![Best tools for HIPAA penetration testing [2025] Best tools for HIPAA penetration testing [2025]](/blog/images/blog-banner-one.webp)
HIPAA penetration testing is not explicitly required by federal regulation, but Security Rule § 164.308(a)(8) mandates “periodic technical evaluations” that make penetration testing the only practical method to validate runtime security controls protecting electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI).
8% of healthcare organizations experienced at least one cyberattack in 2024, with API vulnerabilities accounting for 42% of successful breaches targeting ePHI.
Traditional consultant-driven penetration tests cost $15,000-$35,000 annually, but automated DAST tools can deliver 75-80% equivalent coverage for under $5,000 per year.
This blog dives into practical HIPAA penetration testing requirements, cost-effective tool selections, and implementation strategies that scale with organizational growth while maintaining regulatory compliance effectiveness.
Does HIPAA require penetration testing?
HIPAA does not explicitly require penetration testing, but Security Rule § 164.308(a)(8) mandates “periodic technical evaluations” that penetration testing directly satisfies in practice.
The regulation states: “Conduct an evaluation in accordance with § 164.308(a)(8) to determine if the security measures implemented are sufficient to reduce risks and vulnerabilities to a reasonable and appropriate level.”
In short: explicitly NO, but implicitly YES.
Any time your infrastructure changes, be it a new deployment, a backend refactor, a third-party integration, or an API endpoint handling ePHI you are expected to re-evaluate whether your current security setup still protects sensitive data.
That’s where penetration testing becomes essential. Penetration testing simulates real-world attack scenarios to uncover vulnerabilities.
Proving that your system holds up under simulated compromise attempts from an attacker’s perspective is very important in securing your system against attacks.
This makes penetration testing one of the most effective ways to satisfy HIPAA’s requirement for technical evaluations especially in modern cloud-native, API-driven healthcare applications.
What are the HIPAA penetration testing requirements in 2025?
HIPAA Security Rule establishes three core technical evaluation requirements that penetration testing must address: comprehensive risk analysis, documented vulnerability remediation, and continuous security monitoring.
Meeting HIPAA expectations in practice calls for:
1. Risk analysis requirements
HIPAA requires businesses to conduct regular risk analyses, essentially a deep technical review of your systems to identify potential vulnerabilities. This isn’t just about ticking a box. It’s about understanding where your system is weak before someone else finds out the hard way.
From exposed APIs to misconfigured cloud resources, risk analysis covers all possible entry points where PHI might be at risk. Penetration testing strengthens this process by going beyond surface-level scanning.
Auditors often expect a combination of automated vulnerability scans for speed and coverage, alongside manual or tool-assisted penetration testing for accuracy and depth.
2. Vulnerability remediation
Identifying vulnerabilities is only half the job. HIPAA also emphasizes the timely remediation of issues discovered during assessments.
Penetration test reports are especially valuable here because they prioritize the risks based on risk impact, helping your team focus on what matters most. By addressing critical issues quickly and documenting your actions, you demonstrate not only compliance, but also operational maturity.
3. Continuous scanning
Cloud-native architectures with frequent deployments require ongoing security validation. A single API update can introduce vulnerabilities that compromise ePHI protection.
Organizations need tools that deliver high-accuracy results to reduce false positives and integrate seamlessly with CI/CD pipelines to catch vulnerabilities early in the development lifecycle.
Tool integration requirements: HIPAA-compliant penetration testing tools must provide audit trails, encrypted result storage, and role-based access controls that align with administrative safeguard requirements.
Defining the scope of your HIPAA penetration test
HIPAA penetration testing scope must encompass all systems, applications, and network components that create, receive, maintain, or transmit ePHI, including often-overlooked medical device connectivity and IoMT (Internet of Medical Things) infrastructure.
