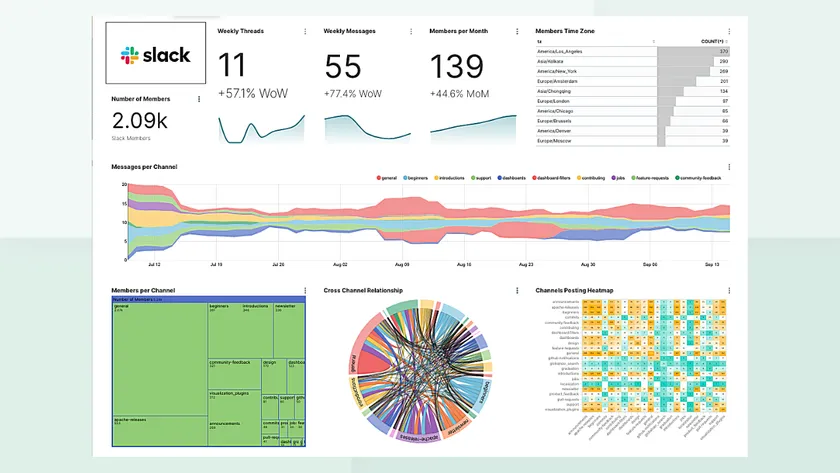
Slack is a communication platform that enables real-time collaboration across engineering, product, design, and operations teams.
It provides channel-based communication, file sharing, and deep integrations with SDLC tools. Slack acts as the communication hub for development teams and supports ChatOps workflows where development and deployment actions can be triggered directly from chat.
Slack’s strength lies in its integration capabilities. It supports thousands of integrations, including GitHub, Jira, Jenkins, Sentry, Figma, and monitoring tools. These integrations push notifications directly into channels, which keep teams informed of deploys, builds, errors, and pull requests. Slack supports workflow automation through bots and custom actions that help automate routine tasks.
Slack enhances transparency and improves coordination across teams. It supports distributed teams, remote work, and cross-functional collaboration. Channels can be organized around projects, teams, or topics to streamline conversation flows.
Key capabilities:
Real-time messaging and collaboration
Channels for teams and projects
File sharing and searchable conversation history
ChatOps integrations
Workflow automations and bots
SDLC phase coverage: Planning, collaboration, coordination
Integration highlights: GitHub, GitLab, Jira, Jenkins, Sentry, CI/CD tools
Best for: Distributed teams requiring fast, reliable communication
Why teams choose Slack: It connects all SDLC tools into one communication layer and supports rapid collaboration.
7. Semgrep
Category: Security tools (SAST)
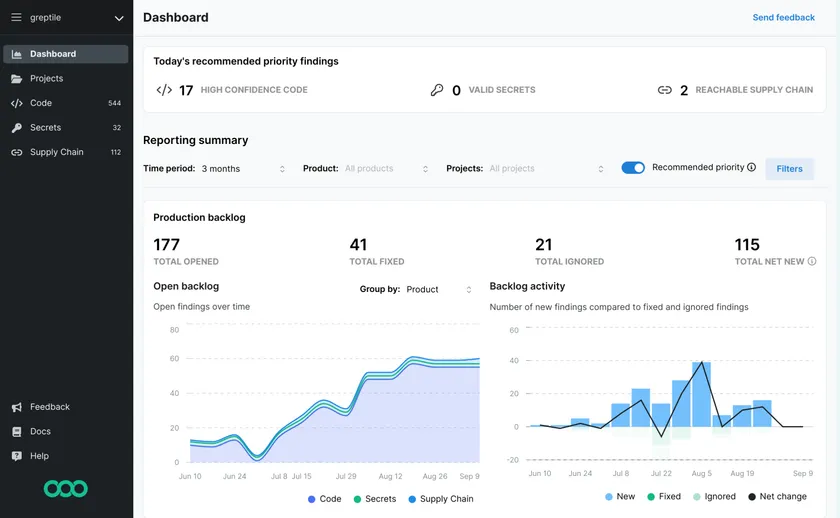
Semgrep is a static application security testing tool that scans source code for vulnerabilities, bad patterns, and insecure coding practices. It is known for its developer-friendly approach and fast scan times. Semgrep supports over 30 programming languages and allows teams to write custom rules that match specific code patterns relevant to their organization.
