![Best tools for SOC 2 compliance penetration testing [2025] Best tools for SOC 2 compliance penetration testing [2025]](/blog/images/blog-banner-two.webp)
SOC 2 Type II auditors require evidence that security controls function under adversarial conditions, not just policy documentation.
Penetration testing provides this evidence by simulating real attack scenarios against your production environment, API endpoints, and cloud infrastructure.
The American Institute of CPAs (AICPA) Trust Services Criteria mandates that organizations demonstrate effective security controls through testing methodologies that mirror actual threat actor techniques. For organisations pursuing SOC 2 certification, this requirement often represents the difference between a successful audit and costly remediation delays.
SOC 2 penetration testing differs from general security assessments in three critical ways: scope must align with your system boundaries as defined in the SOC 2 audit, testing must validate specific trust services criteria (particularly Security and Availability), and results must be documented in formats that auditors can evaluate against compliance requirements.
Modern automated tools now make this process accessible to companies without dedicated security teams, reducing costs from $50,000+ consultant engagements to manageable monthly or yearly subscriptions.
This guide examines penetration testing tools specifically designed for SOC 2 compliance requirements, focusing on solutions that integrate with startup development workflows and provide auditor-ready documentation.
What are the SOC 2 penetration testing requirements in 2025?
SOC 2 penetration testing requirements stem from three specific Trust Services Criteria that auditors evaluate during Type I and Type II examinations.
While AICPA frameworks don’t explicitly mandate penetration testing, the criteria require organizations to validate security controls through testing methodologies that simulate real-world attack scenarios.
Security Principle CC4.1 requires ongoing evaluation of control effectiveness. The criterion states: “The entity selects, develops, and performs ongoing and/or separate evaluations to ascertain whether the components of internal control are present and functioning.” Auditors interpret this to mean that static policy documentation alone is insufficient—controls must be tested under adversarial conditions to prove they function as designed.
Availability Principle A1.2 mandates testing of system resilience and recovery capabilities. This criterion requires testing environmental protections, backup processes, and recovery infrastructure. Penetration testing validates whether these controls can withstand actual attack vectors like DDoS attempts, service disruptions, and infrastructure compromises that could impact system availability.
Confidentiality Principle C1.1 requires validation of data protection measures. Organizations must demonstrate that confidential information remains protected when subjected to real attack methods. Penetration testing provides evidence that access controls, encryption implementations, and data handling procedures work correctly against techniques used by actual threat actors.
2025 auditor expectations have evolved significantly. Major audit firms including Deloitte, PwC, and EY now expect penetration testing evidence for 89% of SOC 2 Type II audits, according to recent compliance surveys. Testing must cover web applications, APIs, network infrastructure, and cloud configurations within the defined system boundaries. Results must include remediation evidence and retesting validation to satisfy auditor documentation requirements.
Does SOC 2 compliance require vulnerability scanning?
SOC 2 compliance does not explicitly mandate vulnerability scanning, but Trust Services Criterion CC7.1 requires organizations to implement procedures for detecting system changes and emerging vulnerabilities.
This criterion creates a de facto requirement for systematic vulnerability identification in production environments.
CC7.1 specifically addresses vulnerability management through monitoring requirements. The criterion states that entities must “conduct vulnerability scans designed to identify potential vulnerabilities or misconfigurations on a periodic basis and after any significant change in the environment.” Auditors evaluate whether organizations have implemented automated scanning processes that cover web applications, network infrastructure, and cloud configurations within their system boundaries.
Vulnerability scanning differs from penetration testing in scope and methodology. Scanning identifies known vulnerabilities using signature-based detection and configuration analysis, while penetration testing validates whether those vulnerabilities can be exploited in practice. SOC 2 auditors expect both: vulnerability scans provide continuous monitoring evidence, and penetration testing demonstrates that identified issues have been properly remediated.
Modern auditor expectations make scanning practically mandatory. A 2024 analysis of SOC 2 Type II audit failures showed that 67% of organizations without regular vulnerability scanning received management letter comments for inadequate security monitoring. Auditors from firms like BDO, Grant Thornton, and Moss Adams now explicitly request vulnerability scan reports as supporting evidence for CC7.1 compliance.
Automated scanning and penetration testing tools provide cost-effective compliance evidence. Tools like Nessus, Beagle Security, and Rapid7 InsightVM generate auditor-ready reports that map directly to SOC 2 requirements. For startups, cloud-based solutions eliminate infrastructure overhead while providing the continuous monitoring documentation that auditors require. Scan frequency should align with change management processes, weekly for production systems and immediately following deployment cycles.