Core application testing scope
Web application security assessment:
Authentication and session management testing across all user roles
Input validation and injection attack simulation (SQL, NoSQL, LDAP, XML)
Business logic flaw identification affecting patient data access controls
File upload security and data export functionality validation
API security testing requirements:
REST and GraphQL endpoint authentication bypass attempts
Parameter manipulation and data exposure testing
Rate limiting and DDoS protection validation
API versioning security and deprecated endpoint assessment
Infrastructure and network testing scope
Internal network penetration testing:
Network segmentation validation between ePHI and non-ePHI systems
Privilege escalation testing from compromised workstations
Database access control validation and data exfiltration testing
Wireless network security assessment including guest access isolation
Cloud infrastructure security testing:
Container and serverless function security validation
Cloud storage permission and encryption testing (S3, Azure Blob, GCP buckets)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) role permission validation
Logging and monitoring system security assessment
Medical device and IoMT security testing
Device connectivity security:
Medical device network isolation and communication encryption
Device authentication and certificate management validation
Firmware update security and default credential testing
Patient monitoring system data transmission security
Integration point testing:
HL7 FHIR API security validation
Electronic Health Record (EHR) integration security testing
Telehealth platform security assessment
Medical imaging system (DICOM) security validation
Third-party integration testing scope
Business associate security validation:
Vendor API access control testing
Data sharing agreement technical implementation validation
Third-party authentication integration security assessment
Backup and disaster recovery system security testing
Testing frequency recommendations:
Full-scope testing: Annually or following major system changes
Application-focused testing: Quarterly for customer-facing applications
Infrastructure testing: Semi-annually or following network modifications
Continuous monitoring: Daily automated scans or monthly automated penetration tests with monthly comprehensive analysis
What are the best tools for HIPAA penetration testing?
Healthcare organizations require penetration testing tools that provide comprehensive vulnerability detection, minimal false positives, and seamless integration with development workflows while maintaining audit trails required for HIPAA compliance documentation.
Web application & API penetration testing tools
Beagle Security - Best for healthtech startups
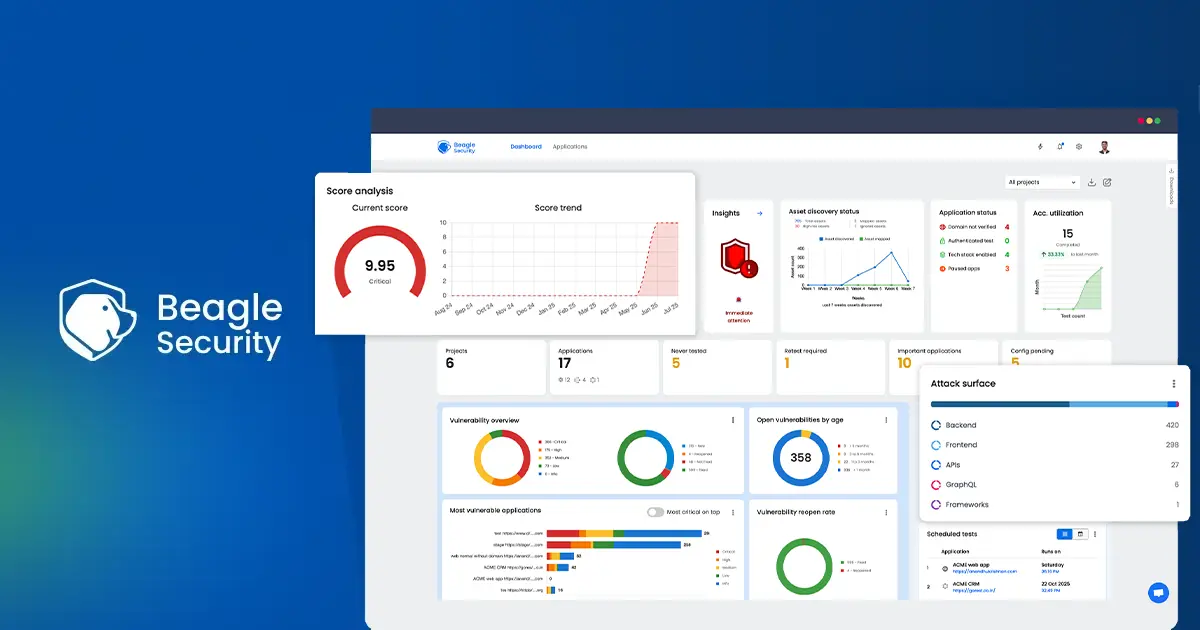
Beagle Security is tailor-made for startups and growing companies navigating the complexities of HIPAA compliance. Designed to simplify penetration testing for modern development teams, Beagle Security enables organizations to run comprehensive, automated security tests on their web applications and APIs.
