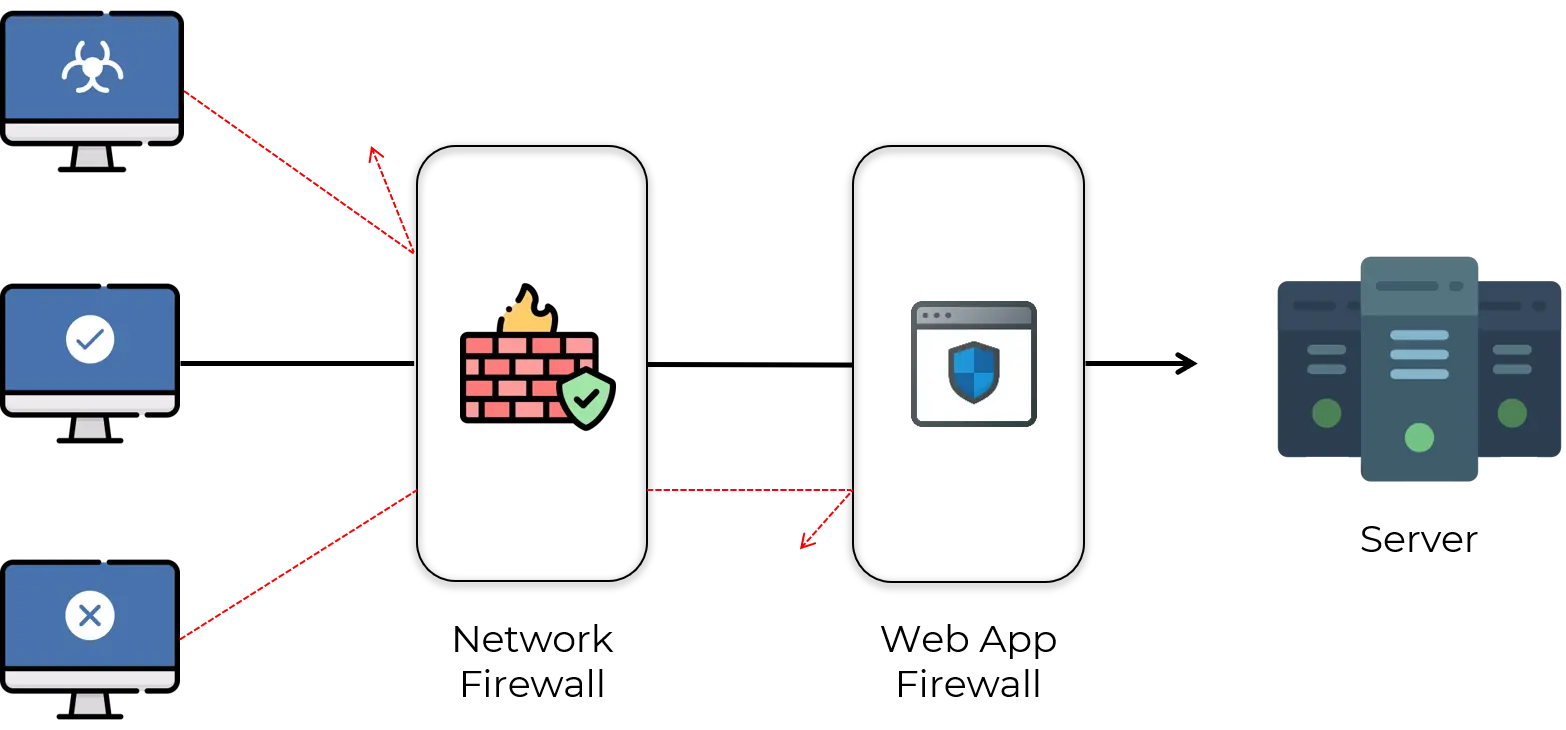
Security threats have always been and continue to be a menace for small and big organisations alike. There’s a possibility of many security threats existing in a typical enterprise distributed application including the likes of DDoS, SQL injection, Cross-Site Scripting, etc.
Hackers are getting increasingly sophisticated and, thankfully, so are cyber defence systems. We have the option to set up the first line of defence against security threats with the help of a web application firewall (WAF).
What is a Web Application Firewall?
A web application firewall or WAF has a promising role in an IT infrastructure. WAF helps protect web applications from attacks such as cross-site forgery, cross-site-scripting (XSS), file inclusion, and SQL injection, etc by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic between a web application and the internet.
Deploying a WAF in front of a web application establishes an initial level of protection between the web application and the internet.
It is a type of reverse-proxy, protecting the server from exposure by having clients pass through the WAF before reaching the server.
WAFs may come in the form of an appliance, server plugin, or filter, and maybe customized to an application. The effort to perform this customization can be significant and needs to be maintained as the application is modified.