Integration with development workflows maximizes security ROI. Vulnerability scanning and penetration testing integrated into CI/CD pipelines catches issues before they reach production, reducing both security risk and audit preparation overhead.
Defining the scope of your SOC 2 penetration test
SOC 2 penetration testing scope must align precisely with your system boundaries as defined in your Type I or Type II audit description. The scope determines which assets undergo testing and directly impacts audit evidence quality—incorrect scoping can invalidate test results for compliance purposes.
System boundary alignment drives scope definition. Your SOC 2 system description document defines which components handle, process, or store customer data covered by the audit.
Penetration testing scope must include every system component within these boundaries. Testing assets outside the defined boundaries provides no audit value, while excluding in-scope systems creates compliance gaps that auditors will flag as exceptions.
Critical components for SOC 2 penetration testing scope include:
Production web applications and customer portals that process confidential data
API endpoints and microservices handling customer authentication or data transactions
Administrative interfaces with elevated privileges or customer data access
Database servers and data stores containing customer information within system boundaries
Cloud infrastructure components including load balancers, CDNs, and container orchestration platforms
Third-party integrations that process customer data on your behalf
Production vs. staging environment considerations affect audit validity. While staging environments reduce business risk, they may not satisfy SOC 2 requirements if the production architecture differs significantly.
Trust Services Criterion CC4.1 requires testing of actual operational controls, not simulated environments. Many auditors accept staging tests only when organizations can demonstrate identical configurations, data flows, and security controls between environments.
Documentation requirements ensure auditor acceptance. Penetration test scope must be documented with specific IP ranges, domain names, application URLs, and system components. Include detailed justification for any exclusions from testing scope.
Auditors require evidence that scope covers all customer data processing systems identified in your system description. Pre-approve scope documents with your audit firm to avoid remediation delays during the audit process.
Scope validation prevents common compliance failures. Review scope against your data flow diagrams and system architecture documentation. Ensure coverage of all data ingress and egress points, authentication systems, and customer data storage locations within your defined system boundaries.
Best tools for SOC 2 compliance penetration testing
SOC 2 penetration testing tools must generate auditor-compliant reports, integrate with development workflows, and provide comprehensive coverage of web applications, APIs, and infrastructure components.
The following tools provide audit acceptance, low implementation complexity, and cost-effectiveness for organizations with limited security resources.
Web application & API penetration testing tools
Beagle Security - Best for SaaS startups pursuing SOC 2
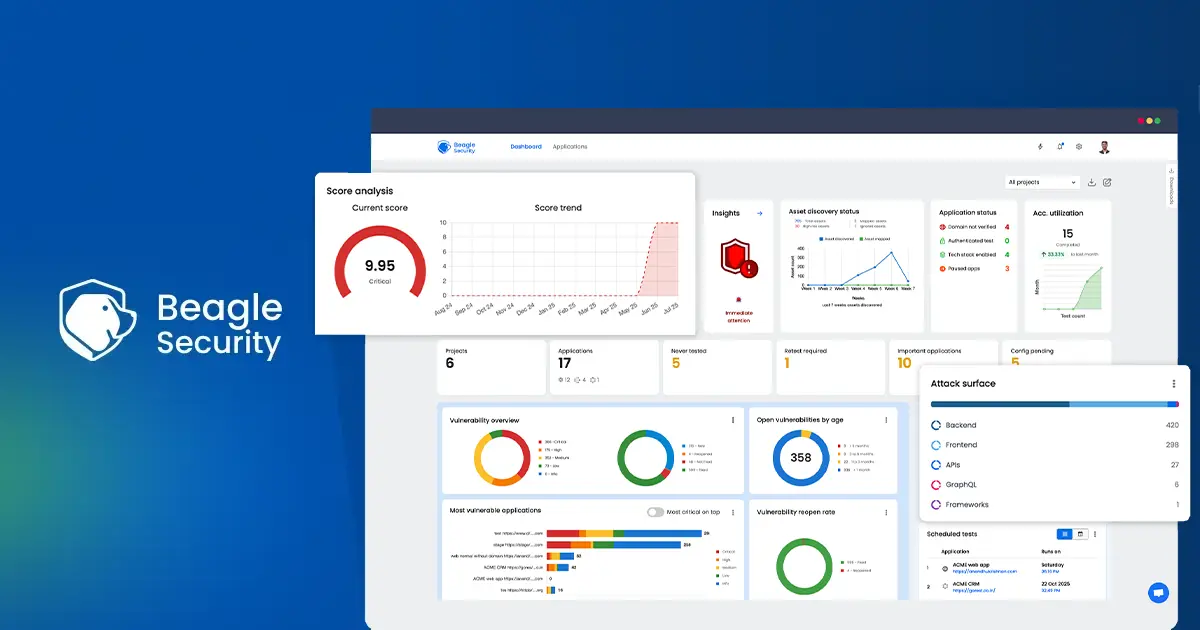
Beagle Security provides automated AI-driven DAST (Dynamic Application Security Testing) specifically engineered for SOC 2 Type II audit requirements.