Beagle Security doesn’t just tackle surface vulnerabilities, rather simulates real-world attack scenarios based on frameworks like the OWASP Top 10, giving teams a practical understanding of how attackers might target their applications.
HIPAA-specific capabilities:
Authentication testing: Comprehensive testing of healthcare application login workflows including SSO, MFA, and role-based access controls
API discovery and testing: Automatic identification of undocumented endpoints handling patient data
Compliance reporting: Pre-built HIPAA mapped penetration test reports
Implementation for healthcare startups:
Setup time: 10 minutes for basic configuration
Learning curve: Minimal - designed for dev & security teams
Pricing: Starting at $119/month for small healthcare teams
Best use cases:
Patient portals and telehealth applications
Healthcare SaaS platforms with API integrations
Medical device connectivity applications
Invicti (formerly Netsparker) - Enterprise healthcare security
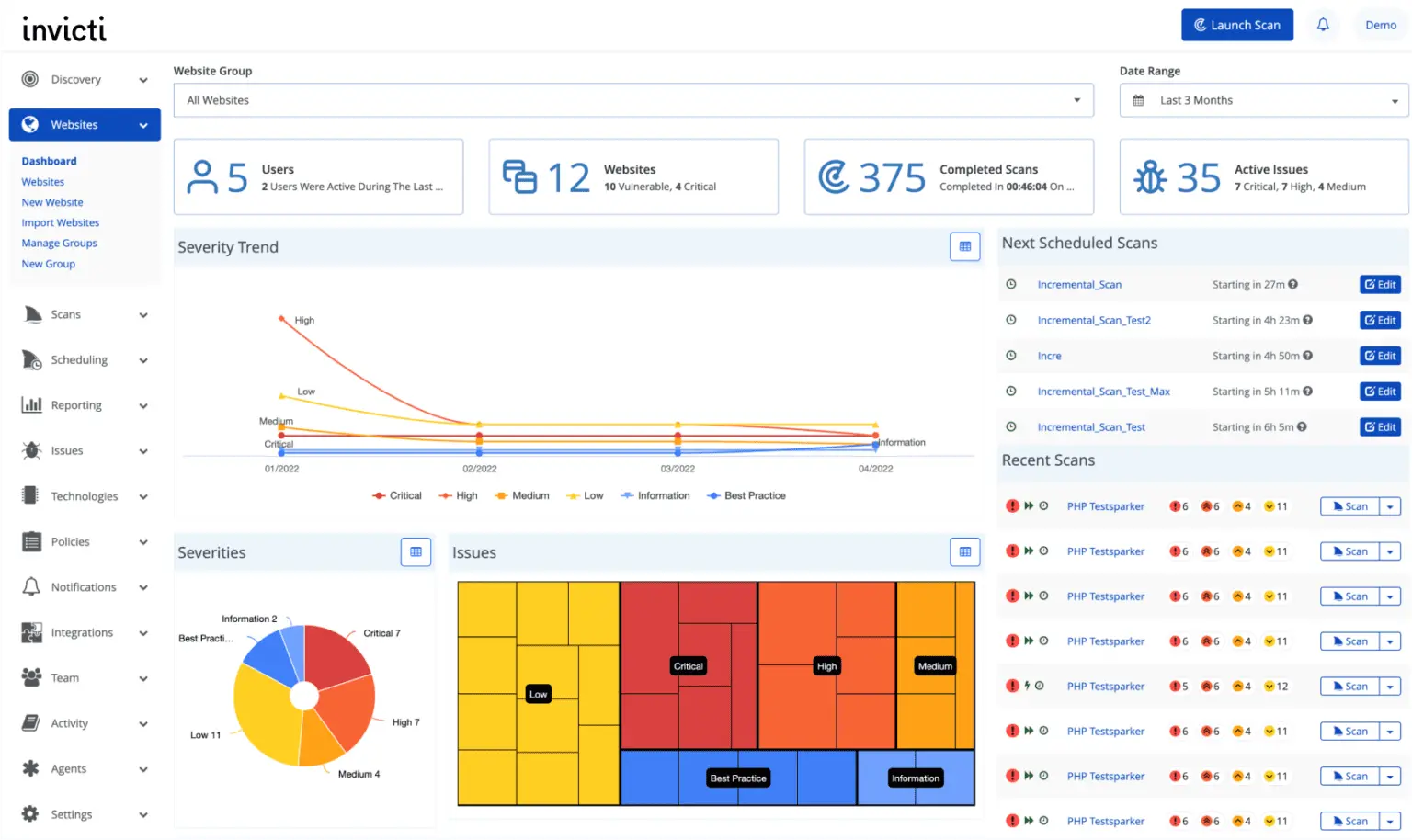
Invicti (formerly Netsparker) is a dynamic application security testing (DAST) tool built for organizations that need deep, automated scanning of web applications and APIs without sacrificing accuracy.