Semgrep integrates into CI/CD pipelines and provides automatic scanning for pull requests, branches, and repositories. Its rule engine supports both security scanning and code quality checks. Organizations use Semgrep to enforce coding standards, catch vulnerabilities early, and maintain consistency across codebases.
The platform offers both open source and enterprise versions. The enterprise version includes centralized management, compliance reporting, and team-level dashboards. Semgrep fits well into DevSecOps workflows by enabling early detection of security risks in the coding phase.
Key capabilities:
Static code analysis across multiple languages
Custom rule creation
CI/CD pipeline support
Fast scans suitable for pull request workflows
Enterprise dashboards and compliance reporting
SDLC phase coverage: Development, security, code review
Integration highlights: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, CI tools
Best for: Teams implementing shift left security and code-level scanning
Why teams choose Semgrep: It provides fast, customizable, developer-friendly security scanning that fits naturally into coding workflows.
8. Embold
Category: Testing tools (code quality analysis)
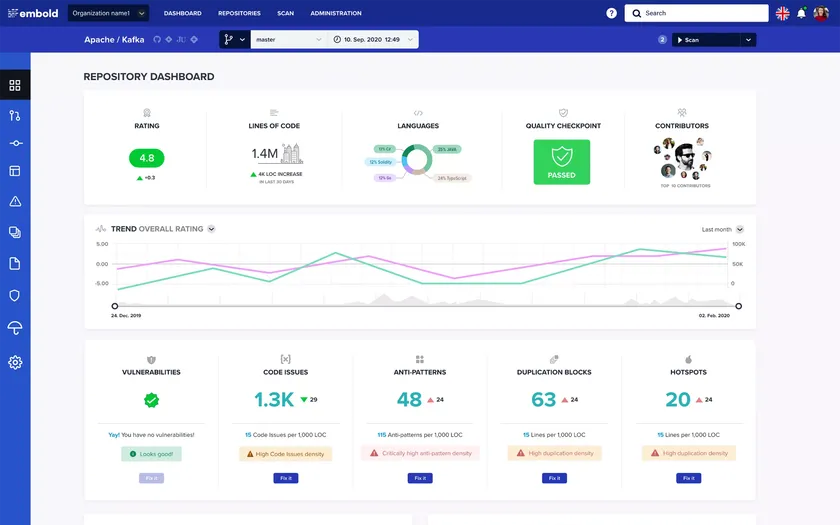
Embold is a code quality and technical debt analysis platform that identifies design issues, code smells, and anti-patterns across complex codebases. It helps development teams improve maintainability and long-term code health.
Embold analyzes code structure, design patterns, duplication, and complexity to highlight areas that need refactoring.
The platform provides actionable recommendations and prioritizes issues based on impact. Its visual dashboards help developers see hotspots in code that contribute most to technical debt. Embold supports multiple languages and integrates with version control systems, CI tools, and IDEs.
Embold helps teams reduce debugging time, improve reliability, and keep codebases clean. By identifying problematic patterns early, teams maintain higher quality and avoid long-term maintenance challenges.
Key capabilities:
Code quality and anti-pattern detection
Design issue identification
Duplicate code detection
Visual dashboards for code health
Integration with CI/CD and IDEs
SDLC phase coverage: Testing, code review, maintenance
Integration highlights: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, Jenkins
Best for: Teams reducing technical debt and improving code maintainability
Why teams choose Embold: It provides deep insights into code quality with clear recommendations for improvement.