The platform performs runtime security validation against production or production replica applications and APIs, generating audit-compliant documentation that maps directly to OWASP Top 10 standards without requiring dedicated security personnel.
Beagle Security executes comprehensive attack simulations and custom business logic testing to identify exploitable vulnerabilities in authentication systems, and API endpoints that process customer data within your SOC 2 system boundaries.
SOC 2-specific capabilities:
API security validation: Comprehensive testing of REST APIs and GraphQL endpoints handling customer data, including authentication bypass and data exposure scenarios
Compliance documentation: Pre-built OWASP mapped penetration test reports for SOC 2 with remediation evidence and retest validation required by Type II auditors
Implementation for startup development teams:
Setup time: 15 to 20 minutes for application configuration and test initialization
Learning curve: Minimal technical requirements - designed for developers without penetration testing expertise
Pricing: Starting at $359/month for Advanced plan that covers compliance reporting, significantly lower than $10,000-$25,000 consultant engagements
Best use cases:
Customer-facing SaaS applications processing confidential data
Multi-tenant platforms with role-based access controls
API-driven applications with third-party integrations
E-commerce platforms handling payment and personal information
Network penetration testing tools
Metasploit - Best for internal network validation
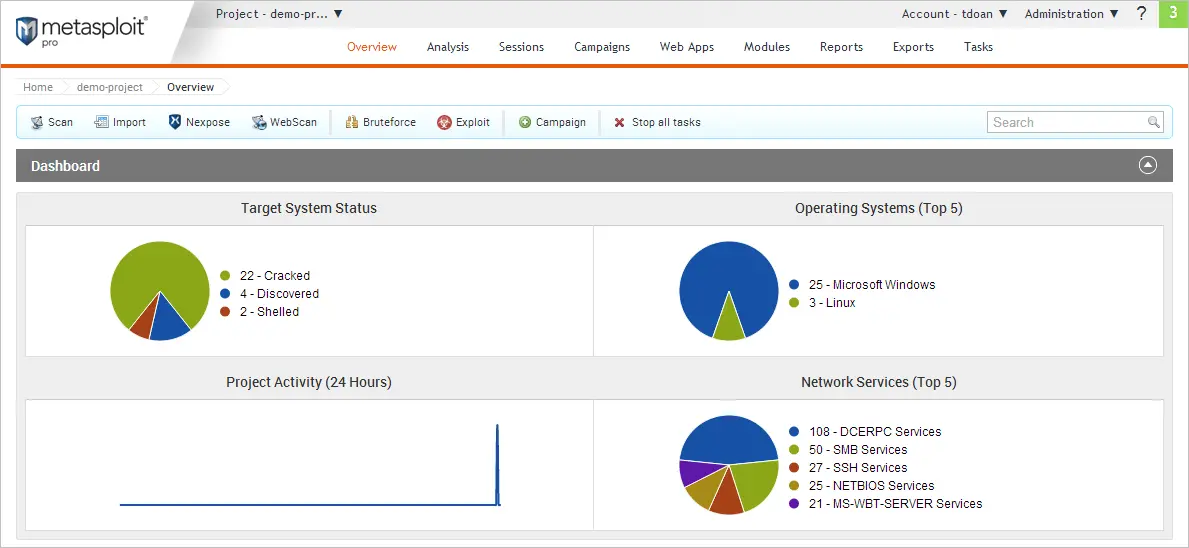
Metasploit provides comprehensive network penetration testing capabilities essential for SOC 2 validation. Developed by Rapid7, this open-source framework contains over 2100 verified exploits and enables systematic testing of internal network segmentation, privilege escalation paths, and lateral movement scenarios that auditors expect to see documented.
The framework excels at validating network-level security controls within your SOC 2 system boundaries, including firewall configurations, network access controls, and intrusion detection system effectiveness.
Metasploit’s post-exploitation modules can demonstrate whether an attacker gaining initial access could compromise additional systems containing customer data.
