ModSecurity (also known as ModSec) is an open-source web application firewall (WAF). It is implemented to protect sites and applications against many common attacks, including XSS, code injection, etc.
70% of all attacks are carried out through the application level of the web. Thus, implementing a WAF would be helpful for organizations in ensuring system security.
It establishes an extra security layer that increases the protection level of web servers, detects, and prevents attacks before they reach web application programs.
Initially, ModSecurity was a module for Apache web servers, and with time, it grew to a full-fledged web application firewall with support for different platforms, including Apache, Nginx, and IIS.
They work on the application layer (the 7th layer in the OSI model).
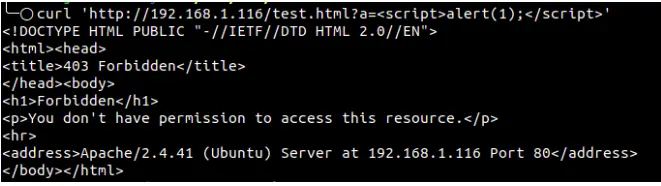
It examines the incoming requests, compares them to patterns described in the rules in the ruleset, and takes actions on the requests based on the results of the tests. If the check succeeds, the HTTP request is passed to the website to retrieve the content. If not, pre-defined actions are performed.
It has a flexible rule engine to perform simple and complex operations and comes with a Core Rule Set (CRS).
And the most popular one among those is the OWASP ModSecurity Core Rule Set, which is updated regularly and can block a wide range of generic attacks, including OWASP’s top-ten list of critical vulnerabilities.
Installation of ModSecurity with Apache on Ubuntu 18.04
The ModSecurity module for Apache is available in the default Debian/Ubuntu repository.
To install it, run the following commands in the terminal:
sudo apt install libapache2-mod-security2
1. Restart the Apache service:
sudo systemctl restart apache2
2. After restarting the Apache service, you can test it with the following command:
apachectl -M | grep security
3. If everything is fine, see the following output:
security2_module (shared)
4. If not, enable the Apache 2 security2 module by running the following command:
sudo a2enmod security2
5. Restart Apache service for the change to take effect.
sudo systemctl restart apache2
Post-installation configuration of ModSecurity
The default rule of ModSecurity is to log suspicious activity. And we need to change the configuration to detect and block traffic according to our requirement.
Let us have a closer look at the steps involved in configuration.
1. By default, the configuration file is at /etc/modsecurity/modsecurity.conf-recommended and we need to copy this file and rename it as modsecurity.conf
sudo cp /etc/modsecurity/modsecurity.conf-recommended /etc/modsecurity/modsecurity.conf
2. Next, we must change the ModSecurity detection mode to detect and block the requests.
sudo nano /etc/modsecurity/modsecurity.conf
3. Locate SecRuleEngine DetectionOnly and change it to
SecRuleEngine on
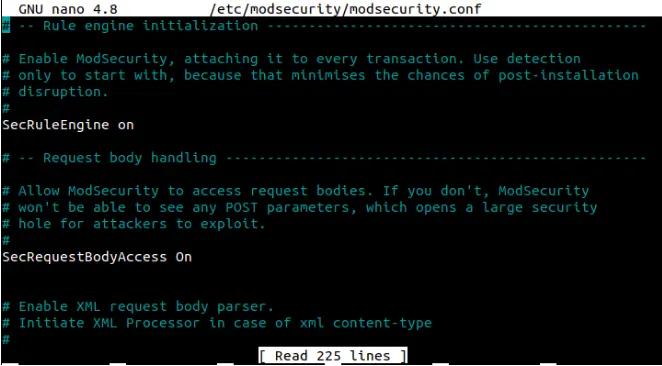
4. Save the file, and then restart the Apache service for the changes to take into effect.
systemctl restart apache2
This will turn to ModSecurity using the basic default rules. And versions of Linux come with OWASP Core Rule at user/share/modesecurity-crs directory.
It is recommended to download the latest CRS from the GitHub repository since the developers frequently update the same.
Adding OWASP ModSecurity rules
1. Remove the default CRS
rm -rf /usr/share/modsecurity-crs
2. Clone the latest OWASP CRS from GitHub to the /usr/share/ directory
git clone https://github.com/SpiderLabs/owasp-modsecurity-crs.git /usr/share/modsecurity-crs
3. Switch to /usr/share/modesecurity-crs directory, and rename the example setup file
cd /usr/share/modsecurity-crs
mv crs-setup.conf.example crs-setup.conf
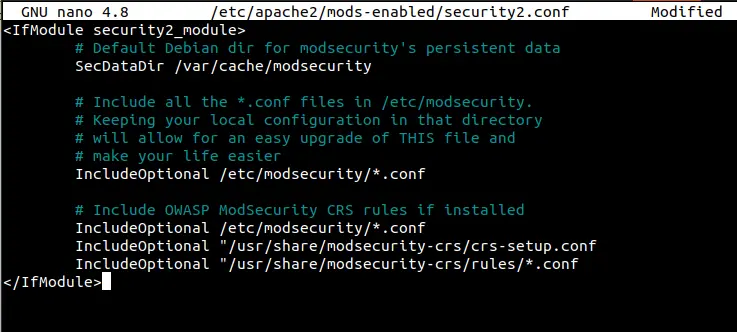
4. Enable these rules in the security2 configuration file to get it working with Apache by making required edits in the /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/security2.conf file
sudo nano /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/security2.conf
5. Locate IncludeOptional /usr/share/modsecurity-crs/*.load and change it to:
<IfModule security2_module>
SecDataDir /var/cache/modsecurity
IncludeOptional /etc/modsecurity/*.conf
IncludeOptional /usr/share/modsecurity-crs/*.conf
IncludeOptional /usr/share/modsecurity-crs/rules/*.conf
</IfModule>