
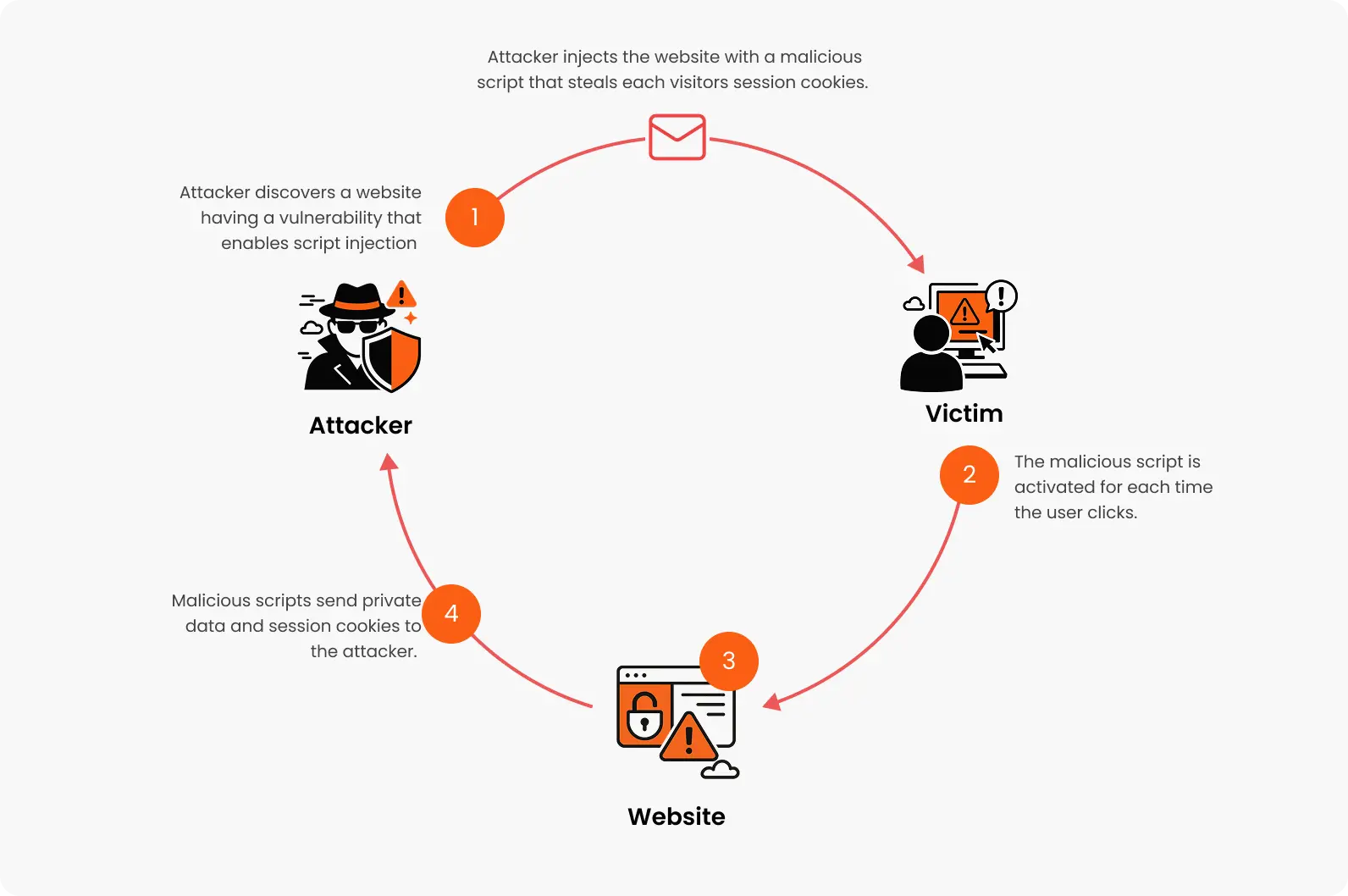
Cross-site scripting (XSS) is an exploit where the attacker adds malicious code onto a trustworthy website that will execute when the victim or end user access the website.
This malicious code can be inserted in numerous ways either by appending to the end of a url or posting to a page that displays user-generated content.
These scripts are then executed in the user’s browser, potentially leading to unauthorized access to sensitive information such as cookies, session tokens, or other critical data.
What are the different types of cross-site scripting?
Reflected XSS: Occurs when malicious scripts are reflected off a web server, such as in error messages or search results, and are immediately executed by the user’s browser.This type of attack requires the user to click on a malicious link or submit a specially crafted form. Learn more about Reflected XSS here.
Stored XSS: Also known as persistent XSS, stored XSS occurs when the attacker inserts malicious code into a web application and is permanently stored on the target server, such as in a forum post, comment, or user profile. Only when a person loads the hacked page does the attack begin.
DOM-based XSS: It is a client-side vulnerability that happens when a page’s Document Object Model (DOM) is altered, allowing the malicious payload to be run fully within the browser. Since everything takes place in the browser and the payload never makes it to the server, these attacks are particularly challenging to detect. DOM-based XSS occurs entirely on the client side.
Let’s have a look at an example of XSS
Consider a web application that displays user comments without proper input validation:
<html>
<body>
<h1>Most Recent Comment</h1>
<?php
echo $_POST['comment'];
?>
</body>
</html>
If an attacker submits the following comment
<script>alert('XSS Attack');</script>
The application will render and execute the script in the browsers of users viewing the comments, leading to potential security breaches.
How does XSS work?
An XSS attack usually occurs in two stages:
An attacker must first figure out how to insert malicious code, or payload, into a webpage that the victim accesses in order to launch malicious JavaScript code in the victim’s browser.
The victim then has to go to the website that contains the malicious code. If a specific victim is the target of the attack, the attacker may deliver a malicious URL to the victim using phishing or social engineering.
Let’s look at the impacts of cross-site scripting
Data theft: Unauthorized account access and identity theft can result from attackers stealing private information, including cookies, session tokens, and personal information.
Session hijacking: By stealing session cookies, hackers can pose as authorized users and obtain sensitive features and user accounts without authorization.
Defacement: Malicious scripts can alter the content and appearance of a website, damaging the organization’s reputation and trustworthiness.
Malware distribution: XSS can be used to redirect users to malicious websites or initiate drive-by downloads, resulting in the spread of malware.
Phishing attacks: By creating convincing phishing forms on the compromised website, attackers can fool users into disclosing private information.
Steps to mitigate XSS vulnerabilities
Input validation and sanitization: Rigorously validate and sanitize all user inputs to ensure that data conforms to expected formats and does not contain executable code.
Output encoding: Encode data before rendering it in the browser to prevent the execution of injected scripts. For example, convert special characters to their HTML entity equivalents.
Content Security Policy (CSP): Implement a CSP header to restrict the sources from which content can be loaded, thereby reducing the risk of executing malicious scripts.
Use secure frameworks: Utilize web development frameworks that offer built-in protections against XSS attacks, reducing the likelihood of introducing vulnerabilities.
The ability of Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) to steal confidential information, alter website content, and take advantage of user trust makes it a persistent security threat.
Strong content security policies, input validation, and safe coding techniques can all be actively implemented to greatly lower the danger of XSS attacks.