SOC 2-specific network testing capabilities:
Network segmentation validation: Testing whether customer data environments are properly isolated from corporate networks
Privilege escalation testing: Systematic validation of whether compromised accounts can access systems outside their authorized scope
Lateral movement simulation: Documentation of attack paths between network segments to validate environmental protections
Implementation considerations for startups:
Technical requirements: Requires network security expertise equivalent to 2-3 years of penetration testing experience
Setup complexity: 2-4 hours for initial configuration, plus ongoing exploit database updates
Learning curve: Command-line interface and networking knowledge essential for effective testing
Cost structure and alternatives:
Metasploit Community: Free version with limited exploit modules
Metasploit Pro: $15,000/year with automated reporting and compliance templates
Alternative solutions: Nessus Professional ($3,990/year) provides easier network scanning with SOC 2 compliance reports, while Core Impact ($40,000/year) offers automated network penetration testing suitable for larger startups
SOC 2 audit considerations: Network penetration testing evidence must demonstrate testing of all network components within system boundaries. Metasploit results require translation into auditor-friendly documentation showing control effectiveness rather than raw exploit output.
Cloud penetration testing tools
Prowler - Best for AWS/Azure/GCP security validation
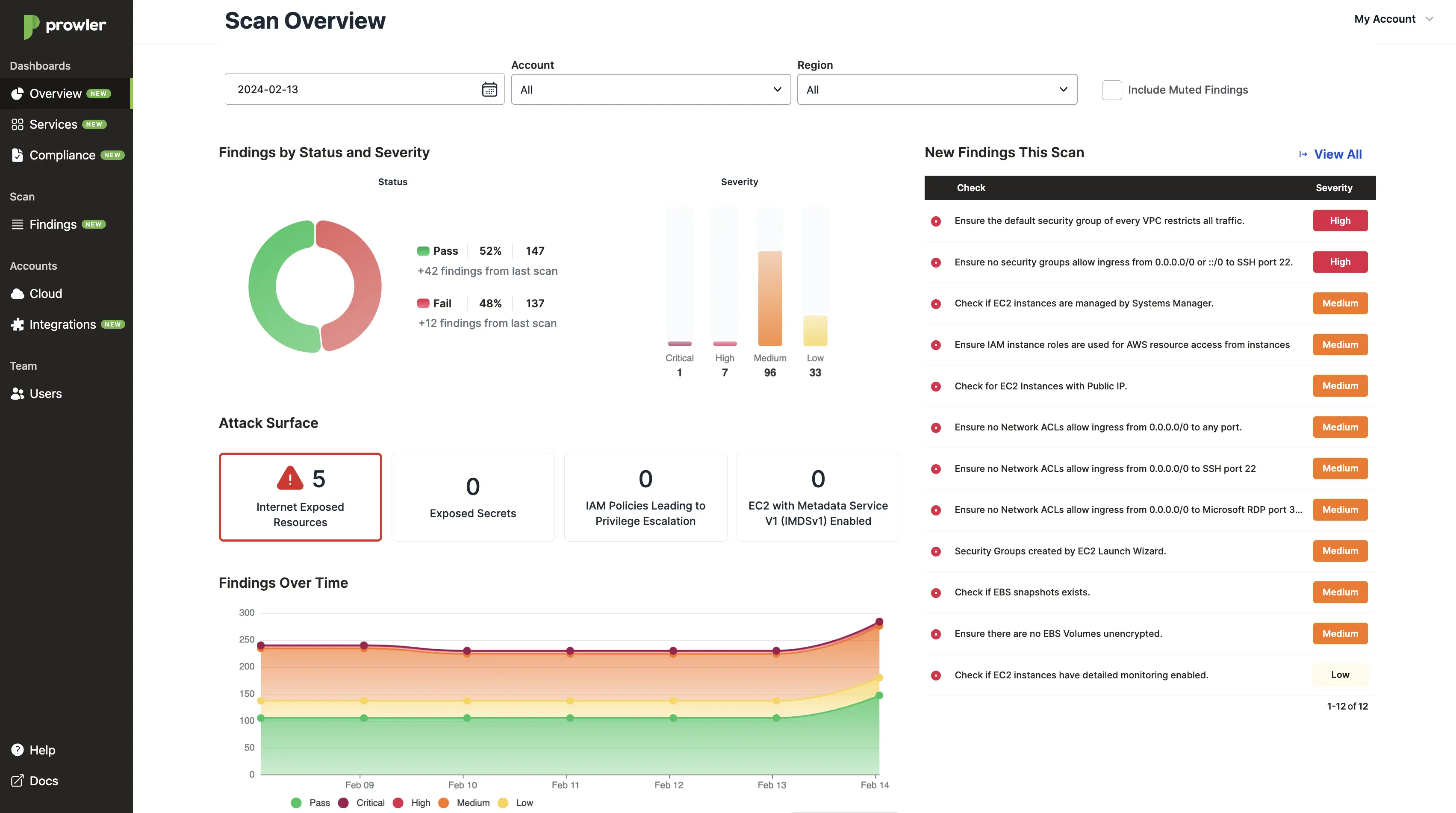
Prowler provides comprehensive cloud security assessment capabilities specifically designed for SOC 2 Trust Services Criteria validation across AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform environments.