9. Jenkins
Category: Automation tools
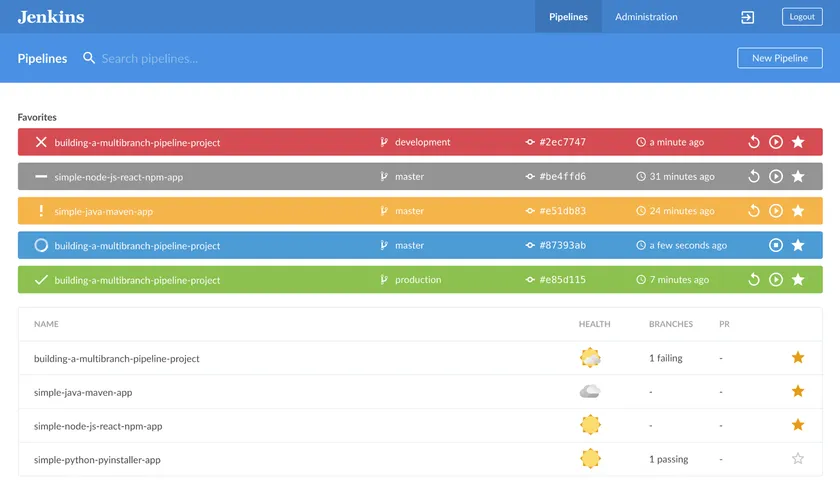
Jenkins is a widely adopted open source automation server used for CI/CD, build automation, and pipeline orchestration. Its massive plugin ecosystem allows teams to customize workflows, integrate with almost any tool, and automate complex processes.
Jenkins supports pipeline as code through Jenkinsfile, which provides version-controlled automation scripts.
Jenkins excels in scalability and flexibility. Teams can create multi-stage pipelines, run parallel jobs, and automate deployments across various environments. It integrates with every major source control system, testing framework, and deployment tool. Jenkins can also manage distributed build nodes, which improves performance for large projects.
The platform remains popular due to its community support, extensibility, and ability to adapt to unique workflows. Jenkins is suitable for organizations that want a customizable CI/CD solution and complete control over automation infrastructure.
Key capabilities:
CI/CD pipeline automation
Jenkinsfile pipeline as code
Plugin ecosystem with 1,800+ plugins
Distributed build support
Integration with testing and deployment tools
SDLC phase coverage: Automation, testing, deployment
Integration highlights: GitHub, GitLab, Docker, Kubernetes, testing tools
Best for: Teams seeking highly customizable CI/CD automation
Why teams choose Jenkins: It offers unmatched flexibility and control over automation workflows.
10. Codacy
Category: Testing tools (automated code review)
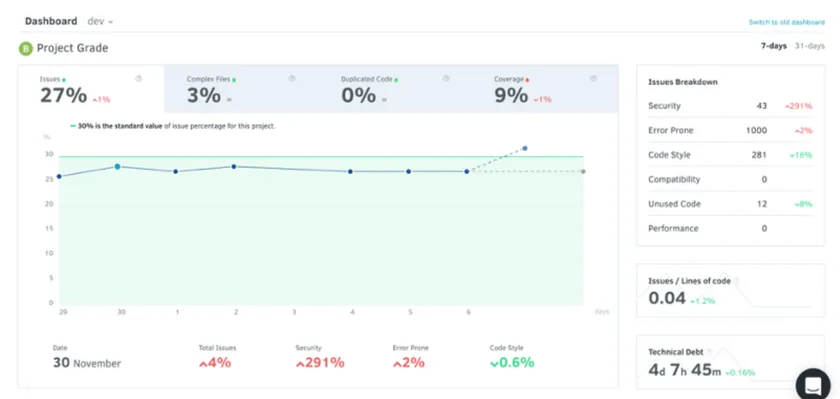
Codacy is an automated code review and quality assurance platform that helps teams enforce coding standards, improve code consistency, and detect security vulnerabilities.
It supports multiple programming languages and integrates seamlessly into developer workflows through Git based version control systems.
Codacy analyzes pull requests and commits in real time, providing feedback on code style issues, complexity, duplication, and potential bugs. It also supports security scanning and checks for known vulnerabilities. Codacy provides quality gates that teams can enforce before merging code into production branches.
Codacy’s dashboards give engineering leaders visibility into code quality trends and team performance. The platform is easy to adopt and fits naturally into existing CI/CD pipelines.
Key capabilities:
Automated code review
Security vulnerability detection
Code quality metrics
Pull request quality gates
Multi-language support
SDLC phase coverage: Testing, review, quality assurance
Integration highlights: GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket, CI pipelines
Best for: Teams wanting automated code review and consistent code quality
Why teams choose Codacy: It provides reliable automation for code reviews and helps maintain high-quality standards across teams.