Its proprietary Proof-Based Scanning engine reduces false positives by safely exploiting vulnerabilities and confirming their existence, making it particularly valuable for lean security teams.
Invicti supports complex authentication workflows, scans modern frameworks and single-page applications, and integrates seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines to catch issues early in the development lifecycle.
For HIPAA-focused organizations, Invicti helps validate access controls, input sanitization, and session management which are core technical safeguards under the HIPAA Security Rule.
Implementation considerations:
Pricing: $37,000 annually based on application complexity
Setup complexity: Requires security team or consultant for optimal configuration
Learning curve: 2-4 weeks for healthcare teams to achieve proficiency
Best fit: Healthcare organizations with 50+ applications or complex infrastructure
Network penetration testing tools
Metasploit - Internal network security validation
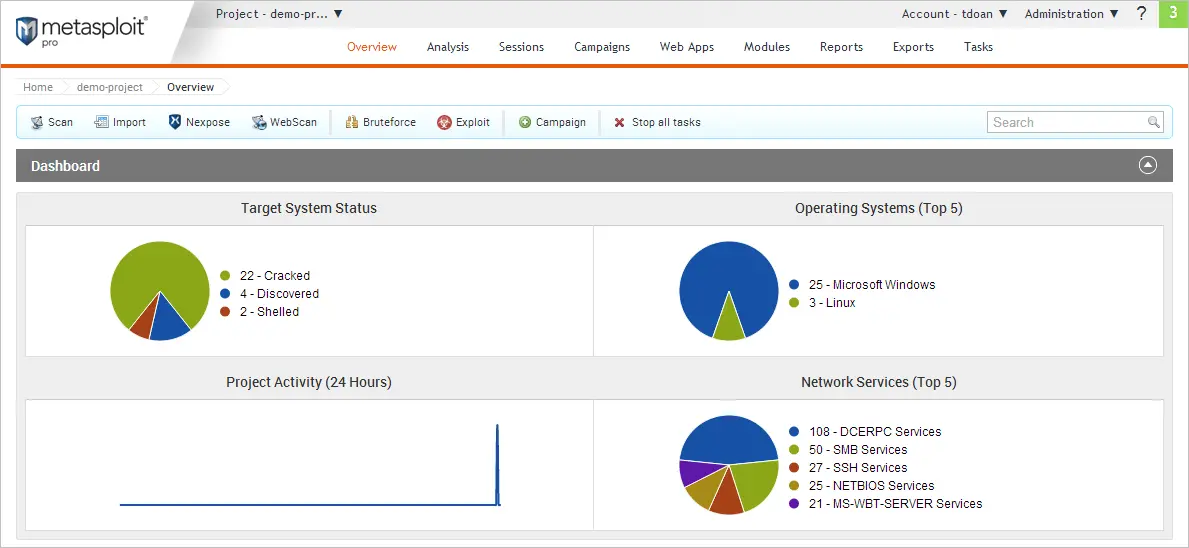
Metasploit remains the industry standard for internal network security testing, providing comprehensive exploit capabilities essential for validating healthcare network segmentation and access controls required under HIPAA Security Rule.