Web application firewalls, positioned between web client and web server, monitor every request and response within the application layers. They search for specific “attack signatures” to identify a specific incoming attack, whilst monitoring for abnormal behaviours that are incompatible with past traffic patterns.
A web application firewall is an essential tool that ensures protection against malicious users and bots.
However, many of the web application firewalls are not configured securely. It is easier for attackers to take advantage of a misconfigured web application firewall.
Web Application Firewall Policies
A WAF operates through a set of rules often called policies. In the WAF policy configurations, you have options to enable rules to detect attacks at the request line, query-string, URI, request headers, request body, response code, or response body.
Some of the WAF policies are listed below:
- Web attack signature policy
The signature database includes signatures that can detect known attacks and exploits found in 22 scan points. In your policy configuration, you can choose classes of scan points to process: HTTP headers, HTTP request body, and HTTP response body.
- URL protection policy
This policy enables you to create rules that detect patterns in the URL or the file extension.
- HTTP protocol constraint policy
The HTTP protocol constraint policy enables you to create rules that restrict URI, header, and body length, HTTP method, or HTTP response code.
- SQL/XSS injection detection policy
This policy includes rules to detect SQL/XSS injection in the HTTP request URI, HTTP referer header, HTTP cookie header, or HTTP request body.
- Bot detection
This policy includes rules to detect bots. A bot is an application that runs automated tasks over the internet. The WAF supports two methods for detecting bad bots: signature detection and behaviour detection. Whitelisting can also be employed for detecting the good ones.
Security Mechanisms of Web Application Firewalls
The main aim of using a WAF is to secure the existing, often productive web applications. Besides the basic protection via blacklisting and whitelisting, the WAF can also act as a central service point for completing tasks which should otherwise be on the application side.
The table below shows the most common issues faced by a web application and how WAF protects the application from them.
| Issues | Countermeasures |
|---|---|
| Cookie protection | Cookies can be signed. Cookies can be encrypted. |
| Information leakage | Cloaking filter, outgoing pages can be “cleaned” (error messages, comments, undesirable information). |
| Session riding (CSRF) | URL encryption/token. |
| File upload | Virus check (generally via external systems) via ICAP linked to the WAF. |
| Parameter tampering | Parameter manipulation can be prevented via URL encryption (GET) and parameter encryption (GET and POST). Site usage enforcement, meaning the possible sequence of URLs can be fixed or can be detected. |
| Forced browsing | Can be prevented via URL encryption. Site usage enforcement. |
| Path traversal (URL) link validation | Can be prevented via URL encryption. Site usage enforcement. |
| Logging | All or only specific/permitted parts of the data of a request and the connected tests can be logged. |
| SSL | WAF can force SSL with pre-defined encryption strength. SSL termination on the WAF forwarding of the SSL data to the application. An SSL connection is possible from WAF to application. |
| HTTP request smuggling | Is prevented via strict testing of the conformity to standards of each request. |
| Data validation and injections | Can be tested to a very detailed degree (length, constant value/range of values, e.g. for SELECT, character area); validation possible with whitelist and/or blacklist (signature). Rules can in part be generated automatically. |
Best Practices for Web Application Firewall Configuration
Even though many companies have implemented a WAF, most of the web application firewall configurations are not secure. It would be more effective if the following points are considered while configuring a web application firewall.
Coordinate Web Application Firewall Configuration and Web Application Update
Configuring the web application firewall in parallel with a web application’s update cycle prevents significant issues. Web application firewalls should be configured when the website is being updated or when patches are implemented.
It is most probable that all or a part of the website will not be protected if the configuration and update do not happen simultaneously. And if the WAF is unable to cover those parts, then the consequences can be severe for the site’s users. Maintain the web application firewall along with a change in the security surface of your application.
Check for vulnerabilities
Always ensure that the code does not contain bugs or vulnerabilities before implementing the web application firewall.
Even though WAF is the first line of defence, if the website itself is not secure, it will drag the whole web infrastructure into danger. So make sure to scan your website regularly to make sure there are no security issues.
Use a web application firewall with built-in acceleration
Prefer a WAF with a built-in acceleration feature, which mitigates web latency and speeds overall traffic so that it will not affect user experience.
Lockdown the backdoor
The protection of databases and back-end applications is also important as front end applications. Securing both ends can be achieved with a database activity monitoring product along with a proper web application firewall configuration and regular vulnerability assessment.
Understanding the web application environment
A greater level of understanding about the application environment, security posture and possible loopholes are necessary to make sure you get the best out of a web application firewall implementation.
Conclusion
Web applications of all kinds have in recent years increasingly become the target of hackers. It’s our responsibility to upgrade our defence systems to overcome the challenges and threats and keep our applications secure.
A web application firewall acts as the first line of defence and it allows you to make sure that an application is safe by putting in a reasonable amount of initial effort. In addition to implementing them, it is also necessary to properly configure them so that it can be an effective defense mechanism in your bid to keep away hackers.