Factors to consider when choosing SDLC tools
Choosing the right SDLC tools requires balancing team needs, project complexity, integration requirements, and long-term scalability. Teams should evaluate how each tool fits into their workflows and how it complements existing systems.
Ease of use
Ease of use is a critical factor because tools must support fast adoption and smooth onboarding. If tools are too complex, they slow down teams rather than improving productivity.
Teams should evaluate user interface quality, documentation, training resources, and the learning curve for new users.
Tools that provide intuitive workflows and strong onboarding experiences generally lead to faster adoption. The balance between usability and advanced features is also important because overly simple tools may not support advanced workflows.
Pricing
Pricing varies widely across SDLC tools. Some follow per-user pricing, others use resource-based billing, and many provide free tiers for small teams.
Organizations should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including implementation, training, maintenance, and potential hidden costs. Teams should also consider scalability because pricing may increase significantly as the team grows.
Evaluating the return on investment is essential, especially when tools provide automation, productivity improvements, or security benefits that reduce long-term costs.
Scalability
Scalability determines whether a tool can grow with your team. As development organizations expand, they manage larger codebases, more contributors, and more complex workflows.
Tools must handle increased load and provide enterprise features such as advanced permissions, multi-team support, and workflow automation. Scalability also applies to performance because tools must remain responsive as projects grow.
Support and integration
Strong vendor support and documentation improve adoption and reduce downtime. Integration capabilities are extremely important because SDLC tools must connect with version control systems, CI/CD platforms, communication tools, and monitoring systems.
Tools with strong API support, webhooks, and pre-built integrations reduce manual overhead and create smooth workflows.
Security and compliance
Security is essential when selecting SDLC tools. Teams should evaluate encryption, authentication options, access control, audit logging, and compliance certifications like SOC 2 and ISO 27001.
Data residency and sovereignty also matter for regulated industries. Tools must provide secure handling of code, data, and secrets. Security tools specifically must demonstrate strong vulnerability detection and timely patching.
Final thoughts
Choosing the right SDLC tools is one of the most important decisions development teams make. The right toolchain increases velocity, improves code quality, enhances team collaboration, and ensures that applications remain secure throughout the development lifecycle. Modern SDLC workflows depend on tools that integrate smoothly and support automation, observability, and continuous testing.
An integrated ecosystem of planning tools, automation platforms, testing tools, and security solutions ensures that development remains predictable and scalable. Security must be treated as a first-class citizen in the SDLC, and tools like Beagle Security make DevSecOps adoption achievable by providing continuous testing and actionable insights.
Teams should evaluate their current toolchains, identify gaps, and invest in platforms that enhance collaboration, quality, and security.
Start with core categories such as planning, automation, testing, and security, then expand your stack based on specific project needs and long-term goals. With the right SDLC tools in place, development teams can deliver faster, build more resilient applications, and confidently scale their engineering operations.
FAQ
What are SDLC tools?
SDLC tools are software platforms that support different phases of the software development lifecycle, including planning, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. They help teams improve productivity, quality, and release velocity through automation and structured workflows.
Which SDLC tools are most important?
Essential categories include project management tools, version control systems, CI/CD automation, testing tools, and security platforms. The specific tools depend on team size, methodology, and technology stack.
What is the difference between SDLC tools and DevOps tools?
SDLC tools cover the entire lifecycle from planning to maintenance. DevOps tools are a subset that focus specifically on automation, collaboration, and delivery. DevOps tools help bridge development and operations, while SDLC tools support broader lifecycle needs.
Are open source SDLC tools good enough?
Many open source tools are reliable and widely adopted. Jenkins, Semgrep, and Modelio are strong examples. Teams should evaluate the total cost of ownership, including setup and maintenance needs. Open source tools can be an excellent choice with the right support.
How do I integrate security into my SDLC toolchain?
Security can be integrated through DevSecOps practices. Use SAST tools for code scanning, DAST tools like Beagle Security for runtime testing, and dependency scanners for vulnerable libraries. Automate security checks in CI/CD pipelines to ensure continuous validation.


![Best rated DAST tools [2025] Best rated DAST tools [2025]](/blog/images/top-rated-dast-tools-cover.webp)