This open-source tool performs automated configuration analysis, identifying misconfigurations and security gaps that could impact customer data protection within cloud-based system boundaries.
Prowler focuses exclusively on cloud infrastructure penetration testing through systematic evaluation of IAM policies, network security groups, storage configurations, and container security settings. The tool generates detailed compliance reports mapping findings directly to SOC 2 requirements, making it essential for startups operating cloud-native architectures.
SOC 2-specific cloud testing capabilities:
Access control validation: Systematic testing of IAM policies and role-based permissions against CC6.1 (logical access controls) requirements
Data encryption verification: Automated validation of encryption-at-rest and encryption-in-transit configurations required by CC6.7 (data transmission)
Network security assessment: Comprehensive analysis of VPC configurations, security groups, and network ACLs supporting CC6.1 network access controls
Implementation for cloud-native startups:
Setup time: 30 minutes for credential configuration across major cloud providers
Technical requirements: Basic cloud architecture knowledge - no penetration testing expertise required
Learning curve: Moderate - uses standard cloud CLI interfaces familiar to DevOps teams
Cost-effective cloud security alternatives:
ScoutSuite: Free multi-cloud security auditing with automated report generation
Prisma Cloud: Enterprise solution starting at $10 per protected resource monthly with comprehensive SOC 2 reporting
Cloud-specific SOC 2 considerations: Cloud penetration testing must validate shared responsibility model implementations, ensuring your organization properly configures security controls within cloud provider environments.
Testing should cover container orchestration platforms, serverless functions, and managed database services handling customer data within your defined system boundaries.
Final thoughts
While neither penetration testing nor vulnerability scanning are explicitly mandated by SOC 2 frameworks, these practices provide critical evidence for Trust Services Criteria CC4.1 (ongoing evaluation), CC6.1 (logical access controls), and CC7.1 (system monitoring). Organizations implementing systematic security testing demonstrate proactive risk management that auditors evaluate favorably during Type II examinations.
Tool selection should align with specific organizational needs:
For SaaS applications and API security: Beagle Security provides automated DAST capabilities starting at $359/month, generating audit-compliant reports that map directly to OWASP standards for SOC 2 compliance reporting. The platform enables continuous security validation throughout development cycles without requiring penetration testing expertise, making it optimal for startups with limited security resources.
For internal network validation: Metasploit offers comprehensive network penetration testing capabilities essential for validating network segmentation and access controls. While requiring technical expertise, the free Community edition provides cost-effective network security validation for organizations with experienced DevOps teams.
For cloud infrastructure assessment: Prowler delivers automated multi-cloud security validation across AWS, Azure, and GCP environments at zero cost. This open-source tool generates SOC 2-compliant reports covering IAM configurations, encryption settings, and network security controls critical for cloud-native applications.
Implementation strategy for audit success: Deploy automated tools early in your compliance journey rather than scrambling during audit preparation. Continuous security testing provides ongoing evidence of control effectiveness while identifying vulnerabilities before they impact customer data. Organizations using automated penetration testing tools report 40-60% reduction in audit preparation time compared to manual assessment approaches.
Modern automated security testing transforms SOC 2 compliance from a costly, consultant-dependent process into a manageable, developer-friendly workflow that scales with organizational growth.
FAQs
Does SOC 2 compliance require penetration testing?
SOC 2 compliance does not explicitly mandate penetration testing, but Trust Services Criteria CC4.1 requires organizations to validate that security controls are “present and functioning” through testing methodologies. Major audit firms expect penetration testing evidence for approximately 89% of SOC 2 Type II audits in 2025.
How much does a SOC 2 penetration test cost?
Traditional consultant-driven SOC 2 penetration testing ranges from $10,000-$30,000 for comprehensive assessments, with hourly rates of $250-400 for experienced testers. Automated DAST solutions like Beagle Security start at $359/month, reducing audit preparation costs by 60-80% compared to consulting approaches.

![Best tools for HIPAA penetration testing [2025] Best tools for HIPAA penetration testing [2025]](/blog/images/blog-banner-one-cover.webp)