Its extensive exploit library, and scripting capabilities make it a favorite among professional penetration testers.
However, Metasploit’s power comes with complexity. Setting up and using the tool effectively requires technical expertise, especially around network configurations.
For startups without a dedicated security engineer or DevSecOps team, this learning curve can be steep.
Implementation requirements:
Technical expertise: Requires experienced penetration tester or security consultant
Learning curve: 3-6 months for healthcare IT teams to achieve proficiency
Infrastructure requirements: Isolated testing environment separate from production ePHI systems
Compliance considerations: Requires careful scoping to avoid ePHI exposure during testing
Cost considerations:
Metasploit Pro: $15,000 annually for commercial healthcare use
Community Edition: Free but requires significant security expertise
Professional services: $25,000-$50,000 for consultant-led healthcare network assessment
Training requirements: $5,000-$10,000 for team certification and proficiency development
Best use cases for healthcare:
Annual comprehensive network security assessment
Medical device security validation
Business associate network access testing
Incident response team training and preparation
Final thoughts
HIPAA penetration testing in 2025 requires a balanced approach combining automated tools for continuous monitoring with professional manual testing for comprehensive compliance validation.
The key to successful implementation lies in selecting tools that match your organization’s technical capabilities while providing thorough documentation required for regulatory compliance.
Essential implementation principles:
Start with automated tools to establish baseline security and build internal expertise
Focus on ePHI data flows and ensure testing covers all systems handling patient information
Document everything with clear mapping to HIPAA Security Rule requirements
Plan for growth by selecting tools that scale with organizational expansion
Integrate with development workflows to catch vulnerabilities before production deployment
Your 2025 HIPAA penetration testing program should prioritize:
Risk-based testing scope aligned with actual ePHI exposure and business impact
Tool selection that balances comprehensive coverage with resource constraints
Documentation standards that satisfy OCR audit requirements and support compliance reviews
Continuous improvement based on threat landscape evolution and regulatory updates
Healthcare organizations that implement comprehensive, well-documented penetration testing programs position themselves for sustainable growth while maintaining patient trust and regulatory compliance.
FAQs
Does HIPAA require annual penetration testing?
HIPAA does not specify annual penetration testing requirements, but Security Rule § 164.308(a)(8) mandates “periodic” technical evaluations that industry standards interpret as annual comprehensive testing.
How much does a HIPAA penetration test cost?
Consultant-driven tests cost $10,000–$25,000 per engagement. Automated penetration testing tools like Beagle Security cost $3,600-$12,000 annually.
What’s the difference between vulnerability scanning and penetration testing for HIPAA compliance?
Vulnerability scanning identifies potential security weaknesses through automated tools, while penetration testing validates whether identified vulnerabilities can actually be exploited to access ePHI. HIPAA Security Rule § 164.308(a)(8) requires demonstrating that implemented security measures are “sufficient to reduce risks and vulnerabilities to a reasonable and appropriate level,” which penetration testing accomplishes through simulated attack validation.
![Best tools for SOC 2 compliance penetration testing [2025] Best tools for SOC 2 compliance penetration testing [2025]](/blog/images/blog-banner-two-cover.